
John Maynard Smith was a British theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he took a second degree in genetics under the biologist J. B. S. Haldane. Maynard Smith was instrumental in the application of game theory to evolution with George R. Price, and theorised on other problems such as the evolution of sex and signalling theory.

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not.

John Burdon Sanderson Haldane, nicknamed "Jack" or "JBS", was a British-Indian scientist who worked in physiology, genetics, evolutionary biology, and mathematics. With innovative use of statistics in biology, he was one of the founders of neo-Darwinism. Despite his lack of an academic degree in the field, he taught biology at the University of Cambridge, the Royal Institution, and University College London. Renouncing his British citizenship, he became an Indian citizen in 1961 and worked at the Indian Statistical Institute for the rest of his life.

Kin selection is a process whereby natural selection favours a trait due to its positive effects on the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even when at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction. Kin selection can lead to the evolution of altruistic behaviour. It is related to inclusive fitness, which combines the number of offspring produced with the number an individual can ensure the production of by supporting others. A broader definition of kin selection includes selection acting on interactions between individuals who share a gene of interest even if the gene is not shared due to common ancestry.

The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, Evolution: The Modern Synthesis. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local populations.

William Donald Hamilton was a British evolutionary biologist, recognised as one of the most significant evolutionary theorists of the 20th century. Hamilton became known for his theoretical work expounding a rigorous genetic basis for the existence of altruism, an insight that was a key part of the development of the gene-centered view of evolution. He is considered one of the forerunners of sociobiology. Hamilton published important work on sex ratios and the evolution of sex. From 1984 to his death in 2000, he was a Royal Society Research Professor at Oxford University.

The neutral theory of molecular evolution holds that most evolutionary changes occur at the molecular level, and most of the variation within and between species are due to random genetic drift of mutant alleles that are selectively neutral. The theory applies only for evolution at the molecular level, and is compatible with phenotypic evolution being shaped by natural selection as postulated by Charles Darwin.
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and population structure.

The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection is a book by Ronald Fisher which combines Mendelian genetics with Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection, with Fisher being the first to argue that "Mendelism therefore validates Darwinism" and stating with regard to mutations that "The vast majority of large mutations are deleterious; small mutations are both far more frequent and more likely to be useful", thus refuting orthogenesis. First published in 1930 by The Clarendon Press, it is one of the most important books of the modern synthesis, and helped define population genetics. It had been described by J. F. Crow as the "deepest book on evolution since Darwin".

Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. Erdős pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered around discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics.

Richard Dagobert Brauer was a leading German and American mathematician. He worked mainly in abstract algebra, but made important contributions to number theory. He was the founder of modular representation theory.

Motoo Kimura was a Japanese biologist best known for introducing the neutral theory of molecular evolution in 1968. He became one of the most influential theoretical population geneticists. He is remembered in genetics for his innovative use of diffusion equations to calculate the probability of fixation of beneficial, deleterious, or neutral alleles. Combining theoretical population genetics with molecular evolution data, he also developed the neutral theory of molecular evolution in which genetic drift is the main force changing allele frequencies. James F. Crow, himself a renowned population geneticist, considered Kimura to be one of the two greatest evolutionary geneticists, along with Gustave Malécot, after the great trio of the modern synthesis, Ronald Fisher, J. B. S. Haldane, and Sewall Wright.

Haldane's dilemma, also known as the waiting time problem, is a limit on the speed of beneficial evolution, calculated by J. B. S. Haldane in 1957. Before the invention of DNA sequencing technologies, it was not known how much polymorphism DNA harbored, although alloenzymes were beginning to make it clear that substantial polymorphism existed. This was puzzling because the amount of polymorphism known to exist seemed to exceed the theoretical limits that Haldane calculated, that is, the limits imposed if polymorphisms present in the population generally influence an organism's fitness. Motoo Kimura's landmark paper on neutral theory in 1968 built on Haldane's work to suggest that most molecular evolution is neutral, resolving the dilemma. Although neutral evolution remains the consensus theory among modern biologists, and thus Kimura's resolution of Haldane's dilemma is widely regarded as correct, some biologists argue that adaptive evolution explains a large fraction of substitutions in protein coding sequence, and they propose alternative solutions to Haldane's dilemma.

John James Waterston was a Scottish physicist and a neglected pioneer of the kinetic theory of gases.
"The Genetical Evolution of Social Behaviour" is a 1964 scientific paper by the British evolutionary biologist W.D. Hamilton in which he mathematically lays out the basis for inclusive fitness.

Sewall Green Wright FRS (For) Honorary FRSE was an American geneticist known for his influential work on evolutionary theory and also for his work on path analysis. He was a founder of population genetics alongside Ronald Fisher and J. B. S. Haldane, which was a major step in the development of the modern synthesis combining genetics with evolution. He discovered the inbreeding coefficient and methods of computing it in pedigree animals. He extended this work to populations, computing the amount of inbreeding between members of populations as a result of random genetic drift, and along with Fisher he pioneered methods for computing the distribution of gene frequencies among populations as a result of the interaction of natural selection, mutation, migration and genetic drift. Wright also made major contributions to mammalian and biochemical genetics.

Biometrika is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Oxford University Press for the Biometrika Trust. The editor-in-chief is Paul Fearnhead. The principal focus of this journal is theoretical statistics. It was established in 1901 and originally appeared quarterly. It changed to three issues per year in 1977 but returned to quarterly publication in 1992.
H. Allen Orr is the Shirley Cox Kearns Professor of Biology at the University of Rochester.
Charles Chamberlain Hurst (1870–1947) was an English geneticist.
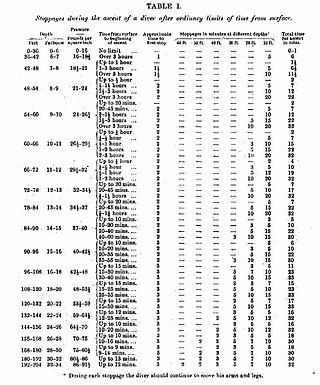
Haldane's decompression model is a mathematical model for decompression to sea level atmospheric pressure of divers breathing compressed air at ambient pressure that was proposed in 1908 by the Scottish physiologist, John Scott Haldane, who was also famous for intrepid self-experimentation.