Hawaiian is a Polynesian language and critically endangered language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the US state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840.

Native Americans, sometimes called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans, are the Indigenous peoples of the United States or portions thereof, such as American Indians from the contiguous United States and Alaska Natives. The United States Census Bureau defines Native American as "all people indigenous to the United States and its territories, including Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islanders, whose data are published separately from American Indians and Alaska Natives". The U.S. census tracks data from American Indians and Alaska Native separately from Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders, who include Samoan Americans and Chamorros.

The Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA), also known as Indian Affairs (IA), is a United States federal agency within the Department of the Interior. It is responsible for implementing federal laws and policies related to Native Americans and Alaska Natives, and administering and managing over 55,700,000 acres (225,000 km2) of reservations held in trust by the U.S. federal government for indigenous tribes. It renders services to roughly 2 million indigenous Americans across 574 federally recognized tribes. The BIA is governed by a director and overseen by the Assistant Secretary for Indian Affairs, who answers to the Secretary of the Interior.

An American Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a U.S. federal government-recognized Native American tribal nation, whose government is autonomous, subject to regulations passed by the United States Congress and administered by the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs, and not to the U.S. state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political, and legal difficulties.
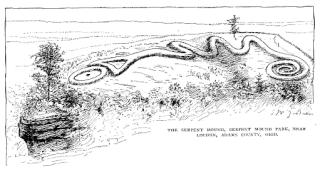
In the classification of the archaeological cultures of North America, the Archaic period in North America, taken to last from around 8000 to 1000 BC in the sequence of North American pre-Columbian cultural stages, is a period defined by the archaic stage of cultural development. The Archaic stage is characterized by subsistence economies supported through the exploitation of nuts, seeds, and shellfish. As its ending is defined by the adoption of sedentary farming, this date can vary significantly across the Americas.

DeSoto Site Historic State Park is a Florida state park located in Tallahassee, Florida. It consists of 5 acres (20,000 m2) of land near Apalachee Parkway, including the residence of former Governor John W. Martin. The site is intended to initiate research and education on nearly four centuries of recorded history beginning with Hernando de Soto's use of the site as a winter encampment in 1539. There is an exhibit of items found at the site in the Governor Martin House.

Bird stones are prehistoric, abstract stone carvings made by Native Americans. The artifacts were a common inclusion in graves and thought to have ceremonial importance. They are noted for their distinctive simplicity and beauty. They first appeared in the middle Archaic period around 5,000 years ago and continued into the early Woodland period to about 2,500 years before present.

Odocoileus is a genus of medium-sized deer containing three species native to the Americas. The name is sometimes spelled odocoeleus; it is from a contraction of the roots odonto- and coelus meaning "hollow-tooth".
Container Revolution refers to the introduction of pottery to use as containers.
Pasuckuakohowog is a Native American game similar to soccer.

The University of Texas Press is a university press that is part of the University of Texas at Austin. Established in 1950, the Press publishes scholarly books and journals in several areas, including Latin American studies, Texana, anthropology, U.S. Latino studies, Native American studies, African American studies, film & media studies, classics and the ancient Near East, Middle East studies, natural history, art, and architecture. The Press also publishes trade books and journals relating to their major subject areas.
The Back River is a 6.5-mile-long (10.5 km) river located in New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the United States. It is a tributary to the Powwow River, part of the Merrimack River watershed. Approximately 3.0 miles (4.8 km) of the river are in New Hampshire, with the remaining 3.5 miles (5.6 km) in Massachusetts.

A series of efforts were made by the United States to assimilate Native Americans into mainstream European–American culture between the years of 1790 and 1920. George Washington and Henry Knox were first to propose, in the American context, the cultural assimilation of Native Americans. They formulated a policy to encourage the so-called "civilizing process". With increased waves of immigration from Europe, there was growing public support for education to encourage a standard set of cultural values and practices to be held in common by the majority of citizens. Education was viewed as the primary method in the acculturation process for minorities.

American Methodist Episcopal Mission was the missionary society of the Methodist Episcopal Church that was involved in sending workers to countries such as Africa, South America, India, Australia and China during the late Qing dynasty.
Tianyuan Cave is near Beijing, where Tianyuan man, one of the earliest modern humans, was found.

Native American religions are the spiritual practices of the Native Americans in the United States. Ceremonial ways can vary widely and are based on the differing histories and beliefs of individual nations, tribes and bands. Early European explorers describe individual Native American tribes and even small bands as each having their own religious practices. Theology may be monotheistic, polytheistic, henotheistic, animistic, shamanistic, pantheistic or any combination thereof, among others. Traditional beliefs are usually passed down in the forms of oral histories, stories, allegories, and principles.

The peyote is a small, spineless cactus which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. Peyote is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl peyōtl, meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root peyōni, "to glisten". Peyote is native to Mexico and southwestern Texas. It is found primarily in the Sierra Madre Occidental, the Chihuahuan Desert and in the states of Nayarit, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, and San Luis Potosí among scrub. It flowers from March to May, and sometimes as late as September. The flowers are pink, with thigmotactic anthers.

Sinkyone Wilderness State Park is a state park in Mendocino County, California. The wilderness area borders the Pacific Ocean to the west and the King Range National Conservation Area to the north. The nearest settlement is the unincorporated town of Leggett. The lack of major road and highway access has led to the Sinkyone Wilderness area being referred to as the Lost Coast.
The Native Americans is a three-part American television documentary miniseries that premiered on TBS on October 10, 1994. The remaining two episodes aired on October 11 and 13, 1994. Directed by John Borden, Phil Lucas and George Burdeau, the six-hour series explores the history of Native American cultures, with each hour of the series devoted to a particular region of the United States.

First Nations Experience (FNX) is a non-profit television network in San Bernardino, California, owned by the San Bernardino Community College District. The network, created by Executive Director Charles Fox, is broadcast from the KVCR-TV studios located on the campus of San Bernardino Valley College. FNX is America's first and only broadcast network aimed at Native Americans and global Indigenous audiences and consumers of Native American culture.












