Related Research Articles
Following the Islamic conquest in 641-642, Lower Egypt was ruled at first by governors acting in the name of the Rashidun Caliphs and then the Umayyad Caliphs in Damascus, but in 750 the Umayyads were overthrown. Throughout Islamic rule, Askar was named the capital and housed the ruling administration. The conquest led to two separate provinces all under one ruler: Upper and Lower Egypt. These two very distinct regions were governed by the military and followed the demands handed down by the governor of Egypt and imposed by the heads of their communities.

Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Ṭalḥa ibn Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn Hārūn Al-Muʿtaḍid bi'Llāh, 853/4 or 860/1 – 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Muʿtaḍid bi-llāh, was the caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 892 until his death in 902.

Abū Muḥammad ʿAlī ibn Aḥmad ibn Ṭalḥa ibn Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn Hārūn al-Muktafī bi'Llāh, better known by his regnal name al-Muktafī bi-Llāh, was the caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 902 to 908. More liberal and sedentary than his militaristic father al-Mu'tadid, al-Muktafi essentially continued his policies, although most of the actual conduct of government was left to his viziers and officials. His reign saw the defeat of the Qarmatians of the Syrian Desert, and the reincorporation of Egypt and the parts of Syria ruled by the Tulunid dynasty. The war with the Byzantine Empire continued with alternating success, although the Arabs scored a major victory in the Sack of Thessalonica in 904. His death in 908 opened the way for the installation of a weak ruler, al-Muqtadir, by the palace bureaucracy, and began the terminal decline of the Abbasid Caliphate that ended in 946 with the caliphs becoming puppet rulers under the Buyid dynasty.
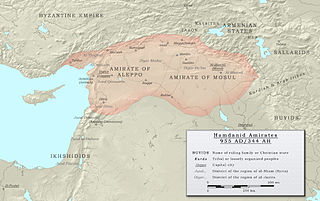
The Hamdanid dynasty was a Shia Muslim Arab dynasty of Northern Mesopotamia and Syria (890–1004). They descended from the ancient Banu Taghlib tribe of Mesopotamia and Arabia.
Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Ṭughj ibn Juff ibn Yiltakīn ibn Fūrān ibn Fūrī ibn Khāqān, better known by the title al-Ikhshīd after 939, was an Abbasid commander and governor who became the autonomous ruler of Egypt and parts of Syria (Levant) from 935 until his death in 946. He was the founder of the Ikhshidid dynasty, which ruled the region until the Fatimid conquest of 969.

The Tulunids, were a Mamluk dynasty of Turkic origin who were the first independent dynasty to rule Egypt, as well as much of Syria, since the Ptolemaic dynasty. They were independent from 868, when they broke away from the central authority of the Abbasid Caliphate, to 905, when the Abbasids restored the Tulunid domains to their control.

Harun ibn Khumarawayh was the fourth Tulunid vassal Emir of Egypt (896–904). He succeeded his elder brother Abu 'l-Asakir Jaysh, who had been murdered by army chiefs. He left state affairs to the vizier, Abu Ja'far ibn Ali, preferring to live a life of dissolute luxury. This led to a growing crisis in the country, since state finances could not be regulated and the army leaders gradually accrued more power to themselves
Ahmad ibn Tulun was the founder of the Tulunid dynasty that ruled Egypt and Syria between 868 and 905. Originally a Turkic slave-soldier, in 868 Ibn Tulun was sent to Egypt as governor by the Abbasid caliph. Within four years he had established himself as a virtually independent ruler by evicting the caliphal fiscal agent, Ibn al-Mudabbir, taking over control of Egypt's finances, and establishing a large military force personally loyal to himself. This process was facilitated by the volatile political situation in the Abbasid court and the preoccupation of the Abbasid regent, al-Muwaffaq, with the wars against the Persian Saffarids and the Zanj Rebellion. Ibn Tulun also established an efficient administration in Egypt. After reforms to the tax system, repairs to the irrigation system, and other measures, the annual tax yield grew markedly. As a symbol of his new regime, he built a new capital, al-Qata'i, north of the old capital Fustat.
Abu 'l-Asakir Jaysh ibn Khumarawayh was the third Emir of the Tulunids in Egypt, ruling briefly in 896.

Abu 'l-Jaysh Khumārawayh ibn Aḥmad ibn Ṭūlūn was a son of the founder of the Tulunid dynasty, Ahmad ibn Tulun. His father, the autonomous ruler of Egypt and Syria, designated him as his successor. When Ibn Tulun died in May 884, Khumarawayh succeeded him. After defeating an attempt to depose him, in 886 he managed to gain recognition of his rule over Egypt and Syria as a hereditary governor from the Abbasid Caliphate. In 893 the agreement was renewed with the new Abbasid Caliph, al-Mu'tadid, and sealed with the marriage of his daughter Qatr al-Nada to the Caliph.
Husayn ibn Hamdan ibn Hamdun ibn al-Harith al-Taghlibi was an early member of the Hamdanid family, who distinguished himself as a general for the Abbasid Caliphate and played a major role in the Hamdanids' rise to power among the Arab tribes in the Jazira.
The al-Madhara'i were a family of officials from Iraq who served as and virtually monopolized the posts of director of finances (‘āmil) of Egypt and Syria for the Tulunid dynasty, the Abbasid Caliphate, and the Ikhshidid dynasty, between 879 and 946. In this role, they amassed "one of the largest personal fortunes in the medieval Arab east".
Abu Ali al-Husayn ibn Ahmad al-Madhara'i, also known as Abu Zunbur, was a member of the bureaucratic al-Madhara'i dynasty of fiscal officials, and served as director of finances of Egypt and Syria for the Abbasid Caliphate in the first decades of the 10th century.
Abu Bakr Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Madhara'i, surnamed al-Atrash, was the founder of the al-Madhara'i family of fiscal bureaucrats.
Ali ibn Ahmad al-Madhara'i was a member of the al-Madhara'i family of fiscal bureaucrats, serving as director of finances and vizier under the Tulunids of Egypt.
Abu Bakr Muhammad ibn Ali al-Madhara'i (871–957) was the last important representative of the bureaucratic al-Madhara'i dynasty of fiscal officials. He served as director of finances of Egypt and Syria under the Tulunid dynasty and the Abbasid Caliphate, as well as becoming vizier for the Tulunid ruler Harun ibn Khumarawayh, and later occupying high office under the Ikhshidids.
Abu'l-Fadl Ja'far ibn al-Fadl ibn al-Furat, also called Ibn Hinzaba, like his father before him, was a member of the bureaucratic Banu'l-Furat family from Iraq. A highly educated man renowned for his strict piety and knowledge of traditions about the early Islamic times, he served as vizier of the Ikhshidids of Egypt from 946 until the end of the dynasty in 969, and continued serving the Fatimid Caliphate after that.
Ahmad ibn Kayghalagh was an Abbasid military officer of Turkic origin who served as governor in Syria and Egypt. He was ousted as governor of Egypt by Muhammad ibn Tughj in 935.
Muhammad ibn Sulayman, surnamed al-Katib, was a senior official and commander of the Abbasid Caliphate, most notable for his victories against the Qarmatians and for his reconquest of Syria and Egypt from the autonomous Tulunid dynasty.
Isa ibn Muhammad al-Nushari or Isa ibn Musa al-Nushari was an Abbasid commander and governor of Isfahan in 896–900 and of Egypt from 905 to his death in spring 910.