See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Achagua. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Achagua or Axagua may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Achagua. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Colombian may refer to:
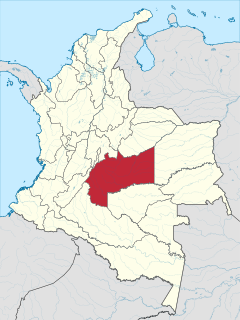
Meta is a department of Colombia. It is close to the geographic center of the country, to the east of the Andean mountains. A large portion of the department, which is also crossed by the Meta River, is covered by a grassland plain known as the Llanos. Its capital is Villavicencio. The department has a monument placed in the very geographic centre of Colombia, at a place known as Alto de Menegua, a few kilometers from Puerto López.
Are is the second-person singular and plural forms of the verb "to be", the copula of the English language.

The Meta River is a major left tributary of the Orinoco River in eastern Colombia and southern Venezuela, South America. The Meta originates in the Eastern Ranges of the Andes and flows through the Meta Department, Colombia as the confluence of the Humea, Guatiquía and Guayuriba rivers. It flows east-northeastward across the Llanos Orientales of Colombia following the direction of the Meta Fault. The Meta forms the northern boundary of Vichada Department, first with Casanare Department, then with Arauca Department, and finally with Venezuela, down to Puerto Carreño where it flows into the Orinoco.

Pisba is a town and municipality in Boyacá Department, Colombia, part of the subregion of La Libertad Province. Pisba is situated in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes at altitudes between 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) and 3,500 metres (11,500 ft). Distance to Sogamoso is 128 kilometres (80 mi) and to Tunja 176 kilometres (109 mi). The municipality borders Paya in the east, Labranzagrande in the south and Mongua in the northwest. The Casanare municipality Támara borders Pisba in the north.

Tame is a town and municipality in the Arauca Department, Colombia. The municipality has a total area of 5,300 km².

The Guahibo people are an indigenous people native to Llanos or savannah plains in eastern Colombia–Arauca, Meta, Guainia, and Vichada departments–and in southern Venezuela near the Colombian border. Their population was estimated at 23,772 people in 1998.

Trinidad is a town and municipality in the Department of Casanare, Colombia.

Zetaquirá is a town and municipality in the Colombian Lengupá Province, part of the department of Boyacá. Zetaquirá is located at 67 kilometres (42 mi) from the department capital Tunja and borders Pesca in the north, Miraflores in the south, in the east Berbeo, San Eduardo and Aquitania and in the west Ramiriquí and Chinavita. The municipality stretches over an area of 262 square kilometres (101 sq mi) on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense at altitudes between 1,875 metres (6,152 ft) and 3,600 metres (11,800 ft).
Achagua, or Achawa, is an Arawakan language spoken in the Meta Department of Colombia, similar to Piapoco. It is estimated that 250 individuals speak the language, many of whom also speak Piapoco or Spanish.
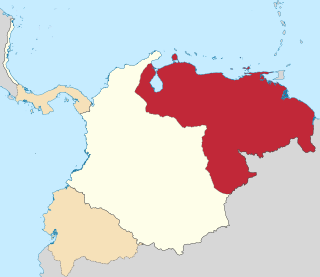
Venezuela Department was one of the three departments of Gran Colombia until 1824.
The Upper Amazon Maipurean languages, a.k.a. North Amazonian or Inland Northern Maipuran, are Arawakan languages of the northern Amazon in Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, and Brazil.
Piapoco is an Arawakan language of Colombia and Venezuela.
The Achagua are an indigenous people of Colombia and Venezuela. At the time of the Spanish colonization of the Americas, their territory covered the present-day Venezuelan states of Bolívar, Guárico and Barinas. In the late twentieth century there were several hundred Achaguas remaining.

Apure Province was a province of Gran Colombia, and later one of the provinces of Venezuela, after Venezuelan independence in 1830. It was created in 1823, being split from Barinas Province, with the Uribante River and Apure River marking the border. The following year, Gran Colombia was reorganised into four Departments, with the Apure Department consisting of Apure Province and Barinas Province. Its capital was Achaguas, for which the Province was sometimes called Achaguas Province.

The Llanero Spanish is the set of linguistic modalities of Spanish language spoken in the region of Venezuelan-Colombian Los Llanos. It is characterized by mixing elements of Old Spanish more indigenous elements.

The Muisca cuisine describes the food and preparation the Muisca elaborated. The Muisca were an advanced civilization inhabiting the central highlands of the Colombian Andes before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca in the 1530s. Their diet and cuisine consisted of many endemic flora and fauna of Colombia. Main product of the Muisca was maize, in various forms. The advantage of maize was that it could be grown in the various climatic zones the Muisca territories experienced. It was the basis for their diet and the alcoholic drink, chicha, made from fermented maize and sugar. In the Muisca religion their agriculture and celebration of harvests, conducted along the complex Muisca calendar, were protected by Chaquén and Nencatacoa. The Muisca ate a variety of roots and tubers and even had a specific word in their Chibcha language for eating those: bgysqua.

The Tegua or Tecua were an Arawak-speaking indigenous people of Colombia who died out in the 19th century.
Achaguas is a small town in Apure State in Venezuela, in the Achaguas Municipality.
Xagua may refer to;