See also
- Active Components, an electronic parts vendor formerly part of Future Electronics
- Active ingredient
Active component may refer to:
Cartridge may refer to:

Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signals to digital signals.
Electronic may refer to:

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller. These devices are typically made from semiconductor materials. Many components of a normal electronic design are available in a microelectronic equivalent. These include transistors, capacitors, inductors, resistors, diodes and (naturally) insulators and conductors can all be found in microelectronic devices. Unique wiring techniques such as wire bonding are also often used in microelectronics because of the unusually small size of the components, leads and pads. This technique requires specialized equipment and is expensive.
Vibrator may refer to:
Buffer may refer to:
Circuit may refer to:
Discrete may refer to:
A device is usually a constructed tool. Device may also refer to:
Counter may refer to:
Fabrication may refer to:

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance. Discrete circuits are made of individual electronic components that only perform one function each as packaged, which are known as discrete components, although strictly the term discrete component refers to such a component with semiconductor material such as individual transistors.

In engineering and systems theory, redundancy is the intentional duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the goal of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the form of a backup or fail-safe, or to improve actual system performance, such as in the case of GNSS receivers, or multi-threaded computer processing.
Hardware may refer to:
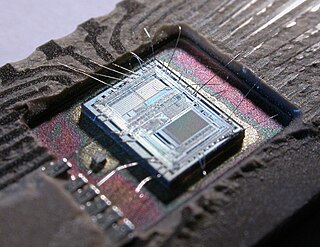
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical circuit. For a circuit to be referred to as electronic, rather than electrical, generally at least one active component must be present. The combination of components and wires allows various simple and complex operations to be performed: signals can be amplified, computations can be performed, and data can be moved from one place to another.
Countersurveillance refers to measures that are usually undertaken by the public to prevent surveillance, including covert surveillance. Countersurveillance may include electronic methods such as technical surveillance counter-measures, which is the process of detecting surveillance devices. It can also include covert listening devices, visual surveillance devices, and countersurveillance software to thwart unwanted cybercrime, such as accessing computing and mobile devices for various nefarious reasons. More often than not, countersurveillance will employ a set of actions (countermeasures) that, when followed, reduce the risk of surveillance. Countersurveillance is different from sousveillance, as the latter does not necessarily aim to prevent or reduce surveillance.
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use passivity to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of power gain. In contrast, control systems engineers will use passivity to refer to thermodynamically passive ones, which consume, but do not produce, energy. As such, without context or a qualifier, the term passive is ambiguous.
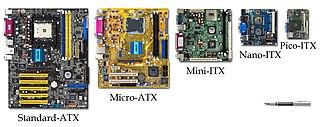
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor.

The trancitor as the combined word of a "transfer-capacitor" is to be considered as another active-device category besides the transistor as a "transfer-resistor". As observed in the table shown, four kinds of active devices are theoretically deduced. Among them, trancitors are missing to be the third and fourth kinds, whereas transistors, such as bipolar junction transistor (BJT) and field-effect transistor (FET), were already invented as the first and second kinds, respectively. Unlike the transistor switching the current at its output, the trancitor transfers its input to the voltage output, so an inverse relationship with each other.