
Lunenburg is a port town on the South Shore of Nova Scotia, Canada. Founded in 1753, the town was one of the first British attempts to settle Protestants in Nova Scotia.

Bluenose was a fishing and racing gaff rig schooner built in 1921 in Lunenburg, Nova Scotia, Canada. A celebrated racing ship and fishing vessel, Bluenose under the command of Angus Walters, became a provincial icon for Nova Scotia and an important Canadian symbol in the 1930s, serving as a working vessel until she was wrecked in 1946. Nicknamed the "Queen of the North Atlantic", she was later commemorated by a replica, Bluenose II, built in 1963. The name Bluenose originated as a nickname for Nova Scotians from as early as the late 18th century.
The Banks dory, or Grand Banks dory, is a type of dory. They were used as traditional fishing boats from the 1850s on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland. The Banks dory is a small, open, narrow, flat-bottomed and slab-sided boat with a particularly narrow transom. They were inexpensive to build and could be stacked or nested inside each other and stored on the decks of larger fishing vessels which functioned as mother ships.

Riverport is a village in Lunenburg County, Nova Scotia, Canada. The harbour of Ritcey Cove is free from shoals and safe from every wind, considered one of the finest in North America. Riverport is a five-minute drive to several public beaches including Hirtle's Beach, Kingsburg Beach, Oxner Beach, Rose Bay Beach and Spindler Beach.

Benjamin Wier was a Canadian businessman and politician.

CCGS Sir Wilfred Grenfell is a Canadian Coast Guard vessel based in Victoria, British Columbia. Designated an "Offshore Ice Strengthened Multi Patrol Vessel", the former offshore supply vessel is named after the medical missionary in Labrador, Sir Wilfred Grenfell. Constructed in 1984–1985, Sir Wilfred Grenfell was purchased by the Canadian Government and converted for Coast Guard service. In 1994, she played an important role in the fishing conflict known as the Turbot War in the Atlantic Ocean.

Bluenose II is a replica of the fishing and racing schooner Bluenose, commissioned by Sidney Culverwell Oland and built in 1963 as a promotional yacht for Oland Brewery. Sidney Oland donated the schooner to Nova Scotia in 1971 and it has since operated as a sailing ambassador and promotional device for Nova Scotia tourism. In honour of her predecessor's record, Bluenose II does not officially race.
William James Roué was a naval architect famous for his design of the Bluenose fishing schooner, which sailed to victory in the Halifax Herald International Fisherman's competition in 1921, 1922, 1923, 1931 and 1938, and held the record for the largest catch of fish ever brought into Lunenburg.

HMCS Saguenay was a St. Laurent-class destroyer that served in the Royal Canadian Navy and later the Canadian Forces from 1956–1990. She was the second vessel in her class and the second Canadian naval unit to carry the name HMCS Saguenay. After being discarded by the Canadian Forces, the ship was sunk as an artificial reef off the coast of Nova Scotia.
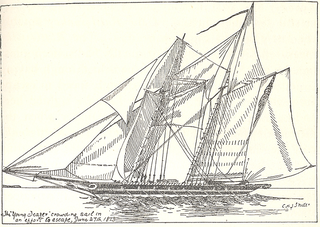
Young Teazer was a United States privateer schooner that captured 12 British vessels, five of which made it to American ports. A member of her crew blew her up at Mahone Bay, Nova Scotia during the War of 1812 after a series of British warships chased her and after HMS Hogue trapped her. The schooner became famous for this deadly explosion, which killed most of her crew, and for the folklore about the ghostly "Teazer Light."

Jeddore is a Canadian rural community in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality. The community itself comprises several smaller communities. Often the inner communities are referred to on their own but much of the time simply the encapsulating region of Jeddore is simply used. This is most likely due to the size of the communities, individually they are relatively unknown to residents outside of Nova Scotia's Eastern Shore.

The Raid on Lunenburg occurred during the American Revolution when the US privateer, Captain Noah Stoddard of Fairhaven, Massachusetts, and four other privateer vessels attacked the British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on July 1, 1782. The raid was the last major privateer attack on a Nova Scotia community during the war.

Sherman Zwicker is a wooden auxiliary fishing schooner built in 1942 at the Smith and Rhuland shipyard, Lunenburg, Nova Scotia. Influenced by the design of the famous Bluenose, Sherman Zwicker was built to fish the Grand Banks. The schooner was built for F. Homer Zwicker of Zwicker and Co. Officially christened in 1942, the F/V Sherman Zwicker is the last operable saltbank fishing vessel in existence.
Nellie J. Banks was a 35 GRT cod fishing schooner turned "rum runner", built in 1910. She was one of the last rum runners seized off the coast of Nova Scotia in 1938. Nellie J. Banks was renamed Leona G. Maguire in 1941.
HMCS Chedabucto was a Bangor-class minesweeper that served with the Royal Canadian Navy during the Second World War. She served primarily in the Battle of the Atlantic. During the Battle of the St. Lawrence in 1943, Chedabucto was sunk in a collision with a cable ship.

Richard Moses Murphy (1838–1916) was a well-known schooner captain who sailed out of Gloucester, Massachusetts during the late 1800s. Some of his experiences as a mariner are detailed in a chapter titled "The Adventures of Captain Richard Murphy" in The Fisherman’s Own Book, published by Proctor Brothers in 1882.
The FV Margaret Jane was a Canadian stern trawler based out of Lunenburg, Nova Scotia. Built in 1965 at Snyder's Shipyard in Dayspring, she was owned by fishing company Adams & Knickle.
The FV Flora Alberta was a Canadian auxiliary fishing schooner based out of Lunenburg, Nova Scotia. She was launched in 1941 by Smith and Rhuland, the company's 187th vessel. The managing owner of the vessel was fishing company Adams & Knickle.

The Province of Nova Scotia was heavily involved in the American Revolutionary War (1776–1783). At that time, Nova Scotia also included present-day New Brunswick until that colony was created in 1784. The Revolution had a significant impact on shaping Nova Scotia, "almost the 14th American Colony". At the beginning, there was ambivalence in Nova Scotia over whether the colony should join the Americans in the war against Britain. Largely as a result of American privateer raids on Nova Scotia villages, as the war continued, the population of Nova Scotia solidified their support for the British. Nova Scotians were also influenced to remain loyal to Britain by the presence of British military units, judicial prosecution by the Nova Scotia Governors and the efforts of Reverend Henry Alline.

The American frigate USS Hancock was captured by the British Royal Navy in a 1777 naval battle during the American Revolutionary War. The two highest ranking naval officers of the war battled each other off the coast of Nova Scotia. HMS Rainbow, under the command of British Admiral George Collier, captured USS Hancock, under the command of Captain John Manley.













