
The British Virgin Islands are located in the Caribbean, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Puerto Rico.Its geographic coordinates are 18°30′N64°30′W. Map references include Central America and the Caribbean. The area totals 151 km² and comprises 16 inhabited and more than 20 uninhabited islands; includes the islands of Tortola, Anegada, Virgin Gorda and Jost van Dyke. There are no bodies of water on the land. There are no land boundaries. There is 80 km of coastline. Maritime claims include 3 nmi of territorial sea and exclusive a 200 nmi fishing zone. It has a tropical, humid climate, with temperatures moderated by trade winds. Its terrain consists of coral islands, and is relatively flat. It has volcanic islands and is steep and hilly. Its lowest point is the Caribbean Sea and its highest point is Mount Sage at 521 metres (1,709 ft) above sea level. Its natural resources are negligible. In terms of land use, it is 20% arable land, 6.67% permanent crops and 73.33% other as of a 2005 figure. Its natural hazards consist of hurricanes and tropical storms from July to October. There is limited natural fresh water resources. It has strong ties to nearby U.S. Virgin Islands and Puerto Rico.

Geography of the United States Virgin Islands

The Virgin Islands are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rican Bank and St. Croix being a displaced part of the same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.

Watertown Township is a civil township of Sanilac County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,376 at the 2000 census.
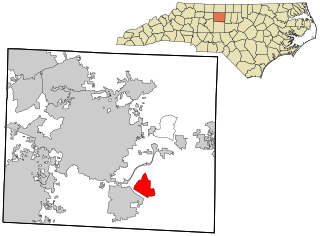
Forest Oaks is a census-designated place (CDP) in Guilford County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 3,890 as of the 2010 census, up from 3,241 at the 2000 census.

Cruz Bay, U.S. Virgin Islands is the main town on the island of Saint John in the United States Virgin Islands. According to the 2000 Census, Cruz Bay has a population of 2,743 people.
The area code (340) is the local telephone area code of U.S. Virgin Islands. The (340) area code was created during a split from the original (809) area code, which began permissive dialing on 1 June 1997 and ended 30 June 1998.

Flanagan Island is an island located within the Virgin Islands archipelago in the Caribbean and forms part of the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The Geodetic Hills are a mountain range on central Axel Heiberg Island, Nunavut, Canada. It is associated with the Arctic Cordillera mountain system.
Acorn is an unincorporated community in Westmoreland County, in the U. S. state of Virginia. Acorn is located 36°57′43.8″N78°59′01″W.

Clarsona is an unincorporated community in Amador County, California. It lies at an elevation of 272 feet and is located at 38°22′26″N120°59′01″W.
Contant is a settlement on the island of Saint Thomas in the United States Virgin Islands. It is located between the capital city of Charlotte Amalie and the Cyril E. King Airport.
Estate Thomas is a settlement adjacent to Charlotte Amalie on the island of Saint Thomas in the United States Virgin Islands.

Louisenhoj is a settlement on the island of Saint Thomas in the United States Virgin Islands.
Solberg is a settlement on the Northside of the island of Saint Thomas in the United States Virgin Islands.

Annaberg is a former sugar factory and plantation on the island of Saint John in the United States Virgin Islands. It is uninhabited and part of Virgin Islands National Park.
Fish Bay is a bay and neighborhood on the island of Saint John in the United States Virgin Islands. Most of this area is part of Virgin Islands National Park.
Robert Heights is an unincorporated community in Gloucester County, in the U. S. state of Virginia.
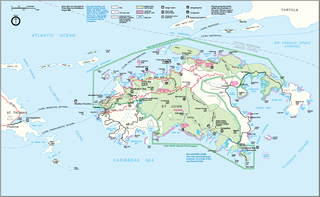
Leduck Island is an island in the United States Virgin Islands, also spelled LeDuck Island, which is located 0.5 miles east of Sabbat Point in Johns Folly, separated from Saint John by the Sabbat Channel. LeDuck Island lies by the entrance to Coral Bay and is 85 feet high. Leduck Island is located within the Virgin Islands National Park and is one of the largest offshore islands to Saint John, along with Grass Cay and Congo Cay. Being home to numerous spur and groove reefs, it is a popular scuba diving destinations and its reefs are habitat for an abundance for endemic tropical fish species. Some of the fish species found here include the Fairy basslet, Sergeant major, French angelfish, Gray angelfish, Queen triggerfish, Jackknife-fish, Blue chromis, Schoolmaster snapper, Mangrove snapper, Red hind, Blacktip shark, Hawksbill sea turtle, Glassy sweeper, Squirrelfish, and numerous species of damsels and jacks.













