
Indemnity is a contractual obligation of one party (indemnifier) to compensate the loss occurred to the other party due to the act of the indemnitor or any other party. The duty to indemnify is usually, but not always, coextensive with the contractual duty to "hold harmless" or "save harmless". In contrast, a guarantee is an obligation of one party assuring the other party that guarantor will perform the promise of the third party if it defaults.
Term life insurance or term assurance is life insurance that provides coverage at a fixed rate of payments for a limited period of time, the relevant term. After that period expires, coverage at the previous rate of premiums is no longer guaranteed and the client must either forgo coverage or potentially obtain further coverage with different payments or conditions. If the life insured dies during the term, the death benefit will be paid to the beneficiary. Term insurance is typically the least expensive way to purchase a substantial death benefit on a coverage amount per premium dollar basis over a specific period of time.
In insurance, the insurance policy is a contract between the insurer and the insured, known as the policyholder, which determines the claims which the insurer is legally required to pay. In exchange for an initial payment, known as the premium, the insurer promises to pay for loss caused by perils covered under the policy language.
A waiver is the voluntary relinquishment or surrender of some known right or privilege.

Subrogation is the assumption by a third party of another party's legal right to collect a debt or damages. It is a legal doctrine whereby one person is entitled to enforce the subsisting or revived rights of another for one's own benefit. A right of subrogation typically arises by operation of law, but can also arise by statute or by agreement. Subrogation is an equitable remedy, having first developed in the English Court of Chancery. It is a familiar feature of common law systems. Analogous doctrines exist in civil law jurisdictions.

Property insurance provides protection against most risks to property, such as fire, theft and some weather damage. This includes specialized forms of insurance such as fire insurance, flood insurance, earthquake insurance, home insurance, or boiler insurance. Property is insured in two main ways—open perils and named perils.
Liability insurance is a part of the general insurance system of risk financing to protect the purchaser from the risks of liabilities imposed by lawsuits and similar claims. It protects the insured in the event he or she is sued for claims that come within the coverage of the insurance policy. Originally, individual companies that faced a common peril formed a group and created a self-help fund out of which to pay compensation should any member incur loss. The modern system relies on dedicated carriers, usually for-profit, to offer protection against specified perils in consideration of a premium.
Whole life insurance, or whole of life assurance, sometimes called "straight life" or "ordinary life," is a life insurance policy which is guaranteed to remain in force for the insured's entire lifetime, provided required premiums are paid, or to the maturity date. As a life insurance policy it represents a contract between the insured and insurer that as long as the contract terms are met, the insurer will pay the death benefit of the policy to the policy's beneficiaries when the insured dies. Because whole life policies are guaranteed to remain in force as long as the required premiums are paid, the premiums are typically much higher than those of term life insurance where the premium is fixed only for a limited term. Whole life premiums are fixed, based on the age of issue, and usually do not increase with age. The insured party normally pays premiums until death, except for limited pay policies which may be paid up in 10 years, 20 years, or at age 65. Whole life insurance belongs to the cash value category of life insurance, which also includes universal life, variable life, and endowment policies.
Directors and officers liability Insurance is liability insurance payable to the directors and officers of a company, or to the organization(s) itself, as indemnification (reimbursement) for losses or advancement of defense costs in the event an insured suffers such a loss as a result of a legal action brought for alleged wrongful acts in their capacity as directors and officers. Such coverage can extend to defense costs arising out of criminal and regulatory investigations/trials as well; in fact, often civil and criminal actions are brought against directors/officers simultaneously. Intentional illegal acts, however, are typically not covered under D&O policies.
Marine insurance covers the loss or damage of ships, cargo, terminals, and any transport by which the property is transferred, acquired, or held between the points of origin and the final destination. Cargo insurance is the sub-branch of marine insurance, though Marine insurance also includes Onshore and Offshore exposed property,, Hull, Marine Casualty, and Marine Liability. When goods are transported by mail or courier, shipping insurance is used instead.
A public adjuster is a professional claims handler/ claims adjuster who advocates for the policyholder in appraising and negotiating a claimant's insurance claim. Aside from attorneys and the broker of record, state licensed public adjusters can legally represent the rights of an insured during an insurance claim process. Their technical expertise and ability to interpret sometimes ambiguous insurance policies allow property owners to receive the maximum amount of indemnification for their claims. Although seen many times as adversarial by the Carriers, public adjusters do substantially increase the settlement value of the loss. Many professionals, and persons who are either incapable due to education, age, or physical impairment, choose public adjuster representation to guide them through the process and minimize the time which must be spent to perfect their claim. Most public adjusters charge a percentage of the settlement like general contractors who add (10/10) to the total repair cost to cover overhead and reasonable profit. Primarily public adjusters prepare detailed scope and cost estimates many times using experts in the fields of remediation, toxicology, and construction engineers to prove their loss. Public adjusters also provide insurance policy interpretation to determine covered and uncovered items and to negotiate with the insurance Carrier to a final and fair settlement.
Insurance bad faith is a legal term of art unique to the law of the United States that describes a tort claim that an insured person may have against an insurance company for its bad acts. Under United States law, insurance companies owe a duty of good faith and fair dealing to the persons they insure. This duty is often referred to as the "implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing" which automatically exists by operation of law in every insurance contract.
A loss payee clause is a clause in a contract of insurance that provides, in the event of payment being made under the policy in relation to the insured risk, that payment will be made to a third party rather than to the insured beneficiary of the policy.
Insurance in the United States refers to the market for risk in the United States, the world's largest insurance market by premium volume. Of the $4.640 trillion of gross premiums written worldwide in 2013, $1.274 trillion (27%) were written in the United States.
According to the law, the term adjustment may appear in varied contexts, as a synonym for terms with unrelated definitions:
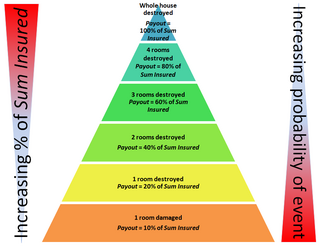
Condition of average is the insurance term used when calculating a payout against a claim where the policy undervalues the sum insured. In the event of partial loss, the amount paid against a claim will be in the same proportion as the value of the underinsurance.
Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is a subsidiary of Reserve Bank of India. It was established on 15 July 1978 under Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961 for the purpose of providing insurance of deposits and guaranteeing of credit facilities. DICGC insures all bank deposits, such as saving, fixed, current, Recurring deposit for up to the limit of Rs. 100,000 of each deposits in a bank.
Insurance in South Africa describes a mechanism in that country for the reduction or minimisation of loss, owing to the constant exposure of people and assets to risks. The kinds of loss which arise if such risks eventuate may be either patrimonial or non-patrimonial.




