
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas.

The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defeated it, in the process stripping the Ottomans of its European provinces, leaving only Eastern Thrace under the Ottoman Empire's control. In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria fought against the other four original combatants of the first war. It also faced an attack from Romania from the north. The Ottoman Empire lost the bulk of its territory in Europe. Although not involved as a combatant, Austria-Hungary became relatively weaker as a much enlarged Serbia pushed for union of the South Slavic peoples. The war set the stage for the Balkan crisis of 1914 and thus served as a "prelude to the First World War".

The Balkans, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

Montenegro is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is a part of the Balkans and is bordered by Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast, Kosovo to the east, Albania to the southeast, Croatia to the southwest, and the Adriatic Sea to the south with a coastline of 293.5 km. Podgorica, the capital and largest city, covers 10.4% of Montenegro's territory of 13,812 square kilometres (5,333 sq mi), and is home to roughly 31% of its total population of 621,000. Cetinje is the former royal capital of Montenegro and is the location of several national institutions, including the official residence of the president of Montenegro.

The First Balkan War lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and involved actions of the Balkan League against the Ottoman Empire. The Balkan states' combined armies overcame the initially numerically inferior and strategically disadvantaged Ottoman armies, achieving rapid success.

The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 (O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counterattacked, entering Bulgaria. With Bulgaria also having previously engaged in territorial disputes with Romania and the bulk of Bulgarian forces engaged in the south, the prospect of an easy victory incited Romanian intervention against Bulgaria. The Ottoman Empire also took advantage of the situation to regain some lost territories from the previous war. When Romanian troops approached the capital Sofia, Bulgaria asked for an armistice, resulting in the Treaty of Bucharest, in which Bulgaria had to cede portions of its First Balkan War gains to Serbia, Greece and Romania. In the Treaty of Constantinople, it lost Adrianople to the Ottomans.

The Balkan mountain range is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs for about 560 kilometres (350 mi), first in a south-easterly direction along the border, then eastward across Bulgaria, forming a natural barrier between the northern and southern halves of the country, before finally reaching the Black Sea at Cape Emine. The mountains reach their highest point with Botev Peak at 2,376 metres (7,795 ft).

The Congress of Berlin was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at the meeting were Europe's then six great powers: Russia, Great Britain, France, Austria-Hungary, Italy, and Germany; the Ottomans; and four Balkan states: Greece, Serbia, Romania and Montenegro. The congress concluded with the signing of the Treaty of Berlin, replacing the preliminary Treaty of San Stefano that had been signed three months earlier.
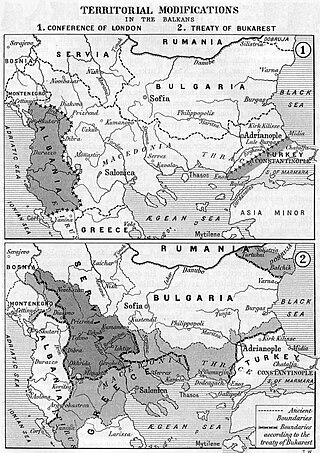
The Treaty of Bucharest was concluded on 10 August 1913, by the delegates of Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Montenegro and Greece. The Treaty was concluded in the aftermath of the Second Balkan War and amended the previous Treaty of London, which ended the First Balkan War. About one month later, the Bulgarians signed a separate border treaty with the Ottomans, who had regained some territory west of the Enos-Midia Line during the second war.

Vratsa is the largest city in northwestern Bulgaria and the administrative and economic centre of the municipality of Vratsa and Vratsa district. It is located about 112 km north of Sofia, 40 km southeast of Montana.
The NATO Medal is an international military decoration which is awarded to various militaries of the world under the authority of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is manufactured by Eekelers-Centini Intl, of Hemiksem, Belgium.
The Balkans Cup was an international football competition for clubs from Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, Turkey, and Yugoslavia. It was introduced in 1961 and was very popular in the 1960s, being the second most important international club competition for clubs from the region. The competition has been dominated by Bulgaria-based teams. The Bulgarian teams have won together a total number of 9 titles.

The Battle of Monastir took place near the town of Bitola, Macedonia during the First Balkan War, between Serbian and Ottoman forces from 16 to 19 November 1912. It resulted in a Serbian victory after heavy fighting north of the city, the routed Turks fled abandoning their guns.
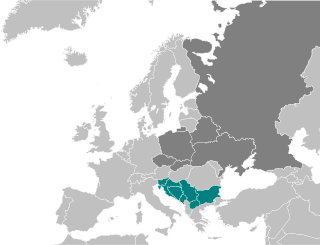
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Serbs, Croats, Bosniaks, Montenegrins, Bulgarians, Macedonians, and Slovenes. The countries they live are:
Serbia
Croatia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Montenegro
Bulgaria
Macedonia
Slovenia
The Balkans Theatre or Balkan Campaign was a theatre of World War I fought between the Central Powers and the Allies.
The European Amateur Boxing Championships is the highest competition for boxing amateurs in Europe, organised by the continent's governing body EUBC, which stands for the European Boxing Confederation. The first edition of the tournament took place in 1924, although the first 'competitive' championships were hosted by the city of Stockholm (Sweden) in 1925.
Dušan T. Bataković was a Serbian historian and diplomat. His specialty was modern and contemporary Serbian and Balkan history as well as French-Serbian relations. The last post he held was that of Director of the Institute for Balkan Studies at the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts.

Balkan Romani, Balkaniko Romanes, or Balkan Gypsy is a specific non-Vlax dialect of the Romani language, spoken by groups within the Balkans, which include countries such as Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Greece, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia, Turkey etc. The Balkan Romani language is typically an oral language.

Kozarnika or Peshtera Kozarnika is a cave in northwestern Bulgaria that was used as a hunters’ shelter as early as the Lower Paleolithic. It marks an older route of early human migration from Africa to Europe via the Balkans, prior to the other currently suggested route - the one across Gibraltar. The cave probably keeps the earliest evidence of human symbolic behaviour and the earliest European Gravette flint assemblages came to light here.













