
A megacity is a very large city, typically with a population of more than 10 million people. Precise definitions vary: the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs in its 2018 "World Urbanization Prospects" report counted urban agglomerations having over 10 million inhabitants. A University of Bonn report held that they are "usually defined as metropolitan areas with a total population of 10 million or more people". Others list cities satisfying criteria of either 5 or 8 million and also have a population density of 2,000 per square kilometre. The terms conurbation, metropolis, and metroplex are also applied to the latter.

A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories under the same administrative division, sharing industry, infrastructure and housing. A metro area usually comprises multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighborhoods, townships, boroughs, cities, towns, exurbs, suburbs, counties, districts, states, and even nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions.

An aire urbaine is an INSEE statistical concept describing a core of urban development and the extent of its commuter activity.
The term regional county municipality or RCM is used in Quebec to refer to one of 87 county-like political entities. In some older English translations they were called county regional municipality.

An urban area, or built-up area, is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbanism, the term contrasts to rural areas such as villages and hamlets; in urban sociology or urban anthropology it contrasts with natural environment. The creation of early predecessors of urban areas during the urban revolution led to the creation of human civilization with modern urban planning, which along with other human activities such as exploitation of natural resources led to a human impact on the environment. "Agglomeration effects" are in the list of the main consequences of increased rates of firm creation since. This is due to conditions created by a greater level of industrial activity in a given region. However, a favorable environment for human capital development would also be generated simultaneously.
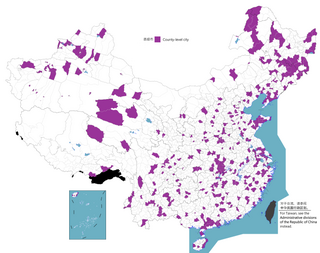
A county-level municipality, county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city, is a county-level administrative division of the People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judicial but no legislative rights over their own local law and are usually governed by prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by province-level divisions.

Montréal is one of the administrative regions of the Canadian province of Quebec. It is also a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) and a census division (CD), for both of which its geographical code is 66. Prior to the merger of the municipalities in Region 06 in 2002, the administrative region was co-extensive with the Montreal Urban Community.

A city proper is the area contained within city limits. A city proper is not limited to a city; it can describe the complete area of any locality that fits the definition. The United Nations defines the term as "the single political jurisdiction which contains the historical city centre."

The Harrisburg–Carlisle, Pennsylvania, metropolitan statistical area is defined by the United States Census Bureau as an area consisting of three counties in Pennsylvania's Susquehanna Valley, anchored by the cities of Harrisburg and Carlisle. As of the 2010 census, the metropolitan statistical area (MSA) had a population of 549,475. In 2009, Harrisburg–Carlisle was the 96th largest metropolitan area in the United States. As of 2010, it is part of the defined Harrisburg–York–Lebanon, PA Combined Statistical Area, which includes York and Adams counties and has a population of 1,233,708 people making it the 43rd most populous in the United States.
The province of Quebec is divided into units at the regional, supralocal and local levels. The primary types of subdivision are administrative regions, regional county municipalities (RCMs), metropolitan communities (CMs), the Kativik Regional Government (KRG), unorganized territories (TNOs), agglomerations, northern villages, Cree villages, Naskapi villages, and a variety of local units which may collectively be referred to as local municipalities and boroughs.
An agglomeration, or urban agglomeration, is an administrative subdivision of Quebec at the local level that may group together a number of municipalities which were abolished as independent entities on 1 January 2002 but reconstituted on 1 January 2006.
The Service de police de l'agglomération de Longueuil or SPAL is the police force for the urban agglomeration of Longueuil, Quebec. This service is divided into two territories, north and south.
In China, a City Cluster is an officially defined type of megalopolis, whereby government policy is to knit the area together more tightly and promote development through transportation and communication links. The Economist Intelligence Unit in 2012 identified 13 megalopolises: Chang-Zhu-Tan, Chengdu, Chongqing, Greater Beijing i.e. Jing-Jin-Ji, Greater Shanghai, Greater Xi'an, Greater Zhengzhou, Greater Guangzhou, Hefei economic circle, Shandong Peninsula, Greater Shenyang, Shenzhen and Wuhan.







