Related Research Articles

The cello ( CHEL-oh; plural celli or cellos) or violoncello ( VY-ə-lən-CHEL-oh; Italian pronunciation: [vjolonˈtʃɛllo]) is a bowed (and occasionally plucked) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually tuned in perfect fifths: from low to high, C2, G2, D3 and A3. The viola's four strings are each an octave higher. Music for the cello is generally written in the bass clef, with tenor clef and treble clef used for higher-range passages.

The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing the strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A plectrum or individual finger picks may be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant chamber on the instrument, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.

The hammered dulcimer is a percussion-stringed instrument which consists of strings typically stretched over a trapezoidal resonant sound board. The hammered dulcimer is set before the musician, who in more traditional styles may sit cross-legged on the floor, or in a more modern style may stand or sit at a wooden support with legs. The player holds a small spoon-shaped mallet hammer in each hand to strike the strings. The Graeco-Roman dulcimer derives from the Latin dulcis (sweet) and the Greek melos (song). The dulcimer, in which the strings are beaten with small hammers, originated from the psaltery, in which the strings are plucked.

The piano is an acoustic, stringed musical instrument invented in Italy by Bartolomeo Cristofori around the year 1700, in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material. It is played using a keyboard, which is a row of keys that the performer presses down or strikes with the fingers and thumbs of both hands to cause the hammers to strike the strings.

The viol, viola da gamba, or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Frets on the viol are usually made of gut, tied on the fingerboard around the instrument's neck, to enable the performer to stop the strings more cleanly. Frets improve consistency of intonation and lend the stopped notes a tone that better matches the open strings. Viols first appeared in Spain in the mid to late 15th century and were most popular in the Renaissance and Baroque (1600–1750) periods. Early ancestors include the Arabic rebab and the medieval European vielle, but later, more direct possible ancestors include the Venetian viole and the 15th- and 16th-century Spanish vihuela, a 6-course plucked instrument tuned like a lute that looked like but was quite distinct from the 4-course guitar.

The viola d'amore is a 7- or 6-stringed musical instrument with sympathetic strings used chiefly in the baroque period. It is played under the chin in the same manner as the violin.
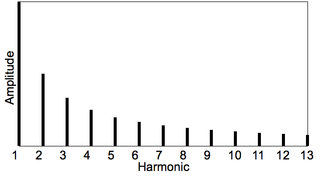
In music, inharmonicity is the degree to which the frequencies of overtones depart from whole multiples of the fundamental frequency.
Piano acoustics are the physical properties of the piano that affect its sound. It is an area of study within musical acoustics.
Piano construction is by now a rather conservative area; most of the technological advances were made by about 1900, and indeed it is possible that some contemporary piano buyers might actually be suspicious of pianos that are made differently from the older kind. Yet piano manufacturers, especially the smaller ones, are still experimenting with ways to build better pianos.

Aliquot stringing is the use of extra, un-struck strings in the piano for the purpose of enriching the tone. Aliquot systems use an additional string in each note of the top three piano octaves. This string is slightly higher than the other three strings so that it is not struck by the hammer. Whenever the hammer strikes the three conventional strings, the aliquot string vibrates sympathetically. Aliquot stringing broadens the vibrational energy throughout the instrument, and creates an unusually complex and colorful tone.

Sympathetic strings or resonance strings are auxiliary strings found on many Indian musical instruments, as well as some Western Baroque instruments and a variety of folk instruments. They are typically not played directly by the performer, only indirectly through the tones that are played on the main strings, based on the principle of sympathetic resonance. The resonance is most often heard when the fundamental frequency of the string is in unison or an octave lower or higher than the catalyst note, although it can occur for other intervals, such as a fifth, with less effect.

Piano tuning is the act of adjusting the tension of the strings of an acoustic piano so that the musical intervals between strings are in tune. The meaning of the term 'in tune', in the context of piano tuning, is not simply a particular fixed set of pitches. Fine piano tuning requires an assessment of the vibration interaction among notes, which is different for every piano, thus in practice requiring slightly different pitches from any theoretical standard. Pianos are usually tuned to a modified version of the system called equal temperament.
Alan Ridout was a British composer and teacher.

The yueqin or yue qin, formerly romanized as yüeh-ch‘in and also known as the moon guitar, moon lute, gekkin, wolgeum, or la-ch‘in, is a traditional Chinese string instrument. It is a lute with a round, hollow wooden body which gives it the nickname moon guitar.

A variety of methods are used to tune different stringed instruments. Most change the pitch produced when the string is played by adjusting the tension of the strings.

The khim is a stringed musical instrument derived from the Mesopotamian or Persian Santur. It is similar to the Hammered Dulcimer or Cimbalom. This khim was introduced to Cambodia, Laos and Thailand from China, where a similar instrument is called yangqin. It is played with two flexible bamboo sticks with soft leather at the tips to produce a soft tone. This instrument can be played by either sitting down on the floor with the khim on the floor, or by sitting on a chair or standing while the khim is on a stand. The khim produces a bright and expressive sound when played. It is made of wood, with brass strings that are laid across the instrument. The Australian-born musician and vocal artist Lisa Gerrard specialises in the use of a khim hammered dulcimer, featuring its music on several albums and performing with the instrument live on tour.

Piano pedals are foot-operated levers at the base of a piano that change the instrument's sound in various ways. Modern pianos usually have three pedals, from left to right, the soft pedal, the sostenuto pedal, and the sustaining pedal. Some pianos omit the sostenuto pedal, or have a middle pedal with a different purpose such as a muting function also known as silent piano.
String resonance occurs on string instruments. Strings or parts of strings may resonate at their fundamental or overtone frequencies when other strings are sounded. For example, an A string at 440 Hz will cause an E string at 330 Hz to resonate, because they share an overtone of 1320 Hz.

A bridge is a device that supports the strings on a stringed musical instrument and transmits the vibration of those strings to another structural component of the instrument—typically a soundboard, such as the top of a guitar or violin—which transfers the sound to the surrounding air. Depending on the instrument, the bridge may be made of carved wood, metal or other materials. The bridge supports the strings and holds them over the body of the instrument under tension.

D-274 is the model name of a concert grand piano, the flagship of the Steinway & Sons piano company, first built in 1884. It is generally described as the first choice of most concert pianists. As of 2017 a D-274 finished in Polished Ebony has a MSRP of $175,700 USD.
References
- Good, Edwin. Giraffes, Black Dragons, and Other Pianos. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 2001. ISBN 9780804745499