
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package, or dual in-line pin package (DIPP) is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB) or inserted in a socket. The dual-inline format was invented by Don Forbes, Rex Rice and Bryant Rogers at Fairchild R&D in 1964, when the restricted number of leads available on circular transistor-style packages became a limitation in the use of integrated circuits. Increasingly complex circuits required more signal and power supply leads ; eventually microprocessors and similar complex devices required more leads than could be put on a DIP package, leading to development of higher-density chip carriers. Furthermore, square and rectangular packages made it easier to route printed-circuit traces beneath the packages.

Hermeticism, also called Hermetism, is a religious, philosophical, and esoteric tradition based primarily upon writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus. These writings have greatly influenced the Western esoteric tradition and were considered to be of great importance during both the Renaissance and the Reformation. The tradition traces its origin to a prisca theologia, a doctrine that affirms the existence of a single, true theology that is present in all religions and that was given by God to man in antiquity.

Canning is a method of preserving food in which the food contents are processed and sealed in an airtight container. Canning provides a shelf life typically ranging from one to five years, although under specific circumstances it can be much longer. A freeze-dried canned product, such as canned dried lentils, could last as long as 30 years in an edible state. In 1974, samples of canned food from the wreck of the Bertrand, a steamboat that sank in the Missouri River in 1865, were tested by the National Food Processors Association. Although appearance, smell and vitamin content had deteriorated, there was no trace of microbial growth and the 109-year-old food was determined to be still safe to eat.

Ultrasonic welding is an industrial technique whereby high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations are locally applied to workpieces being held together under pressure to create a solid-state weld. It is commonly used for plastics and metals, and especially for joining dissimilar materials. In ultrasonic welding, there are no connective bolts, nails, soldering materials, or adhesives necessary to bind the materials together. When applied to metals, a notable characteristic of this method is that the temperature stays well below the melting point of the involved materials thus preventing any unwanted properties which may arise from high temperature exposure of the materials.
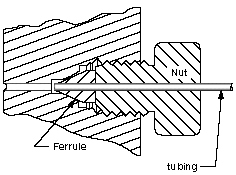
A mechanical seal is a device that helps join systems or mechanisms together by preventing leakage, containing pressure, or excluding contamination. The effectiveness of a seal is dependent on adhesion in the case of sealants and compression in the case of gaskets.

A bung, stopper or cork is a truncated cylindrical or conical closure to seal a container, such as a bottle, tube or barrel. Unlike a lid, which encloses a container from the outside without displacing the inner volume, a bung is partially inserted inside the container to act as a seal.

A heat sealer is a machine used to seal products, packaging, and other thermoplastic materials using heat. This can be with uniform thermoplastic monolayers or with materials having several layers, at least one being thermoplastic. Heat sealing can join two similar materials together or can join dissimilar materials, one of which has a thermoplastic layer.
Hermetic Storage is a method of using sealed, airtight units to control moisture and insects in stored dry agricultural commodities. The hermetic storage restricts gas exchanges between the internal and external environments and the stored commodity, maintaining the initial levels of moisture and controlling pests by the lack of oxygen.
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering.

Induction sealing is the process of bonding thermoplastic materials by induction heating. This involves controlled heating an electrically conducting object by electromagnetic induction, through heat generated in the object by eddy currents.

In electronics, TO-3 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for power semiconductors, including transistors, silicon controlled rectifiers, and, integrated circuits. TO stands for "Transistor Outline" and relates to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC.

A shrink tunnel or heat tunnel is a heated tunnel mounted over or around a conveyor system. Items have shrink film loosely applied; with heat, the film shrinks to fit snugly around the wrapped object.
Coffee bean storage is a broad term describing the packaging and preservation of coffee beans throughout the process from harvesting to brewing. Although the term is applicable to many phases of this process, it is typically applied to ideal home storage for maximum consumer coffee enjoyment.

Resealable packaging is any type of packaging that allows the consumer or user to reseal or reclose the packaging. Often packaging needs to be resealed in order to maintain product freshness or prevent spillage. Reusable packaging allows for multiple uses which can help reduce waste.
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed encapsulation. The wafers' diameter range from 100 mm to 200 mm for MEMS/NEMS and up to 300 mm for the production of microelectronic devices. Smaller wafers were used in the early days of the microelectronics industry, with wafers being just 1 inch in diameter in the 1950s.
Purdue Improved Crop Storage (PICS) bags provide a simple, low-cost method of reducing post-harvest cowpea losses due to bruchid infestations in west and central Africa.
Grain storage on a subsistence farm is primarily based on minimizing grain loss. In modern agricultural practices there are methods of managing under 1% grain loss, but small subsistence farms can see 20% - 100% of grain loss. This causes starvation and an unstable food supply. Grain loss can be caused by mold growth, bugs, birds, or any other contamination. One method of preventing loss is hermetic grain storage. Hermetic grain storage strives to eliminate all exchange of gases within the storage system. This mitigates bacterial activity and prevents rodents and bugs from being able to breathe inside the storage systems. The introduction of hermetic grain storage to subsistence farms can create a more stable food supply in the area and reduce the risk of starvation.













