Attu is the westernmost and largest island in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and the westernmost point of land relative to Alaska. The island became uninhabited in 2010.

Atka Island is the largest island in the Andreanof Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. The island is 50 miles (80 km) east of Adak Island. It is 65 miles (105 km) long and 2–20 miles (3–30 km) wide with a land area of 404.6 square miles (1,048 km2), making it the 22nd largest island in the United States. The northeast of Atka Island contains the Korovin volcano which reaches a peak of 5,030 feet (1,533 m). Oglodak Island is located 3.4 miles off Cape Kigun, Atka's westernmost point.
De Koog is a town in the Dutch province of North Holland. It is a part of the municipality of Texel, and lies about 17 km north of Den Helder. It is the chief centre of tourism on the island, surrounded with many hotels and campgrounds. The village is located on the North Sea coast of the island. Only two narrow lines of dunes separate the village from the beach.

Buldir Island is a small island in the western Aleutian Islands of the U.S. state of Alaska. It lies midway between the Near Islands in the West and the Rat Islands in the East. It is the most westerly of the Aleutian Islands which formed as a result of volcanic activity in the late Quaternary or Recent times. The rocks from which the island formed are of two different ages with a considerable time gap. The rocks of the older dome are mainly olivine basalts and the younger dome consists of hornblende basalts and basaltic andesites. That this island is younger than some of the neighboring islands is also suggested by the fact that there are fewer species of flowering plant on this island.

Agattu is an island in the Near Islands in the western end of the Aleutian Islands. With a land area of 85.558 square miles (221.59 km2) Agattu is one of the largest uninhabited islands in the Aleutians. It is the second largest of the Near Islands, after Attu Island. It is volcanic and considerably mountainous. The treeless island has a tundra-like terrain which reaches a peak of 2,073 feet (632 m) above sea level. Its length is 12.2 miles (19.7 km) and width is 19 miles (30 km).

Samalga Island is the westernmost island in the Fox Islands group of the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska. It is 5.36 miles (8.63 km) long and is situated at the southwestern tip of Umnak Island. It has a land area of 1.589 square miles (4.12 km2) and is uninhabited. It is separated from the Islands of Four Mountains group to the west by the Samalga Pass. Samalga is the farthest point west on the Aleutian Island chain that still keeps the Alaska UTC−9 time zone. It is also the closest Alaskan island to Hawaii.

Sedanka Island is an island in the Fox Islands group of the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska. It is 10.3 miles (16.6 km) long and is situated off the northeast coast of Unalaska Island. It has a land area of 39.889 square miles (103.31 km2) and no permanent population.

Nizki Island is an uninhabited island in the Aleutian Islands in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located at 52°44′28″N173°59′08″E, it is the middle island of the Semichi Islands group of the Near Islands. Flanked by Shemya to the east and Alaid to the west, three-mile-long (5 km) Nizki is periodically joined to Alaid by a sand spit. The name is said to derive from the Russian nizkiy, meaning "low," a term descriptive of the island's topography, with a maximum elevation of 165 feet. Nizki's shoreline is very irregular and is fringed by numerous rocks, reefs, and kelp-marked shoals.

Amlia is an island in the Aleutian Islands. It is located near the eastern end of the Andreanof Islands and is situated between Atka Island and Seguam Island.

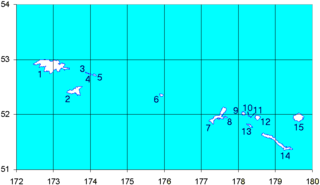
Great Sitkin Island is a volcanic island in the Andreanof Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. The island covers a total area of 60 square miles (160 km2) and lies slightly north of a group of islands which are located between Adak Island and Atka Island.

Igitkin Island is a small island located in an area between Adak Island and Atka Island among other small islands. The island belongs to the Andreanof Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska.

Umak Island is an island lying in a group of small islands situated between Adak Island and Atka Island in the Andreanof Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is 11.7 kilometres long and 7.8 kilometres wide.

Islands of Four Mountains is an island grouping of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska, United States. The chain includes, from west to east, Amukta, Chagulak, Yunaska, Herbert, Carlisle, Chuginadak, Uliaga, and Kagamil islands. This island chain is located between Amukta Pass and the Andreanof Islands to the west, and Samalga Pass and the Fox Islands to the east. These islands have a total land area of 210.656 sq mi (545.596 km²) and have no permanent population. The two largest islands are Yunaska and Chuginadak. Chuginadak is mainly made up of the active volcano Mount Cleveland.

Yunaska is the largest of the Islands of Four Mountains group in the Aleutian Islands of southwestern Alaska, United States. It has a land area of 66.834 square miles and no population at the 2000 census.

Unalga Island is one of the Fox Islands subgroup of the Aleutian Islands of southwestern Alaska, United States. It lies just northeast of Unalaska Island and across Akutan Pass from Akutan Island to its northeast. It is the westernmost island in the Aleutians East Borough. Unalga Island has a land area of 11.004 square miles and is unpopulated. The island is 6.7 kilometres (4.2 mi) long and 8.2 kilometres (5.1 mi) wide.

Carlisle Island is an island in the Islands of Four Mountains subgroup of the Aleutian archipelago. It is 1.9 miles (3.1 km) across the Carlisle Pass from Chuginadak Island and is 5.6 miles (9.0 km) northeast of Herbert Island. Carlisle Island has as diameter of 4.3 miles (6.9 km) and is dominated by the 5,280-foot (1,610 m) conical stratovolcano of the same name.

Unalaska is an island in the Fox Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in the US state of Alaska located at 53°38′N167°00′W. The island has a land area of 1,051 square miles (2,720 km2). It measures 79.4 mi (127.8 km) long and 34.7 mi (55.8 km) wide. The city of Unalaska, Alaska, covers part of the island and all of neighboring Amaknak Island where the Port of Dutch Harbor is located. The population of the island excluding Amaknak as of the 2000 census was 1,759 residents.

The Aleutian Islands, also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller ones belonging to both the U.S. state of Alaska and the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying an area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about 1,200 mi (1,900 km) westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and mark a dividing line between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude and the easternmost by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line. While nearly all the archipelago is part of Alaska and is usually considered as being in the "Alaskan Bush", at the extreme western end, the small, geologically related Commander Islands belong to Russia.
Burgwallen Oude Zijde is a neighborhood of Amsterdam, Netherlands.