Telecommunications in Belarus involves the availability and use of electronic devices and services, such as the telephone, television, radio or computer, for the purpose of communication.

The history of the Internet has its origin in information theory and the efforts of scientists and engineers to build and interconnect computer networks. The Internet Protocol Suite, the set of rules used to communicate between networks and devices on the Internet, arose from research and development in the United States and involved international collaboration, particularly with researchers in the United Kingdom and France.

Telecommunications infrastructure in South Africa provides modern and efficient service to urban areas, including cellular and internet services. The Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) is the watchdog of the telecommunications in the country.
Telkom SA SOC Limited is a South African wireline and wireless telecommunications provider, operating in more than 38 countries across the African continent. Telkom is majority state-owned (55.3%) with the South African government owning 40.5% of Telkom, while another 14.8% is owned by another state-owned company - the Public Investment Corporation (PIC), which is closely linked to the South African government.

Hellkom is an Internet parody site about Telkom, South Africa's telecommunications monopoly. It was started by Gregg Stirton in June 2004 as a protest to the parastatal's excessive pricing for its services. In April 2009, Stirton started a discussion forum named BBLounge to complement the site. Hellkom and BBLounge communities represent South African telecommunication consumers who want to see South Africa benefit from full liberalisation of the telecommunications sector in South Africa by educating the public and the media.

Tarek Kamel was an Egyptian politician and computer engineer expert in global Internet governance issues.

Use of the Internet in Yemen began in 1996 through the ISPs TeleYemen and the Public Telecommunications Corporation. By July 2016 6,732,928 people were Internet users.
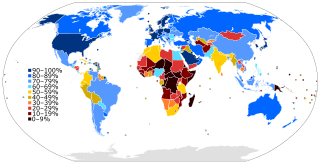
The Internet in Africa is limited by a lower penetration rate when compared to the rest of the world. Measurable parameters such as the number of ISP subscriptions, overall number of hosts, IXP-traffic, and overall available bandwidth are indicators that Africa is far behind the "digital divide". Moreover, Africa itself exhibits an inner digital divide, with most Internet activity and infrastructure concentrated in South Africa, Morocco, Egypt as well as smaller economies like Mauritius and Seychelles. In general, only 24.4% of the African population have access to the Internet, as of 2018. Only 0.4% of the African population has a fixed-broadband subscription. The majority of internet users use it through mobile broadband.

The Internet in South Africa, one of the most technologically resourced countries on the African continent, is expanding. The internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) .za is managed and regulated by the .za Domain Name Authority (.ZADNA) and was granted to South Africa by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) in 1990. Over 60% of Internet traffic generated on the African continent originates from South Africa. As of 2020, 41.5 million people were Internet users.

Internet in Moldova is one of the fastest and least expensive in the world. The country ranks 3rd in the world by gigabit coverage with around 90% of the population having the option to subscribe to a gigabit plan. The overall infrastructure is well developed which allows many users to experience good quality services throughout the country. However, despite high speeds and cheap prices, the penetration level is quite low when compared with many EU or CIS countries. In 2018, 49% of Moldovan households had broadband access. In 2015, there were 80 registered Internet Service Provider's (ISP's) in the country, with the majority being local or regional with only a few offering their services throughout the country. Moldtelecom and StarNet are the country's leading providers sharing around 88% of the market. The remaining 12% are shared between other ISPS, like SunCommunications, Arax Communications and others. Almost all ISPs that offer their services across the country have their headquarters located in the capital-city of Chişinău.
The Internet in Botswana is used by about 28.4% of the population. This is slightly lower than the figure of 28.6% for Africa as a whole in 2015.
The Internet in Zimbabwe has seen rapid expansion in recent years. The Internet country code top-level domain is .zw. In 2009, the Mugabe-Tsvangirai Government of National Unity established a Ministry of Information and Communications Technology to focus on ICT growth and development.
Access to the Internet in Azerbaijan is growing, supported by a national strategy to develop the country into an information and communication technology (ICT) hub for the Caucasus region. The Azerbaijani government actively seeks to attract foreign aid to help boost the telecommunications and ICT sectors. While the government claims 85 percent of the population was online in 2013, service provider Baktelekom has provided free Wi-Fi zones in several points of Baku like the National Flag Square, the Boulevard, Old City, the park around the Heyder Aliyev Centre, parks of Sahil, Sabir, Samad Vurghun, Winter Park, as well as Port Baku Residence and Port Baku Mall.
Internet in Tajikistan became present within the country during the early 1990s. Tajikistan had just become independent in 1992, with Emomali Rahmon as the new ruler, when the internet was introduced to the country. Nevertheless, it was after over a decade that the country’s internet became more accessible. The history of the internet’s foundation in Tajikistan extends from 1992 to present-day Tajikistan. By 2009, internet penetration had developed since the initial conception of the internet in Tajikistan and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) had increased in number. In terms of the ISPs, Tajikistan primarily relied upon satellite-based connections using Discovery Global Networks.

South African wireless community networks are wireless networks that allow members to talk, send messages, share files and play games independent of the commercial landline and mobile telephone networks. Most of them use WiFi technology and many are wireless mesh networks. A wireless community network may connect to the public switched telephone network and/or the Internet, but there are various restrictions on connectivity in South Africa. Wireless community networks are particularly useful in areas where commercial telecommunications services are unavailable or unaffordable.

British Telecommunications plc v. Prodigy Communications Corp. was a patent infringement case which determined whether a patent related to communications between central computers and their clients was infringed by Internet service providers through hyperlinks. Judge Colleen McMahon of the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York ruled that Prodigy Communications Corporation had not infringed the patent held by British Telecommunications plc through its use of hyperlinks. On summary judgment, McMahon held that there were substantial differences between British Telecommunications' patent and the method of operation of the Internet. The decision limited patent protection for Internet service providers' use of hyperlinks, protecting the providers from licensing fees related to this integral part of Internet technology.

Satish Babu is a Free Software activist, early Internet advocate, and development professional based out of Kerala, India. He is the founding Director of the International Centre for Free and Open Source Software (ICFOSS), an autonomous academic/research institution of the Government of Kerala, India, where he worked from March 2011 to September 2015. He was earlier the CEO of SIFFS, an NGO of small-scale artisanal fishers of south India; a co-founder and President of InApp Information Technologies; and is associated with international and national professional societies such as IEEE, Internet Society (ISOC), ICANN, and the Computer Society of India (CSI).

Andreu Veà is a Spanish engineer, president of the Internet Society (ISOC-ES) and member of the advisory board of the Internet Hall of Fame.
Peter Löthberg is a Swedish technology entrepreneur. He played a role in the growth of the Internet in Sweden and was the de facto architect of EBONE, a pan-European Internet backbone, during its lifetime. He was the designer of Cisco's GSR12000 backbone router technology and the TeraStream architecture, along with Guenter Honisch. He was involved with Sprint's Internet infrastructure strategy. Löthberg is the owner of telecommunications company Swedish Telecom Development and Product Innovation (STUPI).










