
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, which is characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that impacts a person's ability to perform everyday activities. This typically involves problems with memory, thinking, behavior, and motor control. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging.

Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of dementia characterized by changes in sleep, behavior, cognition, movement, and regulation of automatic bodily functions. Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease worsens over time and is usually diagnosed when cognitive impairment interferes with normal daily functioning. Together with Parkinson's disease dementia, DLB is one of the two Lewy body dementias. It is a common form of dementia, but the prevalence is not known accurately and many diagnoses are missed. The disease was first described on autopsy by Kenji Kosaka in 1976, and he named the condition several years later.
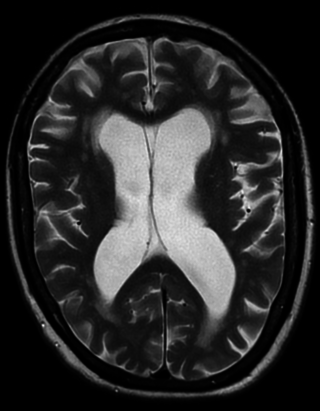
Vascular dementia is dementia caused by a series of strokes. Restricted blood flow due to strokes reduces oxygen and glucose delivery to the brain, causing cell injury and neurological deficits in the affected region. Subtypes of vascular dementia include subcortical vascular dementia, multi-infarct dementia, stroke-related dementia, and mixed dementia.
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two similar and common subtypes of dementia: dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD). Both are characterized by changes in thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. The two conditions have similar features and may have similar causes, and are believed to belong on a spectrum of Lewy body disease that includes Parkinson's disease. As of 2014, they were more often misdiagnosed than any other common dementia.

Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal and temporal lobes. FTD is the second most prevalent type of early onset dementia after Alzheimer's disease. Men and women appear to be equally affected. FTD generally presents as a behavioral or language disorder with gradual onset. Signs and symptoms tend to appear in late adulthood, typically between the ages of 45 and 65, although it can affect people younger or older than this. Currently, no cure or approved symptomatic treatment for FTD exists, although some off-label drugs and behavioral methods are prescribed.

Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken by mouth or via a transdermal patch.

Memantine, sold under the brand name Axura among others, is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth.

Diseases of affluence, previously called diseases of rich people, is a term sometimes given to selected diseases and other health conditions which are commonly thought to be a result of increasing wealth in a society. Also referred to as the "Western disease" paradigm, these diseases are in contrast to "diseases of poverty", which largely result from and contribute to human impoverishment. These diseases of affluence have vastly increased in prevalence since the end of World War II.

Alzheimer's Society is a United Kingdom care and research charity for people with dementia and their carers. It operates in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, while its sister charities Alzheimer Scotland and Alzheimer Society of Ireland cover Scotland and the Republic of Ireland respectively.
Memory disorders are the result of damage to neuroanatomical structures that hinders the storage, retention and recollection of memories. Memory disorders can be progressive, including Alzheimer's disease, or they can be immediate including disorders resulting from head injury.

Organic brain syndrome, also known as organic brain disease, organic brain damage, organic brain disorder, organic mental syndrome, or organic mental disorder, refers to any syndrome or disorder of mental function whose cause is alleged to be known as organic (physiologic) rather than purely of the mind. These names are older and nearly obsolete general terms from psychiatry, referring to many physical disorders that cause impaired mental function. They are meant to exclude psychiatric disorders. Originally, the term was created to distinguish physical causes of mental impairment from psychiatric disorders, but during the era when this distinction was drawn, not enough was known about brain science for this cause-based classification to be more than educated guesswork labeled with misplaced certainty, which is why it has been deemphasized in current medicine. While mental or behavioural abnormalities related to the dysfunction can be permanent, treating the disease early may prevent permanent damage in addition to fully restoring mental functions. An organic cause to brain dysfunction is suspected when there is no indication of a clearly defined psychiatric or "inorganic" cause, such as a mood disorder.
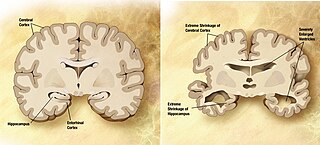
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, tauopathies, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that therapeutic advances against one neurodegenerative disease might ameliorate other diseases as well.
Alcohol-related dementia (ARD) is a form of dementia caused by long-term, excessive consumption of alcohol, resulting in neurological damage and impaired cognitive function.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a neurocognitive disorder which involves cognitive impairments beyond those expected based on an individual's age and education but which are not significant enough to interfere with instrumental activities of daily living. MCI may occur as a transitional stage between normal aging and dementia, especially Alzheimer's disease. It includes both memory and non-memory impairments. The cause of the disorder remains unclear, as well as both its prevention and treatment, with some 50 percent of people diagnosed with it going on to develop Alzheimer's disease within five years. The diagnosis can also serve as an early indicator for other types of dementia, although MCI may remain stable or even remit.
This article provides a list of media documents portraying Alzheimer's disease as a critical feature of the main plot:
As populations age, caring for people with dementia has become more common. Elderly caregiving may consist of formal care and informal care. Formal care involves the services of community and medical partners, while informal care involves the support of family, friends, and local communities. In most mild-to-medium cases of dementia, the caregiver is a spouse or an adult child. Over a period of time, more professional care in the form of nursing and other supportive care may be required medically, whether at home or in a long-term care facility. There is evidence to show that case management can improve care for individuals with dementia and the experience of their caregivers. Furthermore, case management may reduce overall costs and institutional care in the medium term. Millions of people living in the United States take care of a friend or family member with Alzheimer’s disease or a related dementia.

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens, and is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years.
Early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD), also called younger-onset Alzheimer's disease (YOAD), is Alzheimer's disease diagnosed before the age of 65. It is an uncommon form of Alzheimer's, accounting for only 5–10% of all Alzheimer's cases. About 60% have a positive family history of Alzheimer's and 13% of them are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Most cases of early-onset Alzheimer's share the same traits as the "late-onset" form and are not caused by known genetic mutations. Little is understood about how it starts.

Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. The drug can be administered orally or via a transdermal patch; the latter form reduces the prevalence of side effects, which typically include nausea and vomiting.

Giovanna Rachele Mallucci is van Geest Professor of Clinical Neurosciences at the University of Cambridge in England and associate director of the UK Dementia Research Institute at the University of Cambridge. She is a specialist in neurodegenerative diseases.












