Amanieu II (after 1230 – 11 March 1318) was the Archbishop of Auch. Elected in 1261, he received consecration at Rome from Pope Urban IV in 1263.

Rome is the capital city and a special comune of Italy. Rome also serves as the capital of the Lazio region. With 2,872,800 residents in 1,285 km2 (496.1 sq mi), it is also the country's most populated comune. It is the fourth most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. It is the centre of the Metropolitan City of Rome, which has a population of 4,355,725 residents, thus making it the most populous metropolitan city in Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber. The Vatican City is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city: for this reason Rome has been often defined as capital of two states.

Pope Urban IV, born Jacques Pantaléon, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 29 August 1261 to his death in 1264. He was not a cardinal; only a few popes since his time have not been cardinals, including Gregory X, Urban V and Urban VI.
Amanieu was the third son of Roger, viscount of Fezensaguet, and Pucelle d'Albret, and thus a descendant of the Counts of Armagnac and the Sires of Albret. Amanieu's eldest brother was Geraud VI of Armagnac. In 1278 Geraud and Amanieu signed a treaty sharing jurisdiction in Barran, where the bishop had his summer residence, between the Church and the County. The village was fortified as a bastide the next year (1279).

The following is a list of rulers of the county of Armagnac:

The lordship (seigneurie) of Albret (Labrit), situated in the Landes, gave its name to one of the most powerful feudal families of France in the Middle Ages.

Gerald VI, (1235–1285), was Viscount Fezensaguet from 1240 to 1285, then Count of Armagnac and Fezensac from 1256 to 1285. He was the son of Roger d'Armagnac, Viscount of Fezensaguet, and Pincelle d'Albret.
In 1268 Amanieu purchased the hospital of Pont d'Artigues from the Order of Santiago for the Order of the Faith and Peace, a military order founded by his predecessor to keep the peace in Gascony. He also appointed his nephew master of the order, but it did not stave off the order's decline, which had been apparent from the early 1260s. Pope Gregory X dissolved the order in 1273 and its possessions ended up largely in the hands of the Order of Santiago and the church of Auch, though Les Feuillants Abbey laid claim to some.

The Order of Santiago, also known as "The Order of St. James of the Sword," was founded in the 12th century, and owes its name to the Patron Saint of Spain, Santiago. Its initial objective was to protect the pilgrim of St. James' Way, to defend Christendom and to remove the Muslim Moors from the Iberian Peninsula.

The Order of the Faith and Peace or Order of the Sword was a military order in Gascony in the mid-13th century.
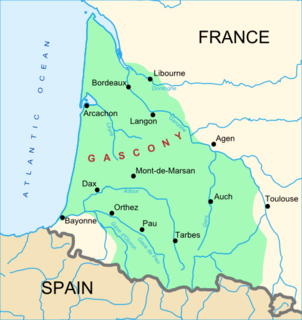
Gascony is an area of southwest France that was part of the "Province of Guyenne and Gascony" prior to the French Revolution. The region is vaguely defined, and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; by some they are seen to overlap, while others consider Gascony a part of Guyenne. Most definitions put Gascony east and south of Bordeaux.