Related Research Articles

Endocrinology is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology.
Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goitre. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. It is a glycoprotein hormone produced by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid.
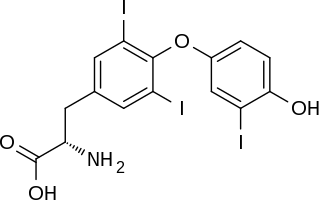
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.

Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment of the thyroid follicles, accounting for approximately half of the protein content of the thyroid gland. Human TG (hTG) is a homodimer of subunits each containing 2768 amino acids as synthesized.

Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. A slightly broader term is autoimmune thyroiditis, identical other than that it is also used to describe a similar condition without a goiter.

A thyroglossal cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct. Thyroglossal cysts can be defined as an irregular neck mass or a lump which develops from cells and tissues left over after the formation of the thyroid gland during developmental stages.

Deborah Doniach MD FRCP was a British clinical immunologist and pioneer in the field of autoimmune diseases.
The Endocrine Society is a professional, international medical organization in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, founded in 1916 as The Association for the Study of Internal Secretions. The official name of the organization was changed to the Endocrine Society on January 1, 1952. It is a leading organization in the field and publishes four leading journals. It has more than 18,000 members from over 120 countries in medicine, molecular and cellular biology, biochemistry, physiology, genetics, immunology, education, industry, and allied health. The Society's mission is: "to advance excellence in endocrinology and promote its essential and integrative role in scientific discovery, medical practice, and human health."
The Academy of Clinical Thyroidologists (ACT) was founded in May 2005 at the annual meeting of the Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) in Washington, D.C. The academy is a professional society consisting of 32 members from the U.S. and Italy who specialize in clinical thyroidology. ACT encourages skill development in diagnostic and interventional ultrasound, nuclear thyroidology, and cytopathology to promote excellence in clinical practice and optimal outcomes for patients.
A thyroidologist is a medical practitioner specializing in the thyroid and related areas.

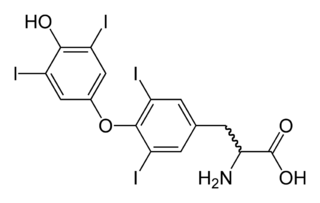
Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre.

Dr. Hossein Gharib is a physician who specializes in thyroid disorders. He was born in Tehran, Iran, on February 2, 1940, and is a consulting physician at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE), formerly known as the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, is a professional community of physicians specializing in endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. AACE's mission is elevating clinical endocrinology to improve global health. The association is headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida, US.

Creswell John Eastman is the Clinical Professor of Medicine at Sydney University Medical School, Principal of the Sydney Thyroid Clinic and Consultant Emeritus to the Westmead Hospital. Eastman is an endocrinologist and has directed or conducted research and public health projects into elimination of iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) in Malaysia, Indonesia, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, several Pacific Islands, Hong Kong, China and Tibet and Australia. For his work in remote areas of China, he has been dubbed the "man who saved a million brains".
Erik K. Alexander is an American medical educator and practicing clinician. He is Vice President of Education for Brigham Health, and Harvard Medical School Associate Dean for Medical Education (BWH). In 2011, he joined the board of directors of the American Thyroid Association. Alexander is a Professor of Medicine in the Department of Medicine at Harvard Medical School (HMS), and is the Executive Director of the Brigham Education Institute (BEI) and Undergraduate Medical Education at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) in Boston, Massachusetts.

Julie Ann Sosa is a professor and chair of the Department of Surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and holds the Leon Goldman, MD, Distinguished Professorship in Surgery. She currently serves as the Treasurer of the American Thyroid Association and Editor-in-Chief of the World Journal of Surgery.
Caroline Renate Pickardt was a German endocrinologist. The main focus of her scientific work was in the area of thyroid diseases (thyroidology). She published fundamental articles on functional thyroid disorders and the pathophysiology of goitre.
The Thyrotroph Thyroid Hormone Sensitivity Index is a calculated structure parameter of thyroid homeostasis. It was originally developed to deliver a method for fast screening for resistance to thyroid hormone. Today it is also used to get an estimate for the set point of thyroid homeostasis, especially to assess dynamic thyrotropic adaptation of the anterior pituitary gland, including non-thyroidal illnesses.
Lewis E. Braverman was a U.S. endocrinologist who specialized in thyroid gland problems. He discovered that humans converted thyroxine to triiodothyronine. He was a mentor to physicians for over 40 years.
References
- "Homepage". American Thyroid Association. Retrieved 10 May 2022.