
Cytochromes are proteins containing heme as a cofactor. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the IUBMB, cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous to the ferric oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature.

An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule that stores energy chemically in the form of highly strained bonds. The molecules of the chain include peptides, enzymes (which are proteins or protein complexes), and others. The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain during aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen although a variety of acceptors other than oxygen such as sulfate exist in anaerobic respiration.
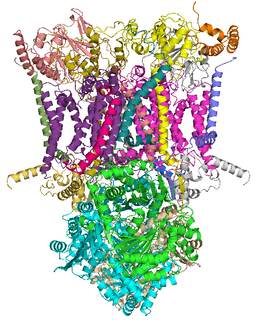
The coenzyme Q : cytochrome c – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome bc1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain, playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP. Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial and the nuclear genomes. Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most eubacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits, 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins.

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.

Cytochrome c peroxidase, or CCP, is a water-soluble heme-containing enzyme of the peroxidase family that takes reducing equivalents from cytochrome c and reduces hydrogen peroxide to water:

Plastocyanin is a copper-containing protein involved in electron-transfer. The protein is a monomer, with a molecular weight around 10,500 Daltons, and 99 amino acids in most vascular plants. It is a member of the plastocyanin family of copper-binding proteins.
Cytochrome C1 is a protein encoded by the CYC1 gene. Cytochrome is a heme-containing subunit of the cytochrome b-c1 complex, which accepts electrons from Rieske protein and transfers electrons to cytochrome c in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It is formed in the cytosol and targeted to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Cytochrome c1 belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins.

Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory Complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Histochemical analysis showing high succinate dehydrogenase in muscle demonstrates high mitochondrial content and high oxidative potential.

The cytochrome b6f complex is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. The reaction is analogous to the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome bc1 of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. During photosynthesis, the cytochrome b6f complex is one step along the chain that transfers electrons from Photosystem II to Photosystem I, and at the same time pumps protons into the thylakoid space that contribute to create an electrochemical (energy) gradient which is later used to synthesize ATP from ADP.

Rieske proteins are iron-sulfur protein (ISP) components of cytochrome bc1 complexes and cytochrome b6f complexes and responsible for electron transfer in some biological systems. John S. Rieske and co-workers first discovered and isolated the proteins in 1964. It is a unique [2Fe-2S] cluster in that one of the two Fe atoms is coordinated by two histidine residues rather than two cysteine residues. They have since been found in plants, animals, and bacteria with widely ranging electron reduction potentials from -150 to +400 mV.
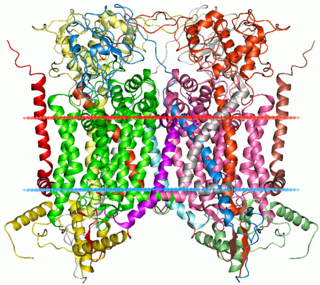
Cytochrome b is a protein found in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It functions as part of the electron transport chain and is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes.

Copper proteins are proteins that contain one or more copper ions as prosthetic groups. The metal centres in the copper proteins can be classified into several types:
Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single electron transfer to produce nitric oxide.
Iron-binding proteins are carrier proteins and metalloproteins that are important in iron metabolism and the immune response. Iron is required for life.
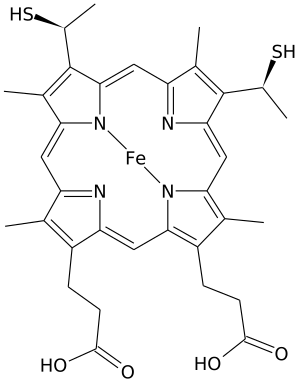
Heme C is an important kind of heme.
Amine Dehydrogenase, also known as methylamine dehydrogenase (MADH), is a tryptophan tryptophylquinone-dependent (TTQ-dependent) enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of a primary amine to an aldehyde and ammonia. The reaction occurs as follows:

Cytochromes c are proteins containing one or more heme groups that are covalently attached to the peptide backbone via one or two thioether bonds. These bonds are in most cases part of a specific Cys-X-X-Cys-His (CXXCH) binding motif, where X denotes a miscellaneous amino acid. Two thioether bonds of cysteine residues bind to the vinyl sidechains of heme, and the histidine residue coordinates one axial binding site of the heme iron. Less common binding motifs can include a single thioether linkage, a lysine or a methionine instead of the axial histidine or a CXnCH binding motif with n>2. The second axial site of the iron can be coordinated by amino acids of the protein, substrate molecules or water. Cytochromes c possess a wide range of properties and function as electron transfer proteins or catalyse chemical reactions involving redox processes. A prominent member of this family is mitochondrial cytochrome c.

Azurin is a bacterial blue copper protein found in Pseudomonas, Bordetella, or Alcaligenes bacteria, which undergoes oxidation-reduction between Cu(I) and Cu(II), and transfers single electrons between enzymes associated with the cytochrome chain. The protein has a molecular weight of approximately 16,000, contains a single copper atom, is intensively blue, and has a fluorescence emission band centered at 308 nm.
Methylamine dehydrogenase (amicyanin) (EC 1.4.9.1, amine dehydrogenase, primary-amine dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name methylamine:amicyanin oxidoreductase (deaminating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
The Disufide bond oxidoreductase D (DsbD) family is a member of the Lysine Exporter (LysE) Superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the DsbD family can be found in the Transporter Classification Base.
1. Victor L. Davidson and Limei Hsu Jones, Biochemistry1996, 35, 8120-8125.
2. Arnout P. Kalverda, Jesus Salgado, Christopher Dennison, and Gerard W. Canters, Biochemistry1996, 35, 3085-3092.
3. Victor L. Davidson and Dapeng Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc.2003, 125, 3224-3225.




















