
Amyl alcohols are alcohols with the formula C5H11OH. Eight are known. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate and other products. The name amyl alcohol without further specification applies to the normal (straight-chain) form, 1-pentanol.

Amyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the formula C5H11ONO. A variety of isomers are known, but they all feature an amyl group attached to the nitrite functional group. The alkyl group (the amyl in this case) is unreactive and the chemical and biological properties are mainly due to the nitrite group. Like other alkyl nitrites, amyl nitrite is bioactive in mammals, being a vasodilator, which is the basis of its use as a prescription medicine. As an inhalant, it also has a psychoactive effect, which has led to its recreational use, with its smell being described as that of old socks or dirty feet. It was first documented in 1844 and came into medical use in 1867.
ATC code V03All other therapeutic products is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup V03 is part of the anatomical group V Various.
Poppers is a slang term referring to recreational drugs belonging to the alkyl nitrite family of chemical compounds. When fumes from these substances are inhaled, they act as potent vasodilators, producing mild euphoria, warmth, and dizziness. Most effects have a rapid onset and are short-acting. Its recreational use is believed to be potentially dangerous for people with heart problems, anaemia, or glaucoma. Reported adverse effects include fainting, retinal toxicity, and vision loss.

A carbenium ion is a positive ion with the structure RR′R″C+, that is, a chemical species with carbon atom having three covalent bonds, and it bears a +1 formal charge. Carbenium ions are a major subset of carbocations, which is a general term for diamagnetic carbon-based cations. In parallel with carbenium ions is another subset of carbocations, the carbonium ions with the formula R5+. In carbenium ions charge is localized. They are isoelectronic with monoboranes such as B(CH3)3.
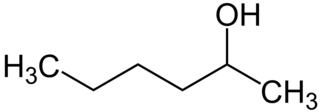
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:

Isoamyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with the formula C
5H
12O, specifically (H3C–)2CH–CH2–CH2–OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol (pentanol). It is also known as isopentyl alcohol, isopentanol, or (in the IUPAC recommended nomenclature) 3-methyl-butan-1-ol. An obsolete name for it was isobutyl carbinol.

In organic chemistry, alkyl nitrites are a group of organic compounds based upon the molecular structure R−O−N=O, where R represents an alkyl group. Formally they are alkyl esters of nitrous acid. They are distinct from nitro compounds.

Amylmetacresol (AMC) is an antiseptic used to treat infections of the mouth and throat. It is used as an active pharmaceutical ingredient in Strepsils, Cēpacol, Gorpils, Cofsils and Lorsept throat lozenges, typically in combination with dichlorobenzyl alcohol, another antiseptic.

2-Naphthylamine is one of two isomeric aminonaphthalenes, compounds with the formula C10H7NH2. It is a colorless solid, but samples take on a reddish color in air because of oxidation. It was formerly used to make azo dyes, but it is a known carcinogen and has largely been replaced by less toxic compounds.
The molecular formula C5H11NO2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H12O (molar mass: 88.15 g/mol, exact mass: 88.088815) may refer to:
Heptanone may refer to the following ketones with seven carbon atoms the formula C7H14O:
Butyl chloride (C4H9Cl) may refer to:

tert-Amyl chloride (2-methyl-2-butyl chloride) is an alkyl chloride used for flavoring and odorizing. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is an isomer of 1-chloropentane (n-amyl chloride).
The molecular formula C7H16O may refer to:

1-Chloropentane is an alkyl halide with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)4Cl. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It can be prepared from 1-pentanol by treatment with hydrogen chloride.
The molecular formula C5H11Cl (molar mass: 106.59 g/mol, exact mass: 106.0549 u) may refer to:

Amyl and the Sniffers are an Australian pub rock and punk rock band based in Melbourne, consisting of vocalist Amy Taylor, drummer Bryce Wilson, guitarist Declan Martens, and bassist Gus Romer. At the ARIA Music Awards of 2019, their self-titled debut record won the Best Rock Album category.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










