An American Ballroom Companion is an online collection of over two hundred social dance manuals at the Library of Congress related to the period of cca. 1490--1920. Along with social dance instruction manuals, this online presentation also includes a significant number of antidance manuals, histories, treatises on etiquette, information about theatrical dance.
The collection presents dance materials from various locations of the Library: General Collections, the Music Division, and the Rare Book and Special Collections Division.
The collection also presents a number of videoclips to illustrate the materials. The clips were recorded on several Library of Congress events starting from the 100th anniversary of the Library's Jefferson Building held in 1997.

Ballroom dance is a set of European partner dances, which are enjoyed both socially and competitively around the world, mostly because of its performance and entertainment aspects. Ballroom dancing is also widely enjoyed on stage, film, and television.
The Library of Congress Classification (LCC) is a system of library classification developed by the Library of Congress in the United States, which can be used for shelving books in a library. LCC is mainly used by large research and academic libraries, while most public libraries and small academic libraries used the Dewey Decimal Classification system. The classification was developed by James Hanson, with assistance from Charles Martel, in 1897, while they were working at the Library of Congress. It was designed specifically for the purposes and collection of the Library of Congress to replace the fixed location system developed by Thomas Jefferson.
Thoinot Arbeau is the anagrammatic pen name of French cleric Jehan Tabourot. Tabourot is most famous for his Orchésographie, a study of late sixteenth-century French Renaissance social dance. He was born in Dijon and died in Langres.

The waltz, meaning "to roll or revolve") is a ballroom and folk dance, normally in triple, performed primarily in closed position.

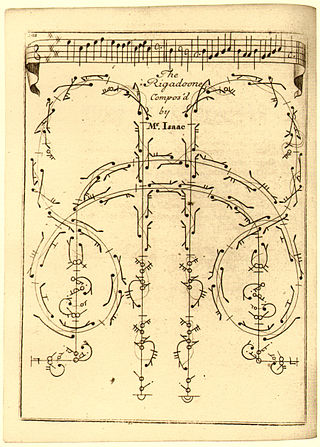
A country dance is any of a very large number of social dances of a type that originated in the British Isles; it is the repeated execution of a predefined sequence of figures, carefully designed to fit a fixed length of music, performed by a group of people, usually in couples, in one or more sets. The figures involve interaction with your partner and/or with other dancers, usually with a progression so that you dance with everyone in your set. It is common in modern times to have a "caller" who teaches the dance and then calls the figures as you dance. Country dances are done in many different styles.

The dime novel is a form of late 19th-century and early 20th-century U.S. popular fiction issued in series of inexpensive paperbound editions. The term dime novel has been used as a catchall term for several different but related forms, referring to story papers, five- and ten-cent weeklies, "thick book" reprints, and sometimes early pulp magazines. The term was used as a title as late as 1940, in the short-lived pulp magazine Western Dime Novels. In the modern age, the term dime novel has been used to refer to quickly written, lurid potboilers, usually as a pejorative to describe a sensationalized but superficial literary work.

Viennese waltz is a genre of ballroom dance. At least four different meanings are recognized. In the historically first sense, the name may refer to several versions of the waltz, including the earliest waltzes done in ballroom dancing, danced to the music of Viennese waltz.
The Country Studies are works published by the Federal Research Division of the United States Library of Congress, freely available for use by researchers. No copyright is claimed on them. Therefore, they have been dedicated to the public domain and can be copied freely, though not all the pictures used therein are in the public domain. The Country Studies Series presents a description and analysis of the historical setting and the social, economic, political, and national security systems and institutions of countries throughout the world. The series examines the interrelationships of those systems and the ways they are shaped by cultural factors.

A librarian is a person who works professionally in a library providing access to information, and sometimes social or technical programming, or instruction on information literacy to users.

Historical dance is a term covering a wide variety of Western European-based dance types from the past as they are danced in the present. Today historical dances are danced as performance, for pleasure at themed balls or dance clubs, as historical reenactment, or for musicological or historical research.
The bunny hug was a dancing style performed by young people, in the early 20th century. It is thought to have originated in San Francisco, California in the Barbary Coast dance halls along with the Texas Tommy, turkey trot, and grizzly bear.
Raoul AugerFeuillet (c.1660–1710) was a French dance notator, publisher and choreographer most well-known today for his Chorégraphie, ou l'art de décrire la danse which described Beauchamp–Feuillet notation, and his subsequent collections of ballroom and theatrical dances, which included his own choreographies as well as those of Pécour.

Pierre Rameau, was the French dancing master to Elisabetta Farnese, and the author of two books that now provide us with valuable information about Baroque dance.

The conservation and restoration of vinyl discs refers to the preventive measures taken to defend against damage and slow degradation, and to maintain fidelity of singles, 12" singles, EP’s, and LP’s in 45 or 33⅓ rpm 10" disc recordings.
Music librarianship is the area of librarianship that pertains to music collections and their development, cataloging, preservation and maintenance, as well as reference issues connected with musical works and music literature. Music librarians often have degrees in both music and librarianship. Music librarians deal with standard librarianship duties such as cataloging and reference, which become more complicated when music scores and recordings are involved. Therefore, music librarians generally read music and have at least a basic understanding of both music theory and music history to aid in their duties.

The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts, Dorothy and Lewis B. Cullman Center, is located at 40 Lincoln Center Plaza, in the Lincoln Center complex on the Upper West Side in Manhattan, New York City. Situated between the Metropolitan Opera House and the Vivian Beaumont Theater, it houses one of the world's largest collections of materials relating to the performing arts. It is one of the four research centers of the New York Public Library's Research library system, and it is also one of the branch libraries.

The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., that serves as the library and research service of the U.S. Congress and the de facto national library of the United States. Founded in 1800, the library is the United States's oldest federal cultural institution. The library is housed in three elaborate buildings on Capitol Hill. It also maintains a conservation center in Culpeper, Virginia. The library's functions are overseen by the Librarian of Congress, and its buildings are maintained by the Architect of the Capitol. The Library of Congress is one of the largest libraries in the world. Its collections contain approximately 173 million items, and it has more than 3,000 employees. Its collections are "universal, not limited by subject, format, or national boundary, and include research materials from all parts of the world and in more than 470 languages".

Smithsonian Libraries and Archives is an institutional archives and library system comprising 21 branch libraries serving the various Smithsonian Institution museums and research centers. The Libraries and Archives serve Smithsonian Institution staff as well as the scholarly community and general public with information and reference support. Its collections number nearly 3 million volumes including 50,000 rare books and manuscripts.
Elizabeth Aldrich is an American dance historian, choreographer, writer, lecturer, consultant, administrator, curator, and archivist. She is internationally known for her research, performance, choreography, teaching, and lectures on Renaissance and Baroque court dance, nineteenth-century social dance, and twentieth-century ragtime dance.