
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, known simply as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work had a major influence on the development of Western art, particularly in relation to the Renaissance notions of humanism and naturalism. He is often considered a contender for the title of the archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival and elder contemporary, Leonardo da Vinci. Given the sheer volume of surviving correspondence, sketches, and reminiscences, Michelangelo is one of the best-documented artists of the 16th century and several scholars have described Michelangelo as the most accomplished artist of his era.

Masaccio, born Tommaso di Ser Giovanni di Simone, was a Florentine artist who is regarded as the first great Italian painter of the Quattrocento period of the Italian Renaissance. According to Vasari, Masaccio was the best painter of his generation because of his skill at imitating nature, recreating lifelike figures and movements as well as a convincing sense of three-dimensionality. He employed nudes and foreshortenings in his figures. This had seldom been done before him.

Masolino da Panicale was an Italian painter. His best known works are probably his collaborations with Masaccio: Madonna with Child and St. Anne (1424) and the frescoes in the Brancacci Chapel (1424–1428).

Pietro da Cortona was an Italian Baroque painter and architect. Along with his contemporaries and rivals Gian Lorenzo Bernini and Francesco Borromini, he was one of the key figures in the emergence of Roman Baroque architecture. He was also an important designer of interior decorations.

Guido Reni was an Italian painter of the Baroque period, although his works showed a classical manner, similar to Simon Vouet, Nicolas Poussin, and Philippe de Champaigne. He painted primarily religious works, but also mythological and allegorical subjects. Active in Rome, Naples, and his native Bologna, he became the dominant figure in the Bolognese School that emerged under the influence of the Carracci.

Pinturicchio, or Pintoricchio, also known as Benetto di Biagio or Sordicchio, was an Italian painter during the Renaissance. He acquired his nickname because of his small stature and he used it to sign some of his artworks that were created during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.

Francesco Albani or Albano was an Italian Baroque painter who was active in Bologna (1591–1600), Rome (1600–1609), Bologna (1609), Viterbo (1609–1610), Bologna (1610), Rome (1610–1617), Bologna (1618–1660), Mantova (1621–1622), Roma (1623–1625) and Florence (1633).

Sant'Andrea della Valle is a minor basilica in the rione of Sant'Eustachio of the city of Rome, Italy. The basilica is the general seat for the religious order of the Theatines. It is located at Piazza Vidoni, 6 at the intersection of Corso Vittorio Emanuele and Corso Rinascimento.

The Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi is the mother church of the Roman Catholic Order of Friars Minor Conventual in Assisi, a town in the Umbria region in central Italy, where Saint Francis was born and died. It is a Papal minor basilica and one of the most important places of Christian pilgrimage in Italy. With its accompanying friary, Sacro Convento, the basilica is a distinctive landmark to those approaching Assisi. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000.

Pellegrino Tibaldi, also known as Pellegrino di Tibaldo de Pellegrini, was an Italian mannerist architect, sculptor, and mural painter.

Melozzo da Forlì was an Italian Renaissance painter and architect. His fresco paintings are notable for the use of foreshortening. He was the most important member of the Forlì painting school.
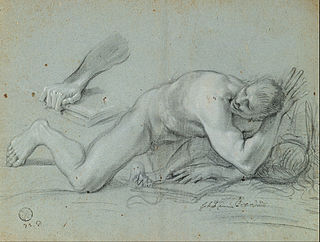
Giovanni Angelo Canini (1609–1666) was an Italian painter and engraver of the Baroque period.

Carlo Maratta or Maratti was an Italian painter, active mostly in Rome, and known principally for his classicizing paintings executed in a Late Baroque Classical manner. Although he is part of the classical tradition stemming from Raphael, he was not exempt from the influence of Baroque painting and particularly in his use of colour. His contemporary and friend, Giovanni Bellori, wrote an early biography on Maratta.

Tommaso di Andrea Vincidor was an Italian Renaissance painter and architect who trained with Raphael and spent most of his career in the Netherlands. He was also called Tommaso Vincitore, Tommaso da Bologna and Thomas Polonier.

Florentine painting or the Florentine School refers to artists in, from, or influenced by the naturalistic style developed in Florence in the 14th century, largely through the efforts of Giotto di Bondone, and in the 15th century the leading school of Western painting. Some of the best known painters of the earlier Florentine School are Fra Angelico, Botticelli, Filippo Lippi, the Ghirlandaio family, Masolino, and Masaccio.

Vittorio Bigari was an Italian painter of the late-Baroque period.

Giotto di Bondone, known mononymously as Giotto and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giotto's contemporary, the banker and chronicler Giovanni Villani, wrote that Giotto was "the most sovereign master of painting in his time, who drew all his figures and their postures according to nature" and of his publicly recognized "talent and excellence". Giorgio Vasari described Giotto as making a decisive break with the prevalent Byzantine style and as initiating "the great art of painting as we know it today, introducing the technique of drawing accurately from life, which had been neglected for more than two hundred years".

The St. Cecilia Altarpiece is an oil painting by the Italian High Renaissance master Raphael. Completed in his later years, in around 1516–17, the painting depicts Saint Cecilia, the patron saint of musicians and Church music, listening to a choir of angels in the company of St. Paul, St. John the Evangelist, St. Augustine and Mary Magdalene. Commissioned for a church in Bologna, the painting now hangs in that city's Pinacoteca Nazionale. According to Giorgio Vasari the musical instruments strewn about Cecilia's feet were not painted by Raphael but by his student, Giovanni da Udine.

The Basilica of San Giacomo Maggiore is an historic Roman Catholic church in Bologna, region of Emilia Romagna, Italy, serving a monastery of Augustinian friars. It was built starting in 1267 and houses, among the rest, the Bentivoglio Chapel, featuring numerous Renaissance artworks.

Stefano da Ferrara was an Italian painter from Ferrara who active in the latter half of the 15th century.




















