Andrew Bee of Martin, Michigan was an American soldier, a private in the 4th Michigan Cavalry, Company L.
On May 7, 1865, the 4th Michigan Cavalry, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Benjamin D. Pritchard, invaded the encampment of Confederate president Jefferson Davis. Private Bee discovered that Davis was in fact present and disguised in women's clothing. Davis's shawl and petticoat became the property of the War Department, which turned them over to the National Archives, where they still reside. He alerted Corporal Munger, who made the capture, ending Davis' hopes of re-establishing the Confederate government in the Trans-Mississippi.
This event concluded one of the two "great man-hunts" following the war... this being the hunt for Davis, the other being the hunt for Lincoln's killer. It should here be noted that there was a $100,000 reward out for Davis's capture, and that this reward was used to build what is now Allegan, Michigan's 'historic district" in the "water-tower hill" neighborhood. It was not until the two great man-hunts were concluded that Reconstruction really got under way.

John Hunt Morgan was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. In April 1862, he raised the 2nd Kentucky Cavalry Regiment, fought at Shiloh, and then launched a costly raid in Kentucky, which encouraged Braxton Bragg's invasion of that state. He also attacked General William Rosecrans's supply lines. In July 1863, he set out on a 1,000-mile raid into Indiana and Ohio, taking hundreds of prisoners. But after most of his men had been intercepted by U.S. Army gunboats, Morgan surrendered at Salineville, Ohio, the northernmost point ever reached by uniformed Confederates. Morgan carried out the diversionary "Morgan's Raid" against orders, which gained no tactical advantage for the Confederacy while losing the regiment. Morgan escaped prison, but his credibility was so low that he was restricted to minor operations. He was killed at Greeneville, Tennessee, in September 1864. Morgan was the brother-in-law of Confederate general A. P. Hill. Various schools and a memorial are dedicated to him.

The Battle of Palmito Ranch, also known as the Battle of Palmito Hill, is considered by some criteria the final battle of the American Civil War. It was fought May 12 and 13, 1865, on the banks of the Rio Grande east of Brownsville, Texas, and a few miles from the seaport of Los Brazos de Santiago, at the southern tip of Texas. The battle took place more than a month after the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia under Robert E. Lee to Union forces at Appomattox Court House, which had since been communicated to both commanders at Palmito. In the intervening weeks the Confederacy had collapsed entirely, so it could also be classified as a postwar action.

Jefferson Columbus Davis was a regular officer of the United States Army during the American Civil War, known for the similarity of his name to that of Confederate President Jefferson Davis and for his killing of a superior officer in 1862.

Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the Union states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, and West Virginia during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11 to July 26, 1863. It is named for the commander of the Confederate troops, Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid failed.

Price's Missouri Expedition, also known as Price's Raid or Price's Missouri Raid, was an unsuccessful Confederate cavalry raid through Arkansas, Missouri, and Kansas in the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. Led by Confederate Major General Sterling Price, the campaign aimed to recapture Missouri and renew the Confederate initiative in the larger conflict.
The Battle of Salineville occurred July 26, 1863, near Salineville, Ohio, during the American Civil War. U.S. Brig. Gen. James M. Shackelford destroyed Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and captured Morgan, ending Morgan's Raid. It was the northernmost military action involving an official command of the Confederate States Army.

The Battle of Monett's Ferry or Monett's Bluff saw a Confederate States Army force led by Brigadier General Hamilton P. Bee attempt to block a numerically superior Union Army column that was commanded by Brigadier General William H. Emory during the Red River Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate commander Major General Richard Taylor set a trap for the retreating army of Major General Nathaniel P. Banks near the junction of the Cane River with the Red River. Taylor assigned Bee's troops to plug up the only outlet from the trap while Taylor's other forces closed in from the rear and sides.

Henry Harnden was an American sailor, Republican politician, and Wisconsin pioneer. He served as a Union Army officer during the American Civil War and led the Wisconsin cavalry regiment which was credited in the capture of Confederate president Jefferson Davis. After the war, he was granted an honorary brevet to brigadier general. He also went on to serve one term in the Wisconsin State Assembly, representing eastern Jefferson County.

Benjamin Dudley Pritchard was a United States Army officer, most known for leading the Union cavalry regiment which captured the fugitive Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America, in the weeks surrounding the close of the American Civil War.

George Munger, Corporal, 4th Michigan Cavalry Company L. is credited with having recognized and helped to capture Jefferson Davis.
4th Michigan Cavalry Regiment was a regiment of cavalry in the Union Army during the American Civil War fighting in the western front as part of the Army of the Cumberland. It was noted as being the regiment that captured the fleeing President of the Confederate States of America, Jefferson Davis, as the Confederacy collapsed in the spring of 1865.

Thomas Henry Hines was a Confederate cavalryman who was known for his spying activities during the last two years of the American Civil War. A native of Butler County, Kentucky, he initially worked as a grammar instructor, mainly at the Masonic University of La Grange, Kentucky. During the first year of the war, he was a field officer, initiating several raids. He was an assistant to John Hunt Morgan, doing a preparatory raid in advance of Morgan's Raid through the states of Indiana and Ohio, and after being captured with Morgan, organized their escape from the Ohio Penitentiary. He was later involved in espionage and tried to stir up insurrections against the United States government in selected Northern locales.

Walker's Greyhounds was the popular name for a division of the Confederate States Army under Major-General John George Walker, composed exclusively of units from Texas. It fought in the Western Theater and the Trans-Mississippi Department, gaining its nickname because the men were able to move long distances rapidly on foot.

The Confederate Monument in Glasgow, Kentucky, built in 1905 by the Kentucky Women's Monumental Association and former Confederate soldier John A. Murray, commemorates those who gave their lives in service for the Confederate States of America. It is located on the side of Glasgow's courthouse. The Confederate soldier, made of bronze, is at parade rest, and features details such as a bedroll, canteen, kepi hat, and rifle. It stands on a limestone pedestal.
The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.

Jefferson Davis Memorial Historic Site is a 12.668-acre (5.127 ha) state historic site located in Irwin County, Georgia that marks the spot where Confederate States President Jefferson Davis was captured by United States Cavalry on Wednesday, May 10, 1865. The historic site features a granite monument with a bronze bust of Davis that is located at the place of capture. The memorial museum, built in 1939 by the Works Progress Administration, features Civil War era weapons, uniforms, artifacts and an exhibit about the president's 1865 flight from Richmond, Virginia to Irwin County, Georgia.

The 1st Virginia Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment raised in Virginia for service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It fought mostly with the Army of Northern Virginia.
The Battle of Brownsville took place on November 2–6, 1863 during the American Civil War. It was a successful effort on behalf of the Union Army to disrupt Confederate blockade runners along the Gulf Coast in Texas. The Union assault precipitated the capture of Matamoros by a force of Mexican patriots, led by exiled officers living in Brownsville.
The capture of Sedalia occurred during the American Civil War when a Confederate force captured the Union garrison of Sedalia, Missouri, on October 15, 1864. Confederate Major General Sterling Price, who was a former Governor of Missouri and had commanded the Missouri State Guard in the early days of the war, had launched an invasion into the state of Missouri on August 29. He hoped to distract the Union from more important areas and cause a popular uprising against Union control of the state. Price had to abandon his goal of capturing St. Louis after a bloody repulse at the Battle of Fort Davidson and moved into the pro-Confederate region of Little Dixie in central Missouri.
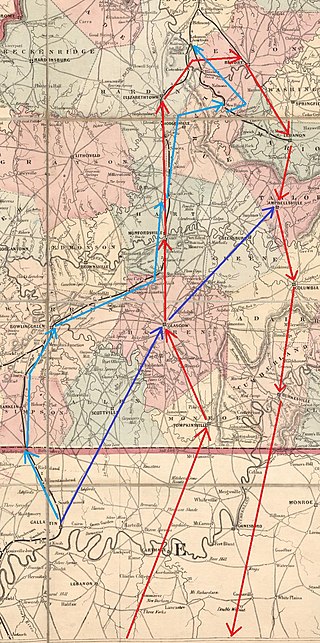
Morgan's Christmas Raid was carried out by Confederate Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan between December 22, 1862, and January 5, 1863. Morgan intended to cut the supply lines to the Union Army of the Cumberland in Tennessee. The Union used the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, and Morgan had identified two 500-foot (150 m) long trestle bridges at Muldraugh Hill that could be burnt. Morgan's 4,000-strong cavalry force left Alexandria, Tennessee, on December 22 and passed into Kentucky on Christmas Eve, defeating part of the 2nd Michigan Cavalry Regiment near Tompkinsville. They fought and defeated an Indiana cavalry detachment on Christmas Day at Bear Wallow, Barren County. The U.S. Army sent forces under Colonel John Marshall Harlan and Major General Joseph J. Reynolds to try to catch Morgan. However, Morgan used ruses to distract his pursuers. Morgan captured a Union stockade at Bonnieville on December 26 and on December 27 captured Elizabethtown before burning the bridges at Muldraugh Hill.














