
Year 460 (CDLX) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magnus and Apollonius. The denomination 460 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Apollonius of Tyana was a first-century Greek philosopher and religious leader from the town of Tyana, Cappadocia in Roman Anatolia, who spent his life travelling and teaching in the Middle East, North Africa and South Asia. He is a central figure in Neopythagoreanism and was one of the most famous "miracle workers" of his day.
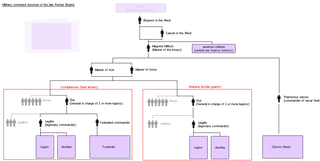
Magister militum was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer of the empire. In Greek sources, the term is translated either as strategos or as stratelates.
Apollonius of Rhodes was an ancient Greek author, best known for the Argonautica, an epic poem about Jason and the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. The poem is one of the few extant examples of the epic genre and it was both innovative and influential, providing Ptolemaic Egypt with a "cultural mnemonic" or national "archive of images", and offering the Latin poets Virgil and Gaius Valerius Flaccus a model for their own epics. His other poems, which survive only in small fragments, concerned the beginnings or foundations of cities, such as Alexandria and Cnidus places of interest to the Ptolemies, whom he served as a scholar and librarian at the Library of Alexandria. A literary dispute with Callimachus, another Alexandrian librarian/poet, is a topic much discussed by modern scholars since it is thought to give some insight into their poetry, although there is very little evidence that there ever was such a dispute between the two men. In fact almost nothing at all is known about Apollonius and even his connection with Rhodes is a matter for speculation. Once considered a mere imitator of Homer, and therefore a failure as a poet, his reputation has been enhanced by recent studies, with an emphasis on the special characteristics of Hellenistic poets as scholarly heirs of a long literary tradition writing at a unique time in history.
Apollonius is a masculine given name which may refer to:

Greek mathematics refers to mathematics texts and ideas stemming from the Archaic through the Hellenistic and Roman periods, mostly from the late 7th century BC to the 6th century AD, around the shores of the Mediterranean. Greek mathematicians lived in cities spread over the entire region, from Anatolia to Italy and North Africa, but were united by Greek culture and the Greek language. The development of mathematics as a theoretical discipline and the use of deductive reasoning in proofs is an important difference between Greek mathematics and those of preceding civilizations.

In Greek mythology, Absyrtus or Apsyrtus, was a Colchian prince and the younger brother of Medea. He was involved in Jason's escape with the golden fleece from Colchis
Cius, later renamed Prusias on the Sea after king Prusias I of Bithynia, was an ancient Greek city bordering the Propontis, in Bithynia and in Mysia, and had a long history, being mentioned by Herodotus, Xenophon, Aristotle, Strabo and Apollonius Rhodius.
In Greek mythology, Melaena or Melena, Melane or Melanis was a Corycian nymph, or member of the prophetic Thriae, of the springs of Delphi in Phocis.

In ancient Greek religion and myth, the Anemoi were wind gods who were each ascribed a cardinal direction from which their respective winds came, and were each associated with various seasons and weather conditions. They were the progeny of the goddess of the dawn Eos and her husband, the god of the dusk, Astraeus.

Life of Apollonius of Tyana, also known by its Latin title Vita Apollonii, is a text in eight books written in Ancient Greece by Philostratus. It tells the story of Apollonius of Tyana, a Pythagorean philosopher and teacher.

The praetorian prefecture of the East, or of the Orient was one of four large praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided. As it comprised the larger part of the Eastern Roman Empire, and its seat was at Constantinople, the praetorian prefect was the second most powerful man in the East, after the Emperor, in essence serving as his first minister.
Magnus was a Roman senator of Narbonne. He was appointed Roman consul in 460 by the Western emperor Majorian, at the same time Apollonius served in the East. Magnus also served as praetorian prefect of Gaul around the same time.
Apollonius was a general of the Eastern Roman Empire.
Apollonius was a politician of the Eastern Roman Empire.

Cytorus was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of Asia Minor. Mentioned by Homer, Cytorus survives in the name of Gideros, which is both
Rhoiteion was an ancient Greek city in the northern Troad region of Anatolia, also known as Ῥοίτιον ἄκρον. Its territory was bounded to the south and west by the Simoeis river and to the east by Ophryneion. It was located on the Baba Kale spur of Çakal Tepe north of Halileli and west of İntepe in Çanakkale Province, Turkey.
The Siege of Tyana occurred in 272 CE. The forces of the Roman Emperor Aurelian were seeking to conquer the Palmyrene Empire.
In Greek mythology, Argus or Argos may refer to the following personages
Ancon or Ankon was a populated place of ancient Pontus, on the Black Sea and on the coast road east of Amisus. It was on a headland and bay both of the same name. It is mentioned by Gaius Valerius Flaccus in his Argonautica, after the Iris, as if it were east of the mouth of that river. Apollonius Rhodius simply speaks of it as a headland.