Related Research Articles

Kennebunkport is a resort town in York County, Maine, United States. The population was 3,629 people at the 2020 census. It is part of the Portland–South Portland–Biddeford metropolitan statistical area.

Harbor Island is an artificial island in the mouth of the Duwamish River in Seattle, Washington, US, where it empties into Elliott Bay. Built by the Puget Sound Bridge and Dredging Company, it was completed in 1909 and was then the largest artificial island in the world, at 350 acres (1.4 km2). Since 1912, the island has been used for commercial and industrial activities including secondary lead smelting, shipbuilding and repair, bulk petroleum storage, metal fabrication and containerized cargo shipping. Warehouses, laboratories and other buildings are located on the island.

The Great Egg Harbor River is a 55.0-mile-long (88.5 km) river in South Jersey. It is one of the major rivers that traverse the largely pristine Pinelands, draining 308 square miles (800 km2) of wetlands into the Atlantic Ocean at Great Egg Harbor, from which it takes its name.

The Wolf River is a 105-mile-long (169 km) alluvial river in western Tennessee and northern Mississippi, whose confluence with the Mississippi River was the site of various Chickasaw, French, Spanish and American communities that eventually became Memphis, Tennessee. It is estimated to be about 12,000 years old, formed by glacier runoff carving into the region's soft alluvial soil. It should not be confused with The Wolf River which flows primarily in Middle Tennessee and southern Kentucky. The Wolf River rises in the Holly Springs National Forest at Baker's Pond in Benton County, Mississippi, and flows northwest into Tennessee, before entering the Mississippi River north of downtown Memphis.

Tuluá, is a city located in the heart of Valle del Cauca, Colombia. A major industrial and commercial center, it is the region's fourth-largest city after Cali—the department capital—Palmira and Buenaventura. Founded around 1741 by Juan de Lemos y Aguirre, it has a population of approximately 178,000. It is also known as the Corazón del Valle, as La Villa de Céspedes and Tierra Fácil.

The Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.

The Caroní River is the second most important river of Venezuela, the second in flow, and one of the longest, 952 kilometres (592 mi) from the Kukenan tepui through to its confluence with the Orinoco River. The name "Caroní" is applied starting from the confluence of the Kukenan with the Yuruaní River at 182 kilometres (113 mi) from the source of the Kukenan and 770 kilometres (480 mi) from its discharge in the Orinoco. The confluence takes place in Bolivar State. The Caroní River is the longest river located entirely within Venezuela.

The Westport River lies between Narragansett Bay and Buzzards Bay in Westport, Massachusetts.

Environmentally, Colombia is a mega-diverse country from its natural land terrain to its biological wildlife. Its biodiversity is a result of its geographical location and elevation. It is the fourth largest South American country and only country in South America to have coasts on the Pacific and Caribbean Sea. Colombia's terrain can be divided into six main natural zones: The Caribbean, the Pacific, The Orinoco region, The Amazonia region, the Andean region, and the Insular region. 52.2% of the environment is predominately the Andes, Amazon, and Pacific Basins, followed by the Orinoco basin 13.9%, the Andes and the Caribbean. The Tropical Andes, Choco, and the Caribbean are considered biodiversity hotspots which puts these areas at high risk of concentration of colonizing activities. Colombia host over 1800 bird species and at least one new species are detected every year. Decades of civil war and political unrest have impeded biological and environmental research in Colombia. The political unrest in Colombia catalyzes the alteration of land patterns through the cultivation of coca and opium crops, the redirection of extractive activities, and land abandonment in some areas.

The Catatumbo River is a river rising in northern Colombia, flowing into Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela. The Catatumbo River is approximately 340 kilometres (210 mi) long. It forms a part of the international boundary between the two countries. The river's name means "House of Thunder" in the language of the Bari people.
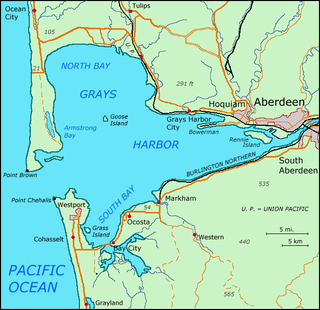
Grays Harbor is an estuarine bay located 45 miles (72 km) north of the mouth of the Columbia River, on the southwest Pacific coast of Washington state, in the United States. It is a ria, which formed at the end of the last ice age, when sea levels flooded the Chehalis River. The bay is 17 miles (27 km) long and 12 miles (19 km) wide. The Chehalis River flows into its eastern end, where the city of Aberdeen stands at that river's mouth, on its north bank, with the somewhat smaller city of Hoquiam immediately to its northwest, along the bayshore. Besides the Chehalis, many lesser rivers and streams flow into Grays Harbor, such as the Hoquiam River and Humptulips River. A pair of low peninsulas separate it from the Pacific Ocean, except for an opening about two miles (3 km) in width. The northern peninsula, which is largely covered by the community of Ocean Shores, ends in Point Brown. Facing that across the bay-mouth is Point Chehalis, at the end of the southern peninsula upon which stands the town of Westport.

Crystal River is a very short river in Citrus County, Florida, flowing into the Gulf of Mexico. It is just seven miles long, and has a drainage basin of five square miles, joining Kings Bay to the Gulf of Mexico. The river's significance is in the thirty natural springs that add an average of 300 million gallons of warm water to the river every day. These springs include Three Sisters Springs.

The Colombian Navy, officially the Colombian National Navy, also known as the "Armada Nacional" or just the "Armada" in Spanish, is the naval branch of the military forces of Colombia. The Navy is responsible for security and defence in the Colombian zones of both the Atlantic (Caribbean) and Pacific oceans, the extensive network of rivers inside the country, and a few small land areas under its direct jurisdiction.

The Daniel Webster Wildlife Sanctuary is a sanctuary owned by the Massachusetts Audubon Society, the largest conservation organization in New England, in the town of Marshfield, Massachusetts. The sanctuary, formerly the farm of Edward Dwyer, statesman Daniel Webster and the William Thomas family of Marshfield, the first English landowner to live on the sanctuary land, was purchased by Mass Audubon in 1984 thanks to the volunteer efforts of the Committee for the Preservation of Dwyer Farm for the People of Marshfield. The sanctuary contains 507 acres (2.1 km2) of mixed cultural grasslands, red maple swamps, a five-tiered wet panne, Webster Pond and a section of the Green Harbor River. It is the site of the annual Daniel Webster Farm Day celebration. Surrounding lands owned by the town of Marshfield and the Marshfield Airport increase the local open space area to more than 1000 acres (4 km2).

The Machias River is a 60.0-mile-long (96.6 km) river in Maine, USA. It flows through Washington County in the eastern part of the state, from Fifth Machias Lake, passing the town of Machias and emptying into Machias Bay.

Elkhorn Slough is a 7-mile-long (11 km) tidal slough and estuary on Monterey Bay in Monterey County, California. It is California's second largest estuary and the United States' first estuarine sanctuary. The community of Moss Landing and the Moss Landing Power Plant are located at the mouth of the slough on the bay.

The Columbia Plateau State Park Trail is a 130-mile-long (210 km), 20-foot-wide (6.1 m) corridor in eastern Washington state maintained as part of the Washington State Park system. The rail trail runs along the abandoned right-of-way of the former Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railway.

Cinaruco River is a river of Colombia and Venezuela. It is part of the Orinoco River basin. It has partially clear tanic waters. In Venezuela this river is part of the Santos Luzardo National Park since the year 1988. The Cinaruco River together with the Capanaparo River, other smaller rivers and the area around them form this national park. It houses a big biodiversity and many fishermen go each year looking for peacock bass. Three different species of peacock bass are found in this river: Cichla intermedia, Cichla orinocensis and Cichla temensis from smallest to biggest.
The South Branch Meduxnekeag River is a 15.2-mile-long (24.5 km) river in Aroostook County, Maine. From the outflow of Johnson Pond in Linneus, the river runs about 5.8 miles (9.3 km) southeast to Cary, before running into the Lt. Gordon Manuel Wildlife Management Area in Hodgdon, then north about 9.4 miles (15.1 km) to its confluence with the Meduxnekeag River at Carys Mills, two miles upstream from Houlton.

The Patía Valley dry forests (NT0225) is an ecoregion in southwestern Colombia. It covers a dry valley surrounded by mountains. The original habitat has mostly been destroyed by human activity, although a few pockets remain.
References
- Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993.