
An architect is a person who plans, designs, and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that have human occupancy or use as their principal purpose. Etymologically, the term architect derives from the Latin architectus, which derives from the Greek, i.e., chief builder.
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.
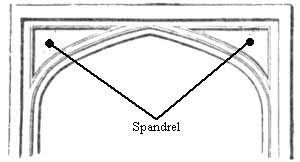
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame, between the tops of two adjacent arches, or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements.

Construction is a general term meaning the art and science of forming objects, systems, or organizations. It comes from the Latin word constructio and Old French construction. To 'construct' is a verb: the act of building, and the noun is construction: how something is built or the nature of its structure.

A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.

The Royal Institute of British Architects (RIBA) is a professional body for architects primarily in the United Kingdom, but also internationally, founded for the advancement of architecture under its royal charter granted in 1837, three supplemental charters and a new charter granted in 1971.
Building design, also called architectural design, refers to the broadly based architectural, engineering and technical applications to the design of buildings. All building projects require the services of a building designer, typically a licensed architect. Smaller, less complicated projects often do not require a licensed professional, and the design of such projects is often undertaken by building designers, draftspersons, interior designers, or contractors. Larger, more complex building projects require the services of many professionals trained in specialist disciplines, usually coordinated by an architect.

A joist is a horizontal structural member used in framing to span an open space, often between beams that subsequently transfer loads to vertical members. When incorporated into a floor framing system, joists serve to provide stiffness to the subfloor sheathing, allowing it to function as a horizontal diaphragm. Joists are often doubled or tripled, placed side by side, where conditions warrant, such as where wall partitions require support.

Russell Lincoln Ackoff was an American organizational theorist, consultant, and Anheuser-Busch Professor Emeritus of Management Science at the Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania. Ackoff was a pioneer in the field of operations research, systems thinking and management science.
A contractor or builder, is responsible for the day-to-day oversight of a construction site, management of vendors and trades, and the communication of information to all involved parties throughout the course of a building project.
Construction management (CM) aims to control the quality of a project's scope, time, and cost to maximize the project owner's satisfaction. It uses project management techniques and software to oversee the planning, design, construction and closeout of a construction project safely, on time, on budget and within specifications.
The architectural technologist, also known as a building technologist, provides technical building design services and is trained in architectural technology, building technical design and construction.

Design management is a field of inquiry that uses design, strategy, project management and supply chain techniques to control a creative process, support a culture of creativity, and build a structure and organization for design. The objective of design management is to develop and maintain an efficient business environment in which an organization can achieve its strategic and mission goals through design. Design management is a comprehensive activity at all levels of business, from the discovery phase to the execution phase. "Simply put, design management is the business side of design. Design management encompasses the ongoing processes, business decisions, and strategies that enable innovation and create effectively-designed products, services, communications, environments, and brands that enhance our quality of life and provide organizational success." The discipline of design management overlaps with marketing management, operations management, and strategic management.

In the United States, an architectural firm or architecture firm is a business that employs one or more licensed architects and practices the profession of architecture; while in South Africa, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Denmark and other countries, an architectural firm is a company that offers architectural services.

GMW Architects was an architectural practice based in the United Kingdom. In August 2015, the firm was taken over by another business, Scott Brownrigg, "as part of plans to move into the airport sector."
Edward Skoyles was the first quantity surveyor employed in the UK to research costs and practices in the construction industry. He did his research from 1960 until 1984 at the Building Research Establishment. Among his research projects was developing a new type of tendering for construction projects called operational bills. He also started the study of the actual amount of waste in the construction industry, and investigated the varying methods of cost estimation practices used in different countries. His contributions are still widely discussed in the academic literature particularly upon operational bills, and building waste

A chimney breast is a portion of a chimney which projects forward from a wall to accommodate a fireplace. Typically on the ground floor of a structure, the masonry extends upwards, containing a flue which carries smoke out of the building through a chimney stack. Chimney jambs similarly project from the wall, but they do so on either side of the fireplace and serve to support the chimney breast. The interior of a chimney breast is commonly filled with brickwork or concrete.
Construction communication, within an organizational context, is to convey an instruction to influence the actions/behaviors of others, or may involve an exchange of, or request for information during a construction project.

Architectural technology, or building technology, is the application of technology to the design of buildings. It is a component of architecture and building engineering and is sometimes viewed as a distinct discipline or sub-category. New materials and technologies generated new design challenges and construction methods throughout the evolution of building, especially since the advent of industrialisation in the 19th century. Architectural technology is related to the different elements of a building and their interactions; it is closely aligned with advances in building science.

Charles Burton "Chuck" Thomsen FAIA FCMAA is an American architect, construction manager, corporate executive and educator. He is the son of Fred Charles Thomsen and Sunbeam Burton Thomsen.











