Giovanni Arduino is the name of:
This is a record of historically important programming languages, by decade.

Quaternary is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene. The informal term "Late Quaternary" refers to the past 0.5–1.0 million years.

Arduino is an open-source hardware and software company, project and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a CC-BY-SA license, while software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL), permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors.

Giovanni Arduino was an Italian geologist who is known as the "Father of Italian Geology".
Arduino is an Italian masculine name, with variants including Ardovino, Ardoino, Ardolino, Arduilio, Arduo and the feminine Arduina. It derives from the Germanic Hardwin (Ortwin), in medieval Italy found in the forms Ardovinus, Ardoinus and Arduinus. In English it is often rendered as Arduin.
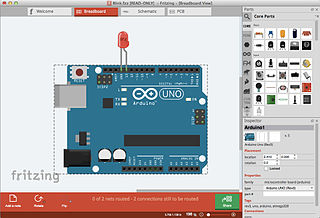
Fritzing is an open-source initiative to develop amateur or hobby CAD software for the design of electronics hardware, to support designers and artists ready to move from experimenting with a prototype to building a more permanent circuit. It was developed at the University of Applied Sciences Potsdam.
OBDuino is an open source trip computer design based on the Arduino platform. An OBDuino may be assembled and customised by an electronics hobbyist; it displays information such as instantaneous fuel economy, engine tuning parameters etc. on an LCD.

Pietro Arduino was an Italian botanist. The standard author abbreviation Ard. is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
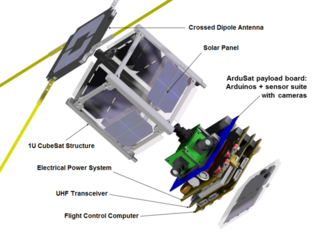
ArduSat is an Arduino based nanosatellite, based on the CubeSat standard. It contains a set of Arduino boards and sensors. The general public will be allowed to use these Arduinos and sensors for their own creative purposes while they are in space.

Guillermo Arduino is a CNN anchor and correspondent. Currently he is the host of Mirador Mundial on CNN en Español and Clix, a tech show on CNN en Español and CNN Latino.

Intel Quark is a line of 32-bit x86 SoCs and microcontrollers by Intel, designed for small size and low power consumption, and targeted at new markets including wearable devices. The line was introduced at Intel Developer Forum in 2013. Quark processors, while slower than Atom processors, are much smaller and consume less power. They lack support for SIMD instruction sets and only support embedded operating systems. Quark powers the Intel Galileo developer microcontroller board. However, in 2016 Arduino released the Arduino 101 board that includes an Intel Quark SoC. The CPU instruction set is the same as a Pentium (P54C/i586) CPU.

Intel Galileo is the first in a line of Arduino-certified development boards based on Intel x86 architecture and is designed for the maker and education communities. Intel released two versions of Galileo, referred to as Gen 1 and Gen 2. These development boards are sometimes called "Breakout boards".

The Arduino Uno is an open-source microcontroller board based on the Microchip ATmega328P microcontroller and developed by Arduino.cc. The board is equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards (shields) and other circuits. The board has 14 digital I/O pins, 6 analog I/O pins, and is programmable with the Arduino IDE, via a type B USB cable. It can be powered by the USB cable or by an external 9-volt battery, though it accepts voltages between 7 and 20 volts. It is similar to the Arduino Nano and Leonardo. The hardware reference design is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 2.5 license and is available on the Arduino website. Layout and production files for some versions of the hardware are also available.

NodeMCU is a low-cost open source IoT platform. It initially included firmware which runs on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi SoC from Espressif Systems, and hardware which was based on the ESP-12 module. Later, support for the ESP32 32-bit MCU was added.

Apache Mynewt is a modular real-time operating system for connected Internet of things (IoT) devices that must operate for long times under power, memory, and storage constraints. It is free and open-source software incubating under the Apache Software Foundation, with source code distributed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive license that is conducive to commercial adoption of open-source software.

The Arduino Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a cross-platform application that is written in functions from C and C++. It is used to write and upload programs to Arduino compatible boards, but also, with the help of third-party cores, other vendor development boards.

Anna Maria Arduino was an Italian regent, socialite, painter and writer. She was the regent of the Principality of Piombino during the minority of her son Prince Niccolò II Ludovisi in 1699-1700.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











