
Squid are cephalopods in the superorder Decapodiformes with elongated bodies, large eyes, eight arms and two tentacles. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin.

Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. It has a wide variety of uses, including speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests, caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources, and aiding security by filtering traffic. Although primarily used for HTTP and FTP, Squid includes limited support for several other protocols including Internet Gopher, SSL, TLS and HTTPS. Squid does not support the SOCKS protocol.
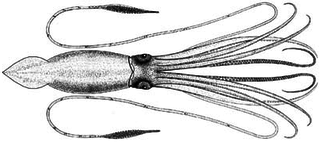
The giant squid is a deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. Giant squid can grow to a tremendous size due to deep-sea gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at 13 m (43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

The vampire squid is a small cephalopod found throughout temperate and tropical oceans in extreme deep sea conditions. Unique retractile sensory filaments justify the vampire squid's placement in its own order, Vampyromorphida, as it shares similarities with both octopuses and squid. As a phylogenetic relict, it is the only known surviving member of its order. The first specimens were collected on the Valdivia Expedition and they were originally described as an octopus in 1903 by German teuthologist Carl Chun, but later assigned to a new order together with several extinct taxa.

The Fiordland penguin, also known as the Fiordlandcrested penguin, is a crested penguin species endemic to New Zealand. It currently breeds along the south-western coasts of New Zealand's South Island as well as on Stewart Island/Rakiura and its outlying islands. Because it originally ranged beyond Fiordland, it is sometimes referred to as the New Zealand crested penguin.

Ommastrephidae is a family of squid containing three subfamilies, 11 genera, and over 20 species. They are widely distributed globally and are extensively fished for food. One species, Todarodes pacificus, comprises around half of the world's cephalopod catch annually.

The Humboldt squid, also known as jumbo squid, jumbo flying squid, pota, or diablo rojo, is a large, predatory squid living in the waters of the Humboldt Current in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It is the only species of the genus Dosidicus of the subfamily Ommastrephinae, family Ommastrephidae.

The longfin inshore squid is a species of squid of the family Loliginidae.
The Hawaiian sling is a device used in spearfishing. The sling operates much like a bow and arrow does on land, but energy is stored in rubber tubing rather than a wooden or fiberglass bow.

Squid is eaten in many cuisines; in English, the culinary name calamari is often used for squid dishes but is also used for some octopus dishes as well, notably fried squid/octopus. There are many ways to prepare and cook squid, with every country and region having its own recipes. Fried squid appears in Mediterranean cuisine. In Lebanon, Syria and Armenia, it is served with a tarator sauce. In New Zealand, Australia and South Africa, it is sold in fish and chip shops. In North America, fried squid is a staple in seafood restaurants. In Britain, it can be found in Mediterranean 'calamari' or Asian 'salt and pepper fried squid' forms in all kinds of establishments, often served as a bar snack, street food or starter.
The Squid is the name of two different villains in DC Comics.

The colossal squid, sometimes called the Antarctic squid or giant cranch squid, is believed to be the largest squid species in terms of mass. It is the only known member of the genus Mesonychoteuthis. It is known from only a few specimens, and current estimates put its maximum size at 12–14 m (39–46 ft) long and weighing possibly up to 750 kilograms (1,650 lb), based on analysis of smaller and immature specimen, making it the largest-known invertebrate.

The kraken is a legendary cephalopod-like sea monster in Scandinavian folklore of giant size. According to the Norse sagas, the kraken dwells off the coasts of Norway and Greenland and terrorizes nearby sailors. Authors over the years have postulated that the legend may have originated from sightings of giant squids that may grow to 13–15 meters in length. The sheer size and fearsome appearance attributed to the kraken have made it a common ocean-dwelling monster in various fictional works. The kraken has been the focus of many superstitious sailors passing the North Atlantic and especially sailors from the Nordic countries due to their close proximity and its Scandinavian origin. Throughout the centuries the kraken has been a staple part of sailors' superstitions and mythos being heavily linked to sailors ability of telling a tall tale.

Neocoleoidea is a large group of marine cephalopods. This cohort contains two extant groups: Decapodiformes and Octopodiformes. Species within this group exist in all major habitats in the ocean, in both the southern and northern polar regions, and from intertidal zones to great depths. Whilst conventionally held to be monophyletic, the only morphological character for the group is the presence of suckers: although the presence of these features in the belemnites suggests that they do not support the Neocoleoidea, and hence that the group may be paraphyletic.

Todarodinae is a squid subfamily in the family Ommastrephidae.
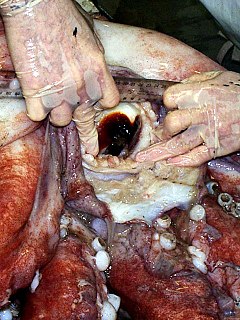
All extant cephalopods have a two-part beak, or rostrum, situated in the buccal mass and surrounded by the muscular head appendages. The dorsal (upper) mandible fits into the ventral (lower) mandible and together they function in a scissor-like fashion. The beak may also be referred to as the mandibles or jaws.
















