
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry.

Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from Latin: stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio.

The Marsh test is a highly sensitive method in the detection of arsenic, especially useful in the field of forensic toxicology when arsenic was used as a poison. It was developed by the chemist James Marsh and first published in 1836. The method continued to be used, with improvements, in forensic toxicology until the 1970s.

Stibnite, sometimes called antimonite, is a sulfide mineral with the formula Sb2S3. This soft grey material crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group. It is the most important source for the metalloid antimony. The name is derived from the Greek στίβι stibi through the Latin stibium as the former name for the mineral and the element antimony.

Realgar ( ree-AL-gar, -gər), also known as "ruby sulphur" or "ruby of arsenic", is an arsenic sulfide mineral with the chemical formula α-As4S4. It is a soft, sectile mineral occurring in monoclinic crystals, or in granular, compact, or powdery form, often in association with the related mineral, orpiment (As2S3). It is orange-red in color, melts at 320 °C, and burns with a bluish flame releasing fumes of arsenic and sulfur. Realgar is soft with a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2 and has a specific gravity of 3.5. Its streak is orange colored. It is trimorphous with pararealgar and bonazziite. Its name comes from the Arabic rahj al-ġār (رهج الغار, "powder of the mine"), via Medieval Latin, and its earliest record in English is in the 1390s.

Arsenic trisulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2S3. It is a dark yellow solid that is insoluble in water. It also occurs as the mineral orpiment (Latin: auripigment), which has been used as a pigment called King's yellow. It is produced in the analysis of arsenic compounds. It is a group V/VI, intrinsic p-type semiconductor and exhibits photo-induced phase-change properties. The other principal arsenic sulfide is As4S4, a red-orange solid known as the mineral realgar.

Arsenic trioxide, sold under the brand name Trisenox among others, is an inorganic compound and medication. As an industrial chemical, whose major uses include in the manufacture of wood preservatives, pesticides, and glass. As a medication, it is used to treat a type of cancer known as acute promyelocytic leukemia. For this use it is given by injection into a vein.
The arsenate ion is AsO3−
4. An arsenate (compound) is any compound that contains this ion. Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid. The arsenic atom in arsenate has a valency of 5 and is also known as pentavalent arsenic or As(V). Arsenate resembles phosphate in many respects, since arsenic and phosphorus occur in the same group (column) of the periodic table. Arsenates are moderate oxidizers, with an electrode potential of +0.56 V for reduction to arsenites.

Phosphorus sulfides comprise a family of inorganic compounds containing only phosphorus and sulfur. These compounds have the formula P4Sx with x ≤ 10. Two are of commercial significance, phosphorus pentasulfide (P4S10), which is made on a kiloton scale for the production of other organosulfur compounds, and phosphorus sesquisulfide (P4S3), used in the production of "strike anywhere matches".

Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P2S5 or dimer P4S10. This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF.

Lorándite is a thallium arsenic sulfosalt with the chemical formula: TlAsS2. Though rare, it is the most common thallium-bearing mineral. Lorandite occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal associations and in gold and mercury ore deposits. Associated minerals include stibnite, realgar, orpiment, cinnabar, vrbaite, greigite, marcasite, pyrite, tetrahedrite, antimonian sphalerite, arsenic and barite.
Antimony sulfide may refer to either of two compounds of antimony and sulfur:
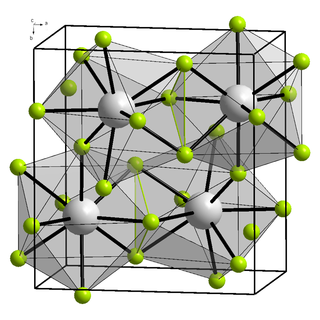
Bismuth(III) fluoride or bismuth trifluoride is a chemical compound of bismuth and fluorine. The chemical formula is BiF3. It is a grey-white powder melting at 649 °C.
Dimorphite, chemical name arsenic sesquisulfide (As4S3), is a very rare orange-yellow arsenic sulfide mineral. In nature, dimorphite forms primarily by deposition in volcanic fumaroles at temperatures of 70–80 °C (158–176 °F). Dimorphite was first discovered in such a fumarole near Naples, Italy in 1849 by the mineralologist Arcangelo Scacchi (1810–1893). Since its discovery, dimorphite has been found in the Alacrán silver mine near Copiapó, Chile. It has also been reported from Cerro de Pasco, Peru, and the Lavrion District Mines in Attica, Greece.

Arsenic pentasulfide is an inorganic compound containing arsenic and sulfur.

Alacránite (As8S9) is an arsenic sulfide mineral first discovered in the Uzon caldera, Kamchatka, Russia. It was named for its occurrence in the Alacrán silver/arsenic/antimony mine. Pampa Larga, Chile. It is generally more rare than realgar and orpiment. Its origin is hydrothermal. It occurs as subhedral to euhedral tabular orange to pale gray crystals that are transparent to translucent. It has a yellow-orange streak with a hardness of 1.5. It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system. It occurs with realgar and uzonite as flattened and prismatic grains up to 0.5 mm across.

Antimony sulfate, Sb2(SO4)3, is a hygroscopic salt formed by reacting antimony or its compounds with hot sulfuric acid. It is used in doping of semiconductors and in the production of explosives and fireworks.

Sodium polysulfide is a general term for salts with the formula Na2Sx, where x = 2 to 5. The species Sx2−, called polysulfide anions, include disulfide (S22−), trisulfide (S32−), tetrasulfide (S42−), and pentasulfide (S52−). In principle, but not in practice, the chain lengths could be longer. The salts are dark red solids that dissolve in water to give highly alkaline and corrosive solutions. In air, these salts oxidize, and they evolve hydrogen sulfide by hydrolysis.
In organic and organometallic chemistry, trisulfide is the functional group R-S-S-S-R.














