
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to efficiently transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension.

Tendinopathy, also known as tendinitis or tendonitis, is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle.
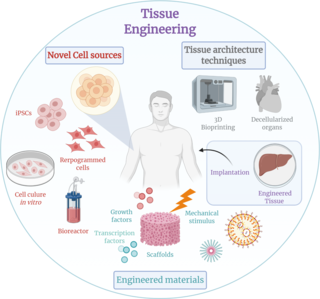
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own.

Achilles tendinitis, also known as achilles tendinopathy, occurs when the Achilles tendon, found at the back of the ankle, becomes sore. Achilles tendinopathy is accompanied by alterations in the tendon’s structure and mechanical properties. The most common symptoms are pain and swelling around the affected tendon. The pain is typically worse at the start of exercise and decreases thereafter. Stiffness of the ankle may also be present. Onset is generally gradual.

Hyaluronic acid, also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about 7 million Da per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention 3–4 million Da.
A soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body. Common soft tissue injuries usually occur from a sprain, strain, a one off blow resulting in a contusion or overuse of a particular part of the body. Soft tissue injuries can result in pain, swelling, bruising and loss of function.
Chin augmentation using surgical implants can alter the underlying structure of the face, providing better balance to the facial features. The specific medical terms mentoplasty and genioplasty are used to refer to the reduction and addition of material to a patient's chin. This can take the form of chin height reduction or chin rounding by osteotomy, or chin augmentation using implants.

Achilles tendon rupture is when the Achilles tendon, at the back of the ankle, breaks. Symptoms include the sudden onset of sharp pain in the heel. A snapping sound may be heard as the tendon breaks and walking becomes difficult.

Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee, or preserved before reconstruction an arthroscopic procedure. ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomaterials is about fifty years old. The study of biomaterials is called biomaterials science or biomaterials engineering. It has experienced steady and strong growth over its history, with many companies investing large amounts of money into the development of new products. Biomaterials science encompasses elements of medicine, biology, chemistry, tissue engineering and materials science.
Davis's law is used in anatomy and physiology to describe how soft tissue models along imposed demands. It is the corollary to Wolff's law, which applies to osseous tissue. It is a physiological principle stating that soft tissue heal according to the manner in which they are mechanically stressed.
A fibrin scaffold is a network of protein that holds together and supports a variety of living tissues. It is produced naturally by the body after injury, but also can be engineered as a tissue substitute to speed healing. The scaffold consists of naturally occurring biomaterials composed of a cross-linked fibrin network and has a broad use in biomedical applications.
Generative Tissue (gTissue) is a living tissue created in a patient by a surgeon, consisting of an extracellular matrix, cells, and supporting vascular supply with generative properties. The 'g' in gTissue is considered a reference to both generated nature of the living tissue, but also to the generative ability of the tissue to be adapted to the dynamic environmental conditions experienced in the host.
Acellular dermis is a type of biomaterial derived from processing human or animal tissues to remove cells and retain portions of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These materials are typically cell-free, distinguishing them from classical allografts and xenografts, can be integrated or incorporated into the body, and have been FDA approved for human use for more than 10 years in a wide range of clinical indications.
An alginate dressing is a natural wound dressing derived from carbohydrate sources released by clinical bacterial species, in the same manner as biofilm formation. These types of dressings are best used on wounds that have a large amount of exudate. They may be used on full-thickness burns, surgical wounds, split-thickness graft donor sites, Mohs surgery defects, refractory decubiti, and chronic ulcers. They can also be applied onto dry wounds after normal saline is first applied to the site of application.
Posterolateral corner injuries of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment to avoid long term consequences. Injuries to the PLC often occur in combination with other ligamentous injuries to the knee; most commonly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). As with any injury, an understanding of the anatomy and functional interactions of the posterolateral corner is important to diagnosing and treating the injury.
The Network of Excellence for Functional Biomaterials (NFB) is a multidisciplinary research centre which hosts over sixty biologists, chemists, scientists, engineers and clinicians. It is based at the National University of Ireland, Galway, and is directed by Professor Abhay Pandit.

Medial knee injuries are the most common type of knee injury. The medial ligament complex of the knee is composed of the superficial medial collateral ligament (sMCL), deep medial collateral ligament (dMCL), and the posterior oblique ligament (POL). These ligaments have also been called the medial collateral ligament (MCL), tibial collateral ligament, mid-third capsular ligament, and oblique fibers of the sMCL, respectively. This complex is the major stabilizer of the medial knee. Injuries to the medial side of the knee are most commonly isolated to these ligaments. A thorough understanding of the anatomy and function of the medial knee structures, along with a detailed history and physical exam, are imperative to diagnosing and treating these injuries.

Diabetic foot ulcer is a major complication of diabetes mellitus, and probably the major component of the diabetic foot.
Artificial ligaments are devices used to replace damaged ligaments. Today, the most common use of artificial ligaments is in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Although autotransplantation remains the most common method of ligament reconstruction, numerous materials and structures were developed to optimize the artificial ligament since its creation in the World War I era. Many modern artificial ligaments are made of synthetic polymers, such as polyethylene terephthalate. Various coatings have been added to improve the biocompatibility of the synthetic polymers. Early artificial ligaments developed in the 1980s were ineffective due to material deterioration. Currently, the Ligament Advanced Reinforcement System (LARS) artificial ligament has been utilized extensively in clinical applications. Tissue engineering is a growing area of research which aims to regenerate and restore ligament function.