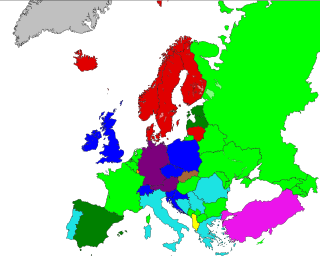
A television licence or broadcast receiving licence is a payment required in many countries for the reception of television broadcasts, or the possession of a television set where some broadcasts are funded in full or in part by the licence fee paid. The fee is sometimes also required to own a radio or receive radio broadcasts. A TV licence is therefore effectively a hypothecated tax for the purpose of funding public broadcasting, thus allowing public broadcasters to transmit television programmes without, or with only supplemental, funding from radio and television advertisements. However, in some cases the balance between public funding and advertisements is the opposite – the Polish TVP broadcaster receives more funds from advertisements than from its TV tax.
Public broadcasting includes radio, television and other electronic media outlets whose primary mission is public service. In much of the world, funding comes from the government, especially via annual fees charged on receivers. In the United States, public broadcasters may receive some funding from both federal and state sources, but generally most financial support comes from underwriting by foundations and businesses ranging from small shops to corporations, along with audience contributions via pledge drives. The great majority are operated as private not-for-profit corporations.

National Educational Television (NET) was a United States educational broadcast television network that operated from May 16, 1954 to November 4, 1982. It was owned by the Ford Foundation and later co-owned by the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. It was succeeded by the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS), which has memberships with many television stations that were formerly part of NET.
WNET, channel 13, is a non-commercial educational, public television station licensed to Newark, New Jersey and serving the New York metropolitan area. WNET is owned by WNET.org and is also the parent of Long Island PBS station WLIW and the operator of the New Jersey Public broadcasting network NJTV. WNET is a member station of, and a primary program provider to, PBS. WNET's main studios and offices are located in Midtown Manhattan with an auxiliary street-level studio in the Lincoln Center complex on Manhattan's Upper West Side. The station's transmitter is located at One World Trade Center.

The New Americans is a seven-hour American documentary, produced by Kartemquin Films, that was originally broadcast on American television over three nights on the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) in late March 2004.
Commercial broadcasting is the broadcasting of television programs and radio programming by privately owned corporate media, as opposed to state sponsorship. It was the United States′ first model of radio during the 1920s, in contrast with the public television model in Europe during the 1930s, 1940s and 1950s which prevailed worldwide until the 1980s.

Munhwa Broadcasting Corporation is one of the leading South Korean television and radio network companies. Munhwa is the Korean word for "culture". Its flagship terrestrial television station MBC TV is Channel 11 (LCN) for Digital.

KFSF-DT, virtual channel 66, is a UniMás owned-and-operated television station licensed to Vallejo, California, United States and serving the San Francisco Bay Area. The station is owned by the Univision Local Media subsidiary of Univision Communications, as part of a duopoly with San Francisco-licensed Univision owned-and-operated station KDTV-DT. The two stations share studios on Zanker Road in San Jose; KFSF's transmitter is located at Sutro Tower in San Francisco.
Mariano "Mar" Elepaño is a Filipino American independent filmmaker, teacher, and has been the production supervisor of the John C. Hench Division of Animation and Digital Arts, USC School of Cinematic Arts since 1993.

The Public Broadcasting Act of 1967 set up public broadcasting in the United States, establishing the Corporation for Public Broadcasting (CPB) and, eventually, the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS), and National Public Radio (NPR).
Moctesuma Esparza is a Mexican-American producer, entertainment executive, entrepreneur and community activist. Moctezuma Esparza is well known for his contributions to the movie industry and commitment to creating opportunities for Latinos everywhere. He is the CEO of Maya Cinemas, a theater chain catering to the United States Latino audience. He is also a partner with Robert Katz in the company Esparza/Katz Productions. Moctezuma founded Maya Entertainment in 2007, a vertically integrated media content company providing full service motion picture distribution and production.
The UCLA Film & Television Archive is an internationally renowned visual arts organization focused on the preservation, study, and appreciation of film and television, based at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). It holds more than 220,000 film and television titles and 27 million feet of newsreel footage, a collection second only to the Library of Congress in Washington, D.C. It has more media materials than any other university in the world.
An underwriting spot is an announcement made on public broadcasting outlets, especially in the United States, in exchange for funding. These spots usually mention the name of the sponsor, and can resemble traditional television advertisements in commercial broadcasting to a limited extent; however, under the terms of a public broadcaster's license from the Federal Communications Commission, such spots are prohibited from being promotional or making any sort of "call to action". In the U.S., these restrictions apply to any television or radio station licensed as a non-commercial educational (NCE) stations, and even for non-sponsoring companies and products.

Visual Communications –– is a community-based non-profit media arts organization based in Los Angeles and founded in 1970 by independent filmmakers Robert Nakamura, Alan Ohashi, Eddie Wong, and Duane Kubo. Fueled by the Civil Rights and Anti-War movements, they set out creating learning kits, photographing community events, recording oral histories, and collecting historical images of Asian American life. Additionally, they created films, video productions, community media productions, screening activities, and photographic exhibits and publications.
Robert Akira Nakamura is a filmmaker and teacher, sometimes referred to as "the Godfather of Asian American media." In 1970 he cofounded Visual Communications (VC) the oldest community-based Asian Pacific American media arts organization in the United States.
America's Public Television Stations (APTS) is a non-profit membership organization established in 1979. The mission of APTS is to conduct – in concert with member stations – advocacy, planning, research, communications, and other activities that foster a strong and financially sound public television system providing essential public services to all Americans. Its affiliate APTS Action, Inc. promotes the legislative interests of non-commercial television stations at the national level through direct advocacy and through grasstops and grassroots campaigns designed to secure and enhance bipartisan congressional support.
The American Archive of Public Broadcasting (AAPB) is a collaboration of the Library of Congress and WGBH Educational Foundation, founded through the efforts of the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. Its Online Reading Room, providing access to a large amount of American public broadcasting content, opened in October, 2015.










