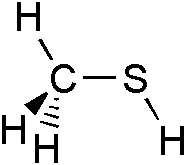
Methanethiol is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH
4S. It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. It is a natural substance found in the blood and brain of humans and animals, as well as in plant tissues. It is disposed of through animal feces. It also occurs naturally in certain foods, such as some nuts and cheese. It is one of the main compounds responsible for bad breath and the smell of flatus. Methanethiol is classified as a thiol and is sometimes abbreviated as MeSH. It is very flammable.

The common asparagus beetle is an important pest of asparagus crops both in Europe and in North America. Asparagus is its only food plant. The beetle is about half a centimeter long, metallic blue-black in color with cream or yellow spots on its red-bordered elytra. The larvae are fat gray grubs with dark heads.

Ornithogalum pyrenaicum, also called Prussian asparagus, wild asparagus, Bath asparagus, Pyrenees star of Bethlehem, or spiked star of Bethlehem, is a plant whose young flower shoots may be eaten as a vegetable, similar to asparagus.

Asparagaceae is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. Its best known member is Asparagus officinalis, garden asparagus.
Asparagusic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula C4H6O2S2 and is systematically named 1,2-dithiolane-4-carboxylic acid. The molecule consists of a heterocyclic disulfide functional group (a 1,2-dithiolane) with a carboxylic acid side chain. It is found in asparagus and is believed to be the metabolic precursor to odorous sulfur compounds responsible for the distinctive smell of urine which has long been associated with eating asparagus.

Asparagus racemosus is a species of asparagus common throughout Nepal, Sri Lanka, India and the Himalayas. It grows 1–2 m tall and prefers to take root in gravelly, rocky soils high up in piedmont plains, at 1,300–1,400 m (4,300–4,600 ft) elevation. It was botanically described in 1799. Because of its multiple uses, the demand for Asparagus racemosus is constantly on the rise. Because of destructive harvesting, combined with habitat destruction, and deforestation, the plant is now considered "endangered" in its natural habitat.

Asparagus asparagoides, commonly known as bridal creeper, bridal-veil creeper, gnarboola, smilax or smilax asparagus, is a herbaceous climbing plant of the family Asparagaceae native to eastern and southern Africa. Sometimes grown as an ornamental plant, it has become a serious environmental weed in Australia and New Zealand.

Puccinia asparagi is the causative agent of asparagus rust. It is an autoecious fungus, meaning that all stages of its life cycle – pycniospores, aeciospores, and teliospores – all develop upon the same host plant
. Rust diseases are among the most destructive plant diseases, known to cause famine following destruction of grains, vegetables, and legumes. Asparagus rust occurs wherever the plant is grown and attacks asparagus plants during and after the cutting season. Asparagus spears are usually harvested before extensive rust symptoms appear. Symptoms are first noticeable on the growing shoots in early summer as light green, oval lesions, followed by tan blister spots and black, protruding blisters later in the season.
The lesions are symptoms of Puccinia asparagi during early spring, mid-summer and later summer to fall, respectively. Severe rust infections stunt or kill young asparagus shoots, causing foliage to fall prematurely, and reduce the ability of the plant to store food reserves. The Puccinia asparagi fungus accomplishes this by rust lowering the amounts of root storage metabolites. The infected plant has reduced plant vigor and yield, often leading to death in severe cases. Most rust diseases have several stages, some of which may occur on different hosts; however, in asparagus rust all the life stages occur on asparagus. Because of this, many observers mistake the different stages of the Puccinia asparagi life cycle as the presence of different diseases. The effects of Puccinia asparagi are present worldwide wherever asparagus is being grown. Asparagus rust is a serious threat to the asparagus industry.

Parahypopta caestrum is a species of moth of the family Cossidae. It is found on the Iberian Peninsula and in France, Italy, Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, on the Balkan Peninsula, as well as in Jordan, Israel, Syria, Iraq, Turkey, south-western Russia and Kazakhstan.

Medeola virginiana, Indian cucumber-root, is an eastern North American plant species in the lily family, Liliaceae. It is the only currently recognized plant species in the genus Medeola. Indian cucumber-root grows in the understory of forests. The plant bears edible rhizomes that have a mild cucumber-like flavor.

Cream of asparagus soup is a soup prepared with asparagus, stock and milk or cream as primary ingredients.

VeggieTales in the House is an American Christian computer-animated children's comedy television series produced by Big Idea Entertainment, DreamWorks Animation Television and Bardel Entertainment. It takes place outside of VeggieTales, a Christian-themed video and film series, featuring anthropomorphic vegetables. The series was executive produced by Doug TenNapel, creator of Earthworm Jim. The series premiered on Netflix on November 26, 2014. Three seasons of the series have been ordered, consisting of a total of 75 22-minute episodes. A fourth season was released on September 23, 2016. A follow-up series, titled VeggieTales in the City, premiered on February 24, 2017, on Netflix.

The Shatavar Vatika Herbal Park, Hisar, named after Shatavar herb, is a 125-acre herbal park for the preservation of several endangered Ayurvedic medicinal herbs, on Dhansu road in the town of Hisar in the Hisar district of Haryana State, India.

The Cooks and Confectioners Dictionary: or, the Accomplish'd Housewives Companion was a cookery book written by John Nott and first published in London in 1723.















