
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft.

A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after some superclusters (of which only one, the Shapley Supercluster, is known to be bound). They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with galactic clusters (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters within galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and clusters can themselves cluster together to form superclusters.

The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. STScI was established in 1981 as a community-based science center that is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). STScI's offices are located on the Johns Hopkins University Homewood Campus and in the Rotunda building in Baltimore, Maryland.

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area about 2.6 arcminutes on a side, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and 28, 1995.

The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) is a deep-field image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, containing an estimated 10,000 galaxies. The original data for the image was collected by the Hubble Space Telescope from September 2003 to January 2004 and the first version of the image was released on March 9, 2004. It includes light from galaxies that existed about 13 billion years ago, some 400 to 800 million years after the Big Bang.

John Mace Grunsfeld is an American physicist and a former NASA astronaut. He is a veteran of five Space Shuttle flights and has served as NASA Chief Scientist. His academic background includes research in high energy astrophysics, cosmic ray physics and the emerging field of exoplanet studies with specific interest in future astronomical instrumentation. After retiring from NASA in 2009, he served as the deputy director of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland. In January 2012, he returned to NASA and served as associate administrator of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD). Grunsfeld announced his retirement from NASA in April 2016.

The Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) is a camera formerly installed on the Hubble Space Telescope. The camera was built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and is roughly the size of a baby grand piano. It was installed by servicing mission 1 (STS-61) in 1993, replacing the telescope's original Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC). WFPC2 was used to image the Hubble Deep Field in 1995, the Engraved Hourglass Nebula and Egg Nebula in 1996, and the Hubble Deep Field South in 1998. During STS-125, WFPC2 was removed and replaced with the Wide Field Camera 3 as part of the mission's first spacewalk on May 14, 2009. After returning to Earth, the camera was displayed briefly at the National Air and Space Museum and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory before returning to its final home at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum.

The Space Telescope – European Coordinating Facility (ST-ECF) was an institution which provided a number of support and service functions primarily for European observers of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope (HST). It was established in 1984 by the European Space Agency (ESA) and the European Southern Observatory (ESO), and was located at the ESO headquarters in Garching bei München, Germany. The ST-ECF ceased operations on 31 December 2010.

The Hubble Deep Field South is a composite of several hundred individual images taken using the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over 10 days in September and October 1998. It followed the great success of the original Hubble Deep Field in facilitating the study of extremely distant galaxies in early stages of their evolution. While the WFPC2 took very deep optical images, nearby fields were simultaneously imaged by the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) and the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS).
Hubble search for transition comets was a study involving amateur astronomers and the use of the Hubble Space Telescope, one of only six studies involving amateur astronomers approved by NASA.
POA CALFOS is the improved Post Operational Archive version of the Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS) calibration pipeline, an earlier instrument aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). STScI made an improved version of the FOS calibration pipeline called POA_CALFOS. POA CALFOS replaces CALFOS, which performed the routine calibration of FOS data in the standard IRAF/STSDAS FOS calibration pipeline. The current version corrects for image motion problems that have led to significant wavelength scale uncertainties in the FOS data archive. The improvements in the calibration enhance the scientific value of the data in the FOS archive, making it a more homogeneous and reliable resource.
In observational astronomy an On-The-Fly Calibration (OTFC) system calibrates data when a user's request for the data is processed so that users can obtain data that are calibrated with up-to-date calibration files, parameters, and software.
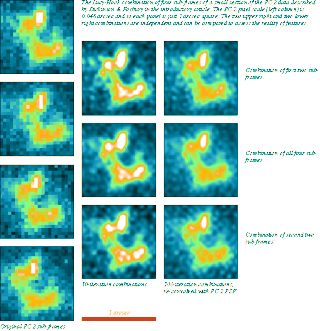
The Lucy–Hook coaddition method is an image processing technique for combining sub-stepped astronomical image data onto a finer grid. The method allows the option of resolution and contrast enhancement or the choice of a conservative, re-convolved, output.
Drizzle is a digital image processing method for the linear reconstruction of undersampled images. The method is normally used for the combination of astronomical images and was originally developed for the Hubble Deep Field observations made by the Hubble Space Telescope. The algorithm, known as variable-pixel linear reconstruction, or informally as "Drizzle", preserves photometry and resolution, can weight input images according to the statistical significance of each pixel, and removes the effects of geometric distortion on both image shape and photometry. In addition, it is possible to use drizzling to combine dithered images in the presence of cosmic rays.

The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS) is a science instrument that was installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during Servicing Mission 4 (STS-125) in May 2009. It is designed for ultraviolet (90–320 nm) spectroscopy of faint point sources with a resolving power of ≈1,550–24,000. Science goals include the study of the origins of large scale structure in the universe, the formation and evolution of galaxies, and the origin of stellar and planetary systems and the cold interstellar medium. COS was developed and built by the Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy (CASA-ARL) at the University of Colorado at Boulder and the Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corporation in Boulder, Colorado.

The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) is the Hubble Space Telescope's last and most technologically advanced instrument to take images in the visible spectrum. It was installed as a replacement for the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 during the first spacewalk of Space Shuttle mission STS-125 on May 14, 2009.

Rodger Evans Doxsey was an American physicist and astronomer who made major contributions to the scientific and operational success of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST). He joined the HST Project at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), in Baltimore, Maryland, in 1981, and was head of the Hubble Missions Office when he died in 2009.
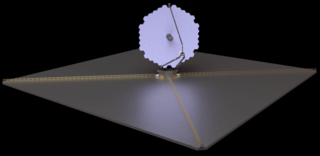
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR, is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astrophysics space mission concepts studied in preparation for the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey.
The Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes (MAST) is an astronomical data archive. The archive brings together data from the visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared wavelength regimes. The NASA funded project is located at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland and is one of the largest astronomical databases in the world.














