
An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. The ammeter is usually connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured. An ammeter usually has low resistance so that it does not cause a significant voltage drop in the circuit being measured.

An electrical telegraph was a point-to-point text messaging system, used from the 1840s until the late 20th century when it was slowly replaced by other telecommunication systems. At the sending station switches connected a source of current to the telegraph wires. At the receiving station the current activated electromagnets which moved indicators, providing either a visual or audible indication of the text. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems called telegraphs, that were devised to communicate text messages more rapidly than by physical transportation. Prior to the electric telegraph, semaphore systems were used, including beacons, smoke signals, flag semaphore, and optical telegraphs for visual signals to communicate over distances of land.

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is carried by electromagnetic fields composed of electric fields and magnetic fields, and it is responsible for electromagnetic radiation such as light. It is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature, together with the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force.

Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ferro- refers to iron, because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4.

A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with magnetic north. Other methods may be used, including gyroscopes, magnetometers, and GPS receivers.

A galvanometer is an electromechanical measuring instrument for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeters, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely.

Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975. Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.

Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial information in flight. They improve safety by allowing the pilot to fly the aircraft in level flight, and make turns, without a reference outside the aircraft such as the horizon. Visual flight rules (VFR) require an airspeed indicator, an altimeter, and a compass or other suitable magnetic direction indicator. Instrument flight rules (IFR) additionally require a gyroscopic pitch-bank, direction and rate of turn indicator, plus a slip-skid indicator, adjustable altimeter, and a clock. Flight into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) require radio navigation instruments for precise takeoffs and landings.
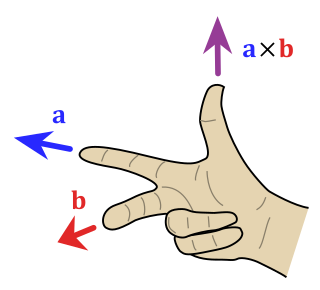
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space.

Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and true north. This angle varies depending on position on the Earth's surface and changes over time.
A non-directional (radio) beacon (NDB) is a radio transmitter at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. As the name implies, the signal transmitted does not include inherent directional information, in contrast to other navigational aids such as low-frequency radio range, VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and tactical air navigation system (TACAN). NDB signals follow the curvature of the Earth, so they can be received at much greater distances at lower altitudes, a major advantage over VOR. However, NDB signals are also affected more by atmospheric conditions, mountainous terrain, coastal refraction and electrical storms, particularly at long range. The system, developed by United States Air Force (USAF) Captain Albert Francis Hegenberger, was used to fly the world's first instrument approach on May 9, 1932.

In geography and geodesy, a meridian is the locus connecting points of equal longitude, which is the angle east or west of a given prime meridian. In other words, it is a line of longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by that longitude and its latitude, measured in angular degrees north or south of the Equator. On a Mercator projection or on a Gall-Peters projection, each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude. A meridian is half of a great circle on Earth's surface. The length of a meridian on a modern ellipsoid model of Earth has been estimated as 20,003.93 km (12,429.87 mi).

Dip circles are used to measure the angle between the horizon and the Earth's magnetic field. They were used in surveying, mining and prospecting as well as for the demonstration and study of magnetism.
Space physics, also known as solar-terrestrial physics or space-plasma physics, is the study of plasmas as they occur naturally in the Earth's upper atmosphere (aeronomy) and within the Solar System. As such, it encompasses a far-ranging number of topics, such as heliophysics which includes the solar physics of the Sun, the solar wind, planetary magnetospheres and ionospheres, auroras, cosmic rays, and synchrotron radiation. Space physics is a fundamental part of the study of space weather and has important implications in not only to understanding the universe, but also for practical everyday life, including the operations of communications and weather satellites.

Hans Christian Ørsted was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism. Oersted's law and the oersted unit (Oe) are named after him.
The Astatic Corporation is a commercial audio products manufacturer founded in Youngstown, Ohio in 1933. Astatic formed CAD Professional Microphones in 1988 as a division of Astatic. The company reorganized as Omnitronics LLC in 2000, and later combined CAD, Astatic and Omnitronics under the CAD Audio brand. DAS Companies purchased the rights for Astatic Citizens Band hand microphones and is one of their acquired brand names.
Myoclonic astatic epilepsy (MAE), also known as myoclonic atonic epilepsy or Doose syndrome, is a generalized idiopathic epilepsy. It is characterized by the development of myoclonic seizures and/or myoclonic astatic seizures. Some of the common monogenic causes include mutations in the genes SLC6A1 (3p25.3),CHD2 (15q26.1), AP2M1 (10q23.2).

The north magnetic pole is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward. There is only one location where this occurs, near the geographic north pole. The geomagnetic north pole is the northern antipodal pole of an ideal dipole model of the Earth's magnetic field, which is the most closely fitting model of Earth's actual magnetic field.

The British and Irish Magnetic Telegraph Company was founded by John Brett in 1850. The Magnetic was the principal competitor to the largest telegraph company in the United Kingdom, the Electric Telegraph Company. The Magnetic was the leading company in Ireland, while the Electric was the leading company in mainland Britain. Between them, they dominated the market until the telegraph was nationalised in 1870.
















