
The Antofagasta Region is one of Chile's sixteen first-order administrative divisions. The second-largest region of Chile, it comprises three provinces, Antofagasta, El Loa and Tocopilla. It is bordered to the north by Tarapacá, by Atacama to the south, and to the east by Bolivia and Argentina. The region's capital is the port city of Antofagasta; another one of its important cities is Calama. The region's main economic activity is copper mining in its giant inland porphyry copper systems.

The Atacama Region is one of Chile's 16 first order administrative divisions. It comprises three provinces: Chañaral, Copiapó and Huasco. It is bordered to the north by Antofagasta, to the south by Coquimbo, to east with Provinces of Catamarca, La Rioja and San Juan of Argentina, and to the west by the Pacific Ocean. The regional capital Copiapó is located at 806 km (501 mi) north of the country's capital of Santiago. The region occupies the southern portion of the Atacama Desert, the rest of the desert is mainly distributed among the other regions of Norte Grande.
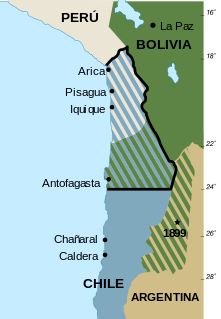
The Atacama border dispute is a dispute between Chile and Bolivia that stems from the transfer of the Bolivian Coast and the southern tip of Peru to Chile in the 19th century through the Treaty of Ancón with Peru and the Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1904 between Chile and Bolivia after the War of the Pacific (1879–1883). The dispute is considered to be ongoing because Bolivia still claims a sovereign access to the Pacific Ocean. The conflict takes its name from the Atacama Desert on which lies the disputed territory. Due to a transfer of land to both Argentina and Chile during the Chilean annexation of the Bolivian coast in 1879, the Puna de Atacama dispute—this spin-off dispute was settled in 1899.

San Pedro de Atacama is a Chilean town and commune in El Loa Province, Antofagasta Region. It is located east of Antofagasta, some 106 km (60 mi) southeast of Calama and the Chuquicamata copper mine, overlooking the Licancabur volcano. It features a significant archeological museum, the R. P. Gustavo Le Paige Archaeological Museum, with a large collection of relics and artifacts from the region. Native ruins nearby now attract increasing numbers of tourists interested in learning about pre-Columbian cultures.

Iquique is a port city and commune in northern Chile, capital of both the Iquique Province and Tarapacá Region. It lies on the Pacific coast, west of the Pampa del Tamarugal, which is part of the Atacama Desert. It had a population of 191,468 according to the 2017 census. It is also the main commune of Greater Iquique. The city developed during the heyday of the saltpetre mining in the Atacama Desert in the 19th century. Once a Peruvian city with a large Chilean population, it was conquered by Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879–1883). Today it is one of only two free ports of Chile, the other one being Punta Arenas, in the country's far south.

Club de Deportes Copiapó — or simply Deportes Copiapó — is a Chilean football club based in Copiapó, Atacama Region. Founded in 1999 after Regional Atacama disappearing, it currently plays in the Primera B (second-tier) and holds its home games at Estadio Luis Valenzuela Hermosilla which has a capacity of 8,000 spectators.

Salar de Atacama is the largest salt flat in Chile. It is located 55 km (34 mi) south of San Pedro de Atacama, is surrounded by mountains, and has no drainage outlets. In the east it is enclosed by the main chain of the Andes, while to the west lies a secondary mountain range of the Andes called Cordillera de Domeyko. Large volcanoes dominate the landscape, including the Licancabur, Acamarachi, Aguas Calientes and the Láscar. The last is one of the most active volcanoes in Chile. All of them are located along the eastern side of the Salar de Atacama, forming a generally north-south trending line of volcanoes that separate it from smaller endorheic basins.

Los Flamencos National Reserve is a nature reserve located in the commune of San Pedro de Atacama, Antofagasta Region of northern Chile. The reserve covers a total area of 740 square kilometres (290 sq mi) in the Central Andean dry puna ecoregion and consists of seven separate sections.

The Atacama people, known as atacameños or atacamas in Spanish and Kunzas, Likan-antai or Likanantaí in English, are indigenous people from the Atacama Desert and altiplano region in the north of Chile and Argentina and southern Bolivia.

The climate of Chile comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large geographic scale, extending across 38 degrees in latitude, making generalizations difficult. According to the Köppen system, Chile within its borders hosts at least seven major climatic subtypes, ranging from low desert in the north, to alpine tundra and glaciers in the east and southeast, tropical rainforest in Easter Island, Oceanic in the south and Mediterranean climate in central Chile. There are four seasons in most of the country: summer, autumn, winter, and spring.

Desierto de Atacama Airport is an airport serving the region around Copiapó, the capital of the Atacama Region of Chile. The airport is in the desert north of the Copiapó River, 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) inland from the Pacific coast.

The Atacama Desert is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in the world, as well as the only true desert to receive less precipitation than the polar deserts and the largest fog desert in the world. Both regions have been used as experimentation sites on Earth for Mars expedition simulations. According to estimates, the Atacama Desert occupies 105,000 km2 (41,000 sq mi), or 128,000 km2 (49,000 sq mi) if the barren lower slopes of the Andes are included. Most of the desert is composed of stony terrain, salt lakes (salares), sand, and felsic lava that flows towards the Andes.

The Puna de Atacama or Atacama Plateau is an arid high plateau, in the Andes of northern Chile (15%) and Argentina (85%). Geomorphologist Walther Penck based his Grossfalt landform association on Puna de Atacama.

The Puna de Atacama dispute, sometimes referred to as Puna de Atacama Lawsuit, was a border dispute involving Argentina, Chile and Bolivia in the 19th century over the arid high plateau of Puna de Atacama located about 4500 meters above the sea around the current borders of the three countries.

Regional Atacama was a Chilean football club based in the city of Copiapó, Atacama Region. The club was founded in 1979, playing a total of six season at the top level of Chilean football during its 18-year existence.
The 1995 Campeonato Nacional, known as Campeonato Nacional Copa Banco del Estado 1995 for sponsorship purposes, was the 63rd season of top-flight football in Chile. Universidad de Chile won their ninth title following a 2–0 home win against Deportes Temuco on 3 December. Universidad Católica also qualified for the next Copa Libertadores as Liguilla winners.
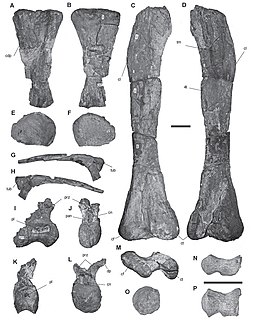
Atacamatitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaurs that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period. The holotype specimen makes Atacamatitan one of the most complete titanosaurs from Chile.
In 2018 Chile produced about 7% of its electricity from solar power. As of year end, it had 2137 MW of solar PV capacity. In July 2020 installed solar capacity had risen to 3104 MW, with another 2801 MW under construction.
The 1992 Campeonato Nacional, known as Campeonato Nacional Copa Banco del Estado 1992 for sponsorship purposes, was the 60th season of top-flight football in Chile. Cobreloa won fifth title following a 3–2 home win against Fernández Vial on 13 December. Universidad Católica also qualified for the next Copa Libertadores as Liguilla winners.
The 1993 Campeonato Nacional, known as Campeonato Nacional Copa Banco del Estado 1993 for sponsorship purposes, was the 61st season of top-flight football in Chile. Colo-Colo won its 19th title following a 3–0 home win against Unión Española on 2 January 1994. Unión Española also qualified for the next Copa Libertadores as Liguilla winners.















