Related Research Articles

A transcontinental railroad is a contiguous network of railroad trackage that crosses a continental land mass with terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single railroad, or over those owned or controlled by multiple railway companies along a continuous route. Although Europe is crisscrossed by railways, the railroads within Europe are usually not considered transcontinental, with the possible exception of the historic Orient Express. Transcontinental railroads helped open up unpopulated interior regions of continents to exploration and settlement that would not otherwise have been feasible. In many cases they also formed the backbones of cross-country passenger and freight transportation networks.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Soo Line Railroad is the primary United States railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway, one of seven U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CP subsidiaries, the Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railroad and Wisconsin Central Railroad. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, the CP's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway, and most equipment has been repainted into the CP's scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all CP's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are located in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

The Southern Railway is a name of a class 1 railroad that was based in the Southern United States. The railroad is the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.
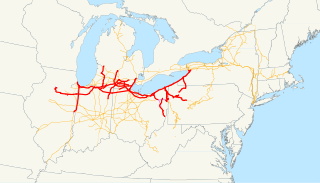
The Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway, established in 1833 and sometimes referred to as the Lake Shore, was a major part of the New York Central Railroad's Water Level Route from Buffalo, New York, to Chicago, Illinois, primarily along the south shore of Lake Erie and across northern Indiana. The line's trackage is still used as a major rail transportation corridor and hosts Amtrak passenger trains, with the ownership in 1998 split at Cleveland between CSX to the east, and Norfolk Southern in the west.

The Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Potomac Railroad was a railroad connecting Richmond, Virginia, to Washington, D.C. The track is now the RF&P Subdivision of the CSX Transportation system; the original corporation is no longer a railroad company.
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.

The Louisville and Nashville Railroad, commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.
Railway companies can interact with and control others in many ways. These relationships can be complicated by bankruptcies.

The Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad, commonly called the Pan Handle Route, was a railroad that was part of the Pennsylvania Railroad system. Its common name came from its main line, which began at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, crossed the Northern Panhandle of West Virginia, and continued west to Bradford, Ohio, where it split into a northern line to Chicago and a southern one through Indianapolis, Indiana, to East St. Louis, Illinois.

The Norfolk Southern Railway was the final name of a railroad that ran from Norfolk, Virginia, southwest and west to Charlotte, North Carolina. It was acquired by the Southern Railway in 1974, which merged with the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1982 to form the current Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Oregon Short Line Railroad was a railroad in the U.S. states of Wyoming, Idaho, Utah, Montana and Oregon. The line was organized as the Oregon Short Line Railway in 1881 as a subsidiary of the Union Pacific Railway. The Union Pacific intended the line to be the shortest route from Wyoming to Oregon. In 1889 the line merged with the Utah & Northern Railway and a handful of smaller railroads to become the Oregon Short Line and Utah Northern Railway. Following the bankruptcy of Union Pacific, the line was taken into receivership and reorganized as the Oregon Short Line Railroad.
The Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad was a Class I railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway in the Midwest United States. Commonly known since its opening in 1884 as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was merged with several other major CP subsidiaries on January 1, 1961, to form the Soo Line Railroad. As time passes, more and more Soo Line equipment is being repainted into the Canadian Pacific's current paint scheme, slowly erasing the Soo's identity as a subsidiary railroad.
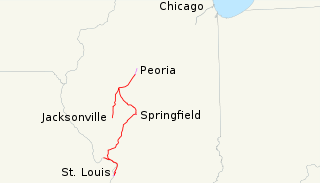
The Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad (CP&StL) was a railroad in the U.S. state of Illinois that operated a main line between Pekin and Madison via Springfield. Its property was sold at foreclosure to several new companies in the 1920s; the portion north of Springfield has since become the Illinois and Midland Railroad, while the remainder has been abandoned, except for a portion near St. Louis that is now owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.
The Carolina & Northwestern Railway (Ca&NW) was a railroad that served South Carolina and North Carolina from 1897 until January 1, 1974. The original line was operated by the Ca&NW as a separate railroad controlled by the Southern Railway until 1974 when the name was changed to the Norfolk Southern Railway. On June 1, 1982, Southern Railway and Norfolk and Western Railroad merged to form Norfolk Southern Railway. Choosing to use the name 'Norfolk Southern Railway' for the merger, in 1981, the original Ca&NW line along with original Norfolk Southern Railway was renamed Carolina and Northwestern once again. In the early 1950s several shortline subsidiaries of the Southern Railway were leased to the Ca&NW for operation, with these lines remaining a part of the Ca&NW into the 1980s.

The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio.
The Houston and Texas Central Railway (H&TC), operated by the Houston and Texas Central Railway Company, was a railway system in Texas.
References
- Lewis, Edward A. (1996). American Shortline Railway Guide. pp. 34–35. ISBN 0-89024-290-9.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
| This United States rail–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article about transportation in the U.S. state of Georgia is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |