
The Armed Forces of Armenia, sometimes referred to as the Armenian Army, is the national military of Armenia. It consists of personnel branches under the General Staff of the Armenian Armed Forces, which can be divided into two general branches: the Ground Forces, and the Air Force. Although it was partially formed out of the former Soviet Army forces stationed in the Armenian SSR, the military of Armenia can be traced back to the founding of the First Republic of Armenia in 1918. Being landlocked, Armenia does not have a navy.

The Malaysian Armed Forces, are the armed forces of Malaysia, consists of three branches; the Malaysian Army, Royal Malaysian Navy and the Royal Malaysian Air Force. The number of MAF active personnel is 113,000 along with the reserve forces at 51,600. The Supreme Commander of the Malaysian Armed Forces is the Yang di-Pertuan Agong; the King of Malaysia.

The Papua New Guinea Defence Force (PNGDF) is the military organisation responsible for the defence of Papua New Guinea. It originated from the Australian Army land forces of the territory of Papua New Guinea before independence, coming into being in January 1973 and having its antecedents in the Pacific Islands Regiment. The PNGDF is a small force, numbering around 3,600 personnel, and consists of a Land Element, an Air Element and a Maritime Element. It is a joint force tasked with defending Papua New Guinea and its territories against external attack, as well as having secondary functions including national-building and internal security tasks.

Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in the Melanesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. This page is about the history of the nation state rather than the broader geographical area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which covers both Solomon Islands and Bougainville Island, a province of Papua New Guinea. For the history of the archipelago not covered here refer to the former administration of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, the North Solomon Islands and the History of Bougainville.

His Majesty's Armed Forces (HMAF) is the military of Tonga. It is composed of three operational components and two support elements.

The Australian Defence Force (ADF) is the military organisation responsible for the defence of the Commonwealth of Australia and its national interests. It has three branches: the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), Australian Army and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The ADF has a strength of just over 89,000 personnel and is supported by the Department of Defence and several other civilian agencies.

The Timor Leste Defence Force is the military of East Timor. The F-FDTL was established in February 2001 and comprises two infantry battalions, small naval and air components and several supporting units.

The Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI), also known as Operation Helpem Fren, Operation Anode and Operation Rata, began in 2003 in response to a request for international aid by the Governor-General of Solomon Islands. Helpem Fren means "help a friend" in Solomon Islands Pidgin. The mission officially ended on 30 June 2017.
The military history of New Zealand is an aspect of the history of New Zealand that spans several hundred years. When first settled by Māori almost a millennium ago, there was much land and resources, but war began to break out as the country's carrying capacity was approached. Initially being fought with close-range weapons of wood and stone, this continued on and off until Europeans arrived, bringing with them new weapons such as muskets. Colonisation by Britain led to the New Zealand Wars in the 19th century in which settler and imperial troops and their Māori allies fought against other Māori and a handful of Pākehā. In the first half of the 20th century, New Zealanders of all races fought alongside Britain in the Boer War and both World Wars. In the second half of the century and into this century the New Zealand Defence Force has provided token assistance to the United States in several conflicts. New Zealand has also contributed troops extensively to multilateral peacekeeping operations.

1st Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment is a regular motorised infantry battalion of the Australian Army. 1 RAR was first formed as the 65th Australian Infantry Battalion of the 34th Brigade (Australia) on Balikpapan in 1945 and since then has been deployed on active service during the Korean War, the Malayan Emergency, the Vietnam War, Unified Task Force in Somalia, East Timor, Iraq War and Afghanistan. Additionally, the battalion has deployed on peacekeeping and other operations to a number of countries including Japan, Rifle Company Butterworth, Timor Leste, Solomon Islands, Tonga and the Philippines. 1 RAR remains one of the Australian Army's most readily deployed units sending individuals and detachments to domestic, regional and other enduring operations. The battalion is currently based in Coral Lines at Lavarack Barracks, Townsville, Queensland, where it forms part of the 3rd Brigade.

The Australia, New Zealand, United States Security Treaty is a 1951 non-binding collective security agreement initially formed as a trilateral agreement between Australia, New Zealand, and the United States; and from 1986 an agreement between New Zealand and Australia, and separately, Australia and the United States, to co-operate on military matters in the Pacific Ocean region, although today the treaty is taken to relate to conflicts worldwide. It provides that an armed attack on any of the three parties would be dangerous to the others, and that each should act to meet the common threat. It set up a committee of foreign ministers that can meet for consultation.

The Ministry of Home Affairs, or simply the Home Ministry, is a ministry of the Government of India. It is mainly responsible for the maintenance of internal security and domestic policy. It is headed by Minister of Home Affairs.

The Mutual Defense Treaty between the Republic of the Philippines and the United States of America (MDT) was signed on August 30, 1951 by their representatives in Washington, D.C. The treaty has eight articles and requires both nations to support each other if another party attacks the Philippines or the United States.

According to the U.S. State Department, relations between New Zealand and the United States as of August 2011 are "the best they have been in decades." New Zealand is a major non-NATO ally of the United States.
The Philippines–Australia Status of Visiting Forces Agreement (SOVFA) is a bilateral visiting forces agreement between the governments of the Republic of the Philippines and the Commonwealth of Australia concerning the status of armed forces from each state while in the territory of the other. A visiting forces agreement is a version of a status of forces agreement that only applies to troops temporarily in a country.

The Royal Solomon Islands Police Force (RSIPF) is the national police force of Solomon Islands and in January 2015 had an establishment of approximately 1,153 officers and 43 police stations across the country.
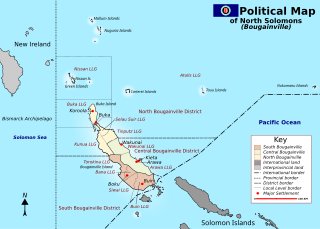
The Bougainville conflict, also known as the Bougainville Civil War, was a multi-layered armed conflict fought from 1988 to 1998 in the North Solomons Province of Papua New Guinea (PNG) between PNG and the secessionist forces of the Bougainville Revolutionary Army (BRA), and between the BRA and other armed groups on Bougainville. The conflict was described by Bougainvillean President John Momis as the largest conflict in Oceania since the end of World War II in 1945, with an estimated 15,000–20,000 Bougainvilleans dead, although lower estimates place the toll at around 1,000–2,000.

Foreign relations exist between Australia and Solomon Islands. Australia has a High Commission in Honiara and Solomon Islands has a High Commission in Canberra. The two countries are members of the Pacific Islands Forum.
The 2021 Solomon Islands unrest was a series of demonstrations and violent riots in Solomon Islands from 24 to 27 November 2021.
















