
The term "United States", when used in the geographical sense, is the contiguous United States, the state of Alaska, the island state of Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, and American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, United Kingdom, Dominican Republic, and the Bahamas in addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.

The Nearctic is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface.
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by WWF, the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". So, for example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The geography of North Carolina falls naturally into three divisions — the Appalachian Mountains in the west, the central Piedmont Plateau, and the eastern Atlantic Coastal Plain. North Carolina covers 53,821 square miles (139,396 km2) and is 503 miles (810 km) long by 150 miles (241 km) wide. The physical characteristics of the state can be pictured as a surface spread out upon a vast declivity, sloping down from the summits of the Smoky Mountains, an altitude of near seven thousand feet (2,130 m), to the ocean level.
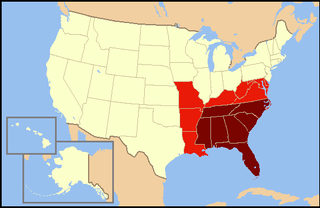
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is, broadly, the eastern portion of the Southern United States and the southern portion of the Eastern United States. It comprises at least a core of states on the lower East Coast of the United States and eastern Gulf Coast. Expansively, it includes everything south of the Mason–Dixon line, the Ohio River and the 36°30' parallel, and as far west as Arkansas and Louisiana. There is no official U.S. government definition of the region, though various agencies and departments use different definitions.

The Atlantic coastal plain is a physiographic region of low relief along the East Coast of the United States. It extends 2,200 miles (3,500 km) from the New York Bight southward to a Georgia/Florida section of the Eastern Continental Divide, which demarcates the plain from the ACF River Basin in the Gulf Coastal Plain to the west. The province is bordered on the west by the Atlantic Seaboard fall line and the Piedmont plateau, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Floridian province. The Outer Lands archipelagic region forms the insular northeasternmost extension of the Atlantic coastal plain.

The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.

The Sandhills or Carolina Sandhills is a 10-35 mi wide physiographic region within the U.S. Atlantic Coastal Plain province, along the updip (inland) margin of this province in the States of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. The extent of the Carolina Sandhills is shown clearly in maps of the ecoregions of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.

Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Frank Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions. Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the borders of the cultural region.

De Soto National Forest, named for 16th-century Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto, is 518,587 acres of pine forests in southern Mississippi. It is one of the most important protected areas for the biological diversity of the Gulf Coast ecoregion of North America.
Northern copperhead may refer to:

North American Atlantic Region is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom identified by Armen Takhtajan and Robert F. Thorne, spanning from the Atlantic and Gulf coasts to the Great Plains and comprising a major part of the United States and southeastern portions of Canada. It is bordered by the Circumboreal floristic region in the north, by the Rocky Mountain and Madrean floristic regions in the west and by the Caribbean floristic region of the Neotropical Kingdom in the south of Florida. The flora of the region comprises two endemic monotypic families, Hydrastidaceae and Leitneriaceae, and is characterized by about a hundred of endemic genera. The degree of species endemism is very high, many species are Tertiary relicts, which survived the Wisconsin glaciation and are now concentrated in the Appalachians and the Ozarks. A number of genera are shared only with the Canadian floristic province of the Circumboreal region. Moreover, as has long been noted, a large number of relict genera are shared with the relatively distant Eastern Asiatic Region and sometimes Southeast Asia. R. F. Thorne counted at least 74 genera restricted to eastern North America and Asia. The fossil record indicates that during the Tertiary period a warm temperate zone extended across much of the Northern Hemisphere, linking America to Asia.

The Southeastern mixed forests are an ecoregion of the temperate broadleaf and mixed forest biome, in the lower portion of the Eastern United States.

The Southeastern conifer forests are a temperate coniferous forest ecoregion of the southeastern United States. It is the largest conifer forest ecoregion east of the Mississippi River.
The Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain Province is a coastal plain floristic province within the North American Atlantic Region, a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom. It lies to the east and south of the Appalachian Province, from southern Nova Scotia to eastern Texas. It encompasses the Atlantic coastal plain minus central and southern Florida, and the Gulf coastal plain as far west as eastern Texas. Additionally, at the Mississippi Embayment the province stretches up to the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi rivers in Cairo, Illinois.
The Temperate Northern Atlantic is a biogeographic region of the Earth's seas, comprising the temperate and subtropical waters of the North Atlantic Ocean and connecting seas, including the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, and northern Gulf of Mexico.











