Absolute magnitude is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object, on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly 10 parsecs, without extinction of its light due to absorption by interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared among each other on a magnitude scale.
The decibel is a relative unit of measurement corresponding to one tenth of a bel (B). It is used to express the ratio of one value of a power or root-power quantity to another, on a logarithmic scale. A logarithmic quantity in decibels is called a level. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 or root-power ratio of 101⁄20.

An integer is colloquially defined as a number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5+1/2, and √2 are not.

In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus, and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others.

In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a given number x is the exponent to which another fixed number, the base b, must be raised, to produce that number x. In the simplest case, the logarithm counts the number of occurrences of the same factor in repeated multiplication; e.g., since 1000 = 10 × 10 × 10 = 103, the "logarithm base 10" of 1000 is 3, or log10(1000) = 3. The logarithm of x to baseb is denoted as logb(x), or without parentheses, logb x, or even without the explicit base, log x, when no confusion is possible, or when the base does not matter such as in big O notation.
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Although MD5 was initially designed to be used as a cryptographic hash function, it has been found to suffer from extensive vulnerabilities. It can still be used as a checksum to verify data integrity, but only against unintentional corruption. It remains suitable for other non-cryptographic purposes, for example for determining the partition for a particular key in a partitioned database.
May 18 is the 138th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 227 days remain until the end of the year.
May 17 is the 137th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 228 days remain until the end of the year.
May 19 is the 139th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 226 days remain until the end of the year.
May 22 is the 142nd day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 223 days remain until the end of the year.
May 20 is the 140th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 225 days remain until the end of the year.
May 21 is the 141st day of the year in the Gregorian calendar; 224 days remain until the end of the year.

In mathematics, the Taylor series of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor's series are named after Brook Taylor who introduced them in 1715.

The Juris Doctor degree, also known as Doctor of Law or Doctor of Jurisprudence, is a graduate-entry professional degree in law and one of several Doctor of Law degrees. In Australia, Canada, the United States, and some other common law countries, the Juris Doctor is earned by completing law school.
The Sicilian Defence is a chess opening that begins with the following moves:
SHA-2 is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher.

A fraction represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight-fifths, three-quarters. A common, vulgar, or simple fraction consists of a numerator displayed above a line, and a non-zero denominator, displayed below that line. Numerators and denominators are also used in fractions that are not common, including compound fractions, complex fractions, and mixed numerals.
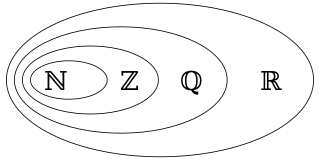
In mathematics, a rational number is a number such as −3/7 that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. Every integer is a rational number: for example, 5 = 5/1. The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by a boldface Q ; it was thus denoted in 1895 by Giuseppe Peano after quoziente, Italian for "quotient".
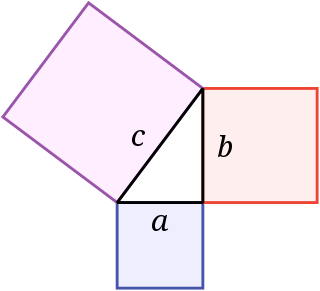
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem, or Pythagoras's theorem, is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides a, b and c, often called the Pythagorean equation: