
Babylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia. It emerged as an Akkadian populated but Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BC. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom centered around the city of Babylon.

Samsu-iluna was the seventh king of the founding Amorite dynasty of Babylon. His reign is estimated from 1749 BC to 1712 BC, or from 1686 to 1648 BC. He was the son and successor of Hammurabi by an unknown mother. His reign was marked by the violent uprisings of areas conquered by his father and the abandonment of several important cities.
Adad-nīrārī II reigned from 911 BCE to 891 BCE. He was the first King of Assyria in the Neo-Assyrian empire. He instigated the first renewed period of major expansion following that of the Middle Assyrian Empire which had begun in 1365 BCE under Ashur-uballit I and ended after the death of Ashur-bel-kala in 1053 BCE.

The history of the Jews in Iraq is documented from the time of the Babylonian captivity c. 586 BCE. Iraqi Jews constitute one of the world's oldest and most historically significant Jewish communities.
Pumbedita was an ancient city located near the modern-day city of Fallujah, Iraq. It is known for having hosted the Pumbedita Academy.

The Talmudic academies in Babylonia, also known as the Geonic academies, were the center for Jewish scholarship and the development of Halakha from roughly 589 to 1038 CE in what is called "Babylonia" in Jewish sources, at the time otherwise known as Asōristān or Iraq. It is neither geopolitically, nor geographically identical with the ancient empires of Babylonia, since the Jewish focus of interest has to do with the Jewish religious academies, which were mainly situated in an area between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates and primarily between Pumbedita, and Sura, a town farther south down the Euphrates.
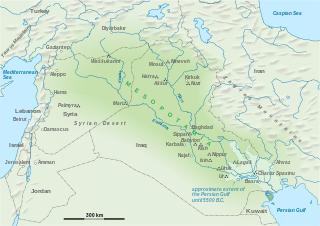
The history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.
Karna is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic Mahābhārata. Alternative transliterations include Karnaa, Karnan and Karn.
Adda bar Ahavah or Adda bar Ahabah is the name of two Jewish rabbis and Talmudic scholars, known as Amoraim, who lived in Lower Mesopotamia, a region known in Jewish texts as "Babylonia".
Talmudic Academy may refer to:

Asoristan or Beth Aramaye was the name of the Sasanian province of Babylonia from 226 to 637.

Incantation bowls are a form of protective magic found in what is now Iraq and Iran. Produced in the Middle East during late antiquity from the sixth to eighth centuries, particularly in Upper Mesopotamia and Syria, the bowls were usually inscribed in a spiral, beginning from the rim and moving toward the center. Most are inscribed in Jewish Babylonian Aramaic.

The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, ancient Persia, Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology, and ancient history.
The Battle of Ctesiphon took place in 263 between the Sassanid Empire and Palmyrene army under the Palmyrene king Odaenathus. Following the Sasanians' defeat and loss of Syria and Cappadocia to the Roman Empire at the hands of Odaenathus and Balista; The Palmyrene monarch invaded Mesopotamia and stood at the walls of Ctesiphon and devastated the region around it, however he could not conquer it. The logistical problems of fighting in enemy territory forced the Palmyrenes to leave the siege carrying with them numerous prisoners and booty. The prisoners were sent to Rome, enabling the Roman emperor Gallienus to hold a triumph.

The Middle Babylonian period, also known as the Kassite period, in southern Mesopotamia is dated from c. 1595 – c. 1155 BC and began after the Hittites sacked the city of Babylon. The Kassites, whose dynasty is synonymous with the period, eventually assumed political control over the region and consolidated their power by subjugating the Sealand dynasty c. 1475 BC. After the subjugation of the Sealand dynasty, the Kassites unified the region of Babylonia into a single political entity. At the height of the Middle Babylonian period, the Kassite kings were engaging in commerce, trade, and organising diplomatic marriages with the kings of Egypt and other regional powers. However, after a period of gradual decline, the Middle Babylonian period collapsed with the fall of the Kassite dynasty c. 1155 BC. The collapse came as a result of an Assyrian invasion, that temporarily displaced the Kassites from their rule over southern Mesopotamia. Finally, the Elamites conducted various raids and eventually invaded Babylonian c. 1158 BC, which brought the Kassite dynasty and Middle Babylonian period to an end.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








