See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Banaba. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Banaba is an island in the Pacific Ocean.
Banaba may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Banaba. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Kiribati consists of 32 atolls and one island scattered over all four hemispheres in an expanse of ocean equivalent in size to the continental United States. The islands lie roughly halfway between Hawaii and Australia in the Micronesian and Polynesian regions of the South Pacific. The three main island groupings are the Gilbert Islands, Phoenix Islands, and Line Islands. On 1 January 1995 Kiribati moved the International Date Line to include its easternmost islands and make it the same day throughout the country.

The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Situated in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of about 7,641 islands that are broadly categorized under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City, both within the single urban area of Metro Manila. Bounded by the South China Sea on the west, the Philippine Sea on the east and the Celebes Sea on the southwest, the Philippines shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia and Brunei to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest.

Southeast Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the regions that are geographically south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent and north-west of Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. The region is the only part of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere, although the majority of it is in the Northern Hemisphere. In contemporary definition, Southeast Asia consists of two geographic regions:

Metropolitan Manila, officially the National Capital Region (NCR), is the seat of government and one of three defined metropolitan areas in the Philippines. It is composed of 16 cities: the city of Manila, Quezon City, Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, San Juan, Taguig, and Valenzuela, as well as the municipality of Pateros. The region encompasses an area of 619.57 square kilometers (239.22 sq mi) and a population of 12,877,253 as of 2015. It is the second most populous and the most densely populated region of the Philippines. It is also the 9th most populous metropolitan area in Asia and the 5th most populous urban area in the world.

Manila, officially the City of Manila, is the capital of the Philippines and a highly urbanized city. It is the most densely populated city proper in the world as of 2019. It was the first chartered city by virtue of the Philippine Commission Act 183 on July 31, 1901 and gained autonomy with the passage of Republic Act No. 409 or the "Revised Charter of the City of Manila" on June 18, 1949. Manila, alongside Mexico City and Madrid are considered the world's original set of Global Cities due to Manila's commercial networks being the first to traverse the Pacific Ocean, thus connecting Asia with the Spanish Americas, marking the first time in world history when an uninterrupted chain of trade routes circled the planet. Manila is also the second most natural disaster-afflicted capital city in the world next to Tokyo, yet it is simultaneously among the most populous and fastest growing cities in Southeast Asia.

Quezon City is a highly urbanized city and the most populous city in the Philippines. It was founded by and named after Manuel L. Quezon, the 2nd President of the Philippines, to replace Manila as the national capital. The city was proclaimed as such in 1948, though a significant number of government buildings remained in Manila. Quezon City held status as the official capital until 1976 when a presidential decree was issued to reinstate and designate Manila as the capital and Metro Manila as the seat of government.
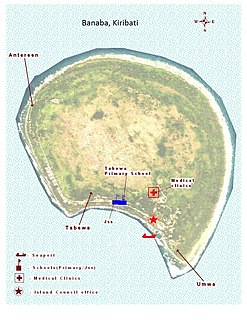
Banaba, an island of Kiribati in the Pacific Ocean, and as a solitary raised coral island west of the Gilbert Island chain, it is the Westernmost of Kiribati, that is 185 miles (298 km) east of Nauru. It has an area of 6.0 km2, and the highest point on the island is also the highest point in Kiribati, at 81 metres (266 ft) high. Along with Nauru and Makatea, it is one of the important elevated phosphate-rich islands of the Pacific.

Batangas City, officially the City of Batangas, is a 1st class city in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 329,874 people.
Filipino Canadians are Canadians of Filipino descent. Filipino Canadians are the third largest subgroup of the overseas Filipinos and one of the fastest growing groups in Canada.

San Mateo, officially the Municipality of San Mateo, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Rizal, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 252,527.

Famy, officially the Municipality of Famy, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Laguna, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 16,587 people.

Datu Abdullah Sangki, officially the Municipality of Datu Abdullah Sangki, is a — municipality in the province of Maguindanao, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 23,878 people.

Bamban, officially the Municipality of Bamban, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Tarlac, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 69,466 people.

Tarlac City, officially the City of Tarlac, is a 1st class city and capital of the province of Tarlac, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 342,493 people.

Lagerstroemia speciosa is a species of Lagerstroemia native to tropical southern Asia.
Cotenna or Kotenna was a city in the Roman province of Pamphylia I in Asia Minor. It corresponds to modern Gödene, near Konya, Turkey.

General Antonio Luna Avenue, also known as simply General Luna Avenue, is one of the major thoroughfares of San Mateo, Rizal in the Philippines. It was named after General Antonio Luna who fought in the Philippine-American War.

Paoay Lake is a lake within the municipality of Paoay, in northwestern Luzon, Philippines. It is the largest lake in the province of Ilocos Norte and one of the largest natural lakes in the area.
The Philippine highway network refers to the highway system of the Philippines. It is a network of national roads owned and maintained by the Department of Public Works and Highways which are organized into three classifications depending on their function or purpose they serve within the road network: national primary, national secondary, and national tertiary roads. The national roads connecting major cities are numbered N1–N82. They are mostly single and dual carriageways linking two or more cities.