See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Bandpass. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Bandpass or band-pass may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Bandpass. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
French may refer to:
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. Most radio systems in the 20th century used frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM) for radio broadcast.

A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.
Web usually refers to:
A duplexer is an electronic device that allows bi-directional (duplex) communication over a single path. In radar and radio communications systems, it isolates the receiver from the transmitter while permitting them to share a common antenna. Most radio repeater systems include a duplexer. Duplexers can be based on frequency, polarization, or timing.

An interference filter or dichroic filter is an optical filter that reflects one or more spectral bands or lines and transmits others, while maintaining a nearly zero coefficient of absorption for all wavelengths of interest. An interference filter may be high-pass, low-pass, bandpass, or band-rejection.
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all the radio waves picked up by its antenna. The passband of a receiver is the range of frequencies it can receive.

A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level. Depending on application, the required attenuation within the stopband may typically be a value between 20 and 120 dB higher than the nominal passband attenuation, which often is 0 dB.

A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
In general, a model is a representation of a person or a system which provides some information about it.

In signal processing, undersampling or bandpass sampling is a technique where one samples a bandpass-filtered signal at a sample rate below its Nyquist rate, but is still able to reconstruct the signal.
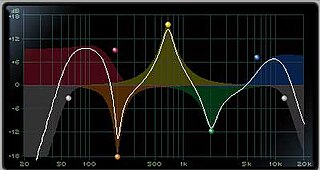
An audio filter is a frequency dependent amplifier circuit, working in the audio frequency range, 0 Hz to beyond 20 kHz. Audio filters can amplify (boost), pass or attenuate (cut) some frequency ranges. Many types of filters exist for different audio applications including hi-fi stereo systems, musical synthesizers, sound effects, sound reinforcement systems, instrument amplifiers and virtual reality systems.

An active filter is a type of analog circuit implementing an electronic filter using active components, typically an amplifier. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the cost, performance and predictability of a filter.
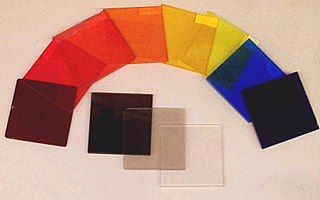
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter.
A revolver is a type of firearm.
The Vilnius photometric system is a medium-band seven-colour photometric system (UPXYZVS), created in 1963 by Vytautas Straižys and his coworkers. This system was highly optimized for classification of stars from ground-based observations. The system was chosen to be medium-band, to ensure the possibility to measure faint stars.

Electronic filter topology defines electronic filter circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected.
Android may refer to:
European, or Europeans, may refer to:
Subway, Subways, The Subway, or The Subways may refer to: