Related Research Articles
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans more than 198 million base pairs and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 190 million base pairs and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 5 spans about 182 million base pairs and represents almost 6% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 5 is the 5th largest human chromosome, yet has one of the lowest gene densities. This is partially explained by numerous gene-poor regions that display a remarkable degree of non-coding and syntenic conservation with non-mammalian vertebrates, suggesting they are functionally constrained.

Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (ankyra) for "anchor".

The ankyrin repeat is a 33-residue motif in proteins consisting of two alpha helices separated by loops, first discovered in signaling proteins in yeast Cdc10 and Drosophila Notch. Domains consisting of ankyrin tandem repeats mediate protein–protein interactions and are among the most common structural motifs in known proteins. They appear in bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic proteins, but are far more common in eukaryotes. Ankyrin repeat proteins, though absent in most viruses, are common among poxviruses. Most proteins that contain the motif have four to six repeats, although its namesake ankyrin contains 24, and the largest known number of repeats is 34, predicted in a protein expressed by Giardia lamblia.

SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK1 gene.

Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1, or Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANKRD1 gene also known as CARP. CARP is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and is a transcription factor involved in development and under conditions of stress. CARP has been implicated in several diseases, including dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and several skeletal muscle myopathies.
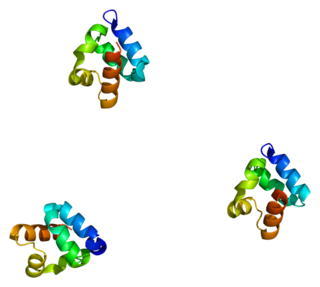
SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains 3 (Shank3), also known as proline-rich synapse-associated protein 2 (ProSAP2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK3 gene on chromosome 22. Additional isoforms have been described for this gene but they have not yet been experimentally verified.

KN motif and ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KANK1 gene.

Kinase D-interacting substrate of 220 kDa or ARMS is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the KIDINS220 gene.

Ankyrin 1, also known as ANK-1, and erythrocyte ankyrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANK1 gene.

Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 26 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANKRD26 gene. This protein has a function that is not currently understood.

Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASB13 gene.

Caseinolytic peptidase B protein homolog (CLPB), also known as Skd3, is a mitochondrial AAA ATPase chaperone that in humans is encoded by the gene CLPB, which encodes an adenosine triphosphate-(ATP) dependent chaperone. Skd3 is localized in mitochondria and widely expressed in human tissues. High expression in adult brain and low expression in granulocyte is found. It is a potent protein disaggregase that chaperones the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Mutations in the CLPB gene could cause autosomal recessive metabolic disorder with intellectual disability/developmental delay, congenital neutropenia, progressive brain atrophy, movement disorder, cataracts, and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria. Recently, heterozygous, dominant negative mutations in CLPB have been identified as a cause of severe congenital neutropenia (SCN).

Ankyrin repeat, SAM and basic leucine zipper domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASZ1 gene.

Ankyrin-2, also known as Ankyrin-B, and Brain ankyrin, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ANK2 gene. Ankyrin-2 is ubiquitously expressed, but shows high expression in cardiac muscle. Ankyrin-2 plays an essential role in the localization and membrane stabilization of ion transporters and ion channels in cardiomyocytes, as well as in costamere structures. Mutations in ANK2 cause a dominantly-inherited, cardiac arrhythmia syndrome known as long QT syndrome 4 as well as sick sinus syndrome; mutations have also been associated to a lesser degree with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Alterations in ankyrin-2 expression levels are observed in human heart failure.

Ankyrin-3 (ANK-3), also known as ankyrin-G, is a protein from ankyrin family that in humans is encoded by the ANK3 gene.

POTE ankyrin domain family, member B is a protein in humans that is encoded by the POTEB gene.(Prostate, Ovary, Testes Expressed ankyrin domain family member B).It is most likely involved in mediating protein-protein interaction via its 5 ankyrin domains. POTEB is most probably aids in intracellular signaling, but is not likely to be a secreted or nuclear protein. POTEB's function is likely to be regulated via 17 potential phosphorylation sites. There is currently no evidence to suggest that POTEB has nuclear localization signals.

Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 24 is a protein in humans that is coded for by the ANKRD24 gene. The gene is also known as KIAA1981. The protein's function in humans is currently unknown. ANKRD24 is in the protein family that contains ankyrin-repeat domains.

Ankycorbin is an ankyrin repeat and coiled-coil domain containing protein that in humans is encoded by the RAI14 gene. It is expressed in a variety of human tissues and is thought to play a role in actin regulation of ectoplasmic specialization, establishment of sperm polarity and sperm adhesion. It may also promote the integrity of Sertoli cell tight junctions at the blood testis barrier.
References
- ↑ "BANK1 B-cell scaffold protein with ankyrin repeats 1 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NIH. 15 January 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2014.