
Antigua and Barbuda is a sovereign archipelagic country in the Caribbean. It lies at the conjuncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles.

The politics of Antigua and Barbuda takes place in a framework of a unitary parliamentary representative democratic monarchy, wherein the sovereign of Antigua and Barbuda is the head of state, appointing a governor-general to act as vice-regal representative in the nation. A prime minister is appointed by the governor-general as the head of government, and of a multi-party system; the prime minister advises the governor-general on the appointment of a Council of Ministers. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of the Parliament. The bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate and the House of Representatives.

The history of Antigua and Barbuda covers the period from the arrival of the Archaic peoples thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands encompassing present-day Antigua and Barbuda were inhabited by three successive Amerindian societies. The island was claimed by England, who settled the islands in 1632. Under English/British control, the islands witnessed an influx of both Britons and African slaves migrate to the island. In 1981, the islands were granted independence as the modern state of Antigua and Barbuda.

Sir Vere Cornwall Bird, KNH was the first Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda. His son, Lester Bryant Bird, succeeded him as prime minister. In 1994, he was declared a "National Hero".

The Antigua and Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) is a political party in Antigua and Barbuda. The current leader of the party is Gaston Browne, who serves as the Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda. The party had previously been led by Lester Bird, who was chairman of the party since 1971, and was Prime Minister and political leader in 1994.

The prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda is the head of government of the Antigua and Barbuda. The prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda is appointed by the Governor-General under the terms of the Constitution.
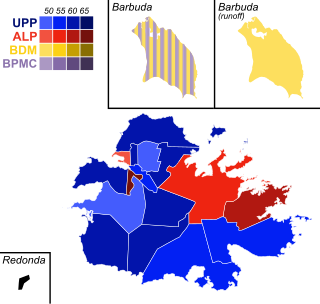
General elections were held in Antigua and Barbuda on 23 March 2004. The result was a victory for the opposition United Progressive Party (UPP), which defeated the incumbent Antigua Labour Party. Baldwin Spencer, leader of the UPP, replaced Lester Bird as Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda, with Bird being one of eight Labour MPs to lose his seat. Spencer became only the second Prime Minister from outside the Bird family or the Labour Party.

The Barbuda People's Movement is a left-wing Barbudan nationalist political party in Antigua and Barbuda active only on the island of Barbuda. The party's symbol is the European fallow deer, national animal of Barbuda. The party seeks the secession of Barbuda from Antigua and Barbuda. The party is allied with the United Progressive Party.
Progressive Labor Party or Progressive Labour Party may refer to:

The Barbuda People's Movement for Change was a political party in Barbuda, part of Antigua and Barbuda.

The Barbuda Independence Movement was a political party in Antigua and Barbuda. The party was formed in 1988 by Arthur Nibbs. It participated in the 1989 general elections, but received only 71 votes and failed to win a seat. It did not contest another election.
Sir Thomas Hilbourne Frank was a politician from Antigua and Barbuda. He was a political leader of the Barbuda People's Movement, which favours greater independence of Barbuda from Antigua and supports the United Progressive Party.
Arthur Nibbs is a politician from Antigua and Barbuda. He represented the Antigua Labour Party in both chambers of Parliament at various times. Born in Barbuda, he was educated at the Holy Trinity School and the Antigua Grammar School.
National Reform or National Reformation may refer to:

General elections were held in Antigua and Barbuda on 17 April 1984, the first after the country had become an independent Commonwealth realm in 1981.
Sir Robert Hall (1909–1994) was a politician of Antigua and Barbuda. Hall was an opponent of the dominant Antigua Labour Party throughout his career. He was politically active mainly during Antigua and Barbuda's time as a West Indies Associated State.

Antigua, officially the Associated State of Antigua, was an associated state of the United Kingdom, which was established on 27 February 1967. The associated state was abolished on November 1, 1981, by the Antigua Order.

Federalism in Antigua and Barbuda refers to political theories that the central government of Antigua and Barbuda should share a certain degree of sovereignty with its parishes and dependencies under a form of federalism. These proposals were first made during the era of the Associated State of Antigua, prior to independence. However, due to disputes during the Barbuda Land crisis since 2017, members of the Barbuda People's Movement, the United Progressive Party, and other entities have proposed this in an effort to avoid Barbudan secession. In Antigua and Barbuda, the Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is usually used as an example of how an Antiguan and Barbudan federal system could work.

The Barbudan independence movement is a political movement that seeks the independence of Barbuda from Antigua. Proponents state that Barbudan independence would allow Barbudans to exercise their right to self-determination, especially after the start of the Barbuda land crisis, while opponents state that this movement would set a precedent for other small islands in the region to secede, and would deprive Antigua of critical resources.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








