
Barkas was the East German manufacturer of small delivery vans and minibuses named the B 1000. In addition to delivery vans, Barkas also made engines for Trabant cars.
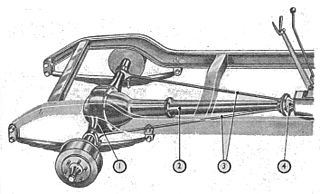
A torque tube system is a power transmission and braking technology that involves a stationary housing around the drive shaft, often used in automobiles with a front engine and rear drive. The torque tube consists of a large diameter stationary housing between the transmission and rear end that fully encloses a rotating tubular steel or small-diameter solid drive shaft that transmits the power of the engine to a regular or limited-slip differential. The purpose of a torque tube is to hold the rear end in place during acceleration and braking. Otherwise, the axle housing would suffer axle wrap, such that the front of the differential would lift up excessively during acceleration and sink down during braking. Its use is not as widespread in modern automobiles as is the Hotchkiss drive, which holds the rear end in place and prevents it from flipping up or down, during acceleration and braking, by anchoring the axle housings to the leaf springs using spring perches.

The Ford Super Duty is a series of trucks manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Introduced in 1998 for the 1999 model year, the F-Series Super Duty trucks marked the addition of a heavy-duty pickup to the Ford F-Series range with the new versions of the F-250, F-350, and F-450 trucks, while the previous 1987–1997 F-Super Duty chassis cabs were replaced by the F-450 chassis cab and F-550 Super Duty.
The Austin 15-20 is the smaller-engined of the almost identical pair of new cars announced by Herbert Austin in February 1906. A very complete catalogue with detailed specifications was issued at the same time. As well as the engine's smaller bore the 15-20 differed from the 25-30 by being only available with a live rear axle and not chain-drive. Otherwise the specifications were the same, the very minor differences are detailed below.

The DKW Typ 4=8 is a small rear-wheel drive two-stroke V4 engined car produced at the company's Spandau plant by DKW. It was launched at the Berlin Motor-show in 1929 as a successor to the DKW Typ P built at the same factory, although the DKW Typ P 4=8 was significantly larger than the Typ P: in terms of market positioning a more direct successor to the DKW Type P was probably the DKW F1 produced in Zwickau from 1931.

The IFA G5 is an East German three-axle truck produced by IFA from 1952 to 1964.

Sisu KB-24 is a two-axle lorry and special vehicle chassis made by the Finnish heavy vehicle manufacturer Suomen Autoteollisuus (SAT) from 1955 to 1960. It is a six-tonne delivery lorry planned to operate on narrow streets in Finnish cities.

ZT 300 is a series of 20 kN agricultural tractors, produced from 1 September 1967 to 1984 by the VEB Traktorenwerk Schönebeck. It succeeded the RS14 Famulus series, and unlike the Famulus, the ZT 300 series was sold under the brand name Fortschritt. ZT 300 refers both to the initial ZT 300 model, and the ZT 300 series. In total, 72,382 units of the ZT 300 series were made. The model with the highest production figure was the ZT 303, which was introduced in 1972. It features an automatic all-wheel-drive system; in the early 1980s, it cost 81.000 Mark. Starting in 1983, the ZT 300 series was succeeded by the ZT 320.

The Goliath GD750 was a three-wheeler pickup truck built by the Goliath division of the Borgward Group in Bremen from April 1949 to 1955 in various body variants. In the early 1950s, low-cost vans were popular with small craft businesses. In 1949, the purchase price for flatbed variant was DM 3600. In total, 30,093 units of the GD750 were built. In 1950 and 1951, a huge quantity of vehicles were built, 8468 and 7136 units respectively. The number 750 in the type designation indicated the possible payload of 750 kg.

The Barkas B 1000 is a forward control panel van made by the East German manufacturer VEB Barkas-Werke in Chemnitz. It was made in several different body styles: as a panel van, minibus seating eight, and pickup truck. Special-purpose vehicles based on the Barkas B 1000 were made as well. In June 1961, the production of the four-door panel van commenced, with the minibus following in spring 1964, and the pickup truck in spring 1965. With its payload of 1,000 kg, and its spacious interior, the Barkas B 1000 proved to be very durable and reliable. During its 27-year production period, it received some minor updates in 1963 and 1972, but all efforts to develop a successor failed, and there were no major design alterations for the remainder of its production. The successor Barkas B 1000-1, introduced in autumn 1989, carried over the technical design, but it was fitted with a different engine. In 1990, manufacture was sold to a Russian company, but production never was restarted.

The Ikarus 55 is a high-floor coach designated for long-distance as well as interurban traffic, and the first rear-engine Ikarus bus. It was made from 1952 – 1973, alongside the technically related Ikarus 66, by the Hungarian bus maker Ikarus. In total, 8,350 Ikarus 55 and 66 were delivered to East-Germany.

The Trabant 1.1 is the fourth and final series production model of the East German Trabant series, made by VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau. Unlike its predecessors, which have a two-stroke engine, the Trabant 1.1 has a four-stroke Otto engine. In total, 39,474 units of the Trabant 1.1 were made from May 1990 to 30 April 1991, which makes it the rarest Trabant model.

The IFA Horch H3, also known as IFA H3, is a short bonnet lorry, and the first series production vehicle by East German VEB HORCH Kraftfahrzeug- und Motorenwerke Zwickau, later known as VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau. The short-lived H3 was produced from 1947 to 1949 in Zwickau ; 852 were produced. Several parts used in the H3, most notably the engine, were originally intended to be used for Sd.Kfz. 11 half tracks.

The IFA H6 is a 6.5 tonne lorry, made by East German manufacturer VEB Kraftfahrzeugwerk »Ernst Grube« Werdau. It was available in long wheelbase lorry (H6), and short wheelbase tractor (H6Z) versions. Approxiamtely 7,500 were built from 1952 to 1959. The bus IFA H6B was based upon IFA H6 components. For political reasons, there were no successors to the H6. Such had been developed, but production of the smaller IFA S 4000-1 commenced at IFA's Werdau plant instead.

The IFA Horch H3A, later known as just the IFA H3A, is a 3 tonne lorry, made by East German manufacturer VEB HORCH Kraftfahrzeug- und Motorenwerke Zwickau. It was presented as a flatbed lorry at the Leipzig Trade Fair in early 1949, and officially offered for sale from mid 1950. The H3A tractor followed in 1951. In total, 180 IFA H3A chassis were used for manufacturing the IFA H3B bus in 1952 and 1953. The IFA H3S succeeded the H3A in 1957. The first prototypes were built in 1948-1949, using cabs from some scrapped Daimler-Benz L 701 trucks.

The Csepel D-344 is a medium size, 3-tonne, 4×4 off-road lorry, made by Hungarian manufacturer Csepel Autógyár, from 1961 to 1975. It was first presented to the public on the Leipzig Trade Fair in early 1963. The Hungarian People's Army purchased huge quantities of the D-344, and eventually used it as their standard lorry. It proved to be robust and reliable.

The MAN 630 is a five-tonne lorry, made by German manufacturer Maschinenfabrik Augsburg Nürnberg, from 1953 until 1972. It was made in three major variants, the civilian L1, the military L2, and the civilian L3 with L being an abbreviation for the German word for Lorry, Lastkraftwagen. The military L2 versions were by far the most common MAN 630s. The German Bundeswehr purchased approximately 30,000 units of the L2, and used it as their standard lorry alongside the similar five-tonne Mercedes-Benz LG 315.

The Porsche-Diesel 419 is an agricultural tractor made by Porsche-Diesel Motorenbau, and part of Porsche's Master series. It was the biggest and most powerful series-production tractor ever sold under the Porsche brand. In total, 1175 units were produced from 1960 until 1963. The 419 was preceded by the 418, and had no successor, since Porsche-Diesel Motorenbau stopped producing tractors in 1963. That same year, the catalogue price for a Porsche-Diesel 419 was DM 15,290.

The Trabant P 50, also known as the Trabant 500, is the first series production model of the East German Trabant series, made by VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau. It was produced from 1957 until 1962; in total, 131,495 units were built. In 1962, VEB Sachsenring switched production from the P 50 to the short-lived intermediate model Trabant 600, which combined the exterior styling of the Trabant P 50 with the technical design of the next generation Trabant model, the Trabant 601.

The Trabant 600, also known as the Trabant P 60, is the second series production model of the East German Trabant series, made by VEB Sachsenring Automobilwerke Zwickau. It was produced from 1962 until 1965; in total, 106,117 units were built. The Trabant 600 was a short-lived intermediate model that combined the exterior styling of the Trabant P 50 with the technical design of the next generation Trabant model, the Trabant 601. For a short period of time, the Trabant 600 estate was built alongside the 601 saloon.
























