Movable type is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document usually on the medium of paper.

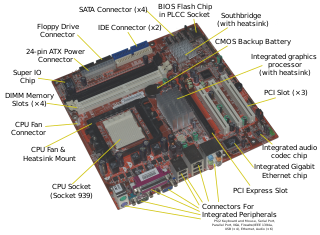
A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers were made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.

Oriented strand board (OSB), also known as flakeboard, sterling board and aspenite in British English, is a type of engineered wood similar to particle board, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood strands (flakes) in specific orientations. It was invented by Armin Elmendorf in California in 1963. OSB may have a rough and variegated surface with the individual strips of around 2.5 cm × 15 cm, lying unevenly across each other and comes in a variety of types and thicknesses.

Clogs are a type of footwear made in part or completely from wood. Clogs are used worldwide and although the form may vary by culture, within a culture the form often remained unchanged for centuries.

A hand plane is a tool for shaping wood using muscle power to force the cutting blade over the wood surface. Some rotary power planers are motorized power tools used for the same types of larger tasks, but are unsuitable for fine scale planing where a miniature hand plane is used.

Panelling is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.

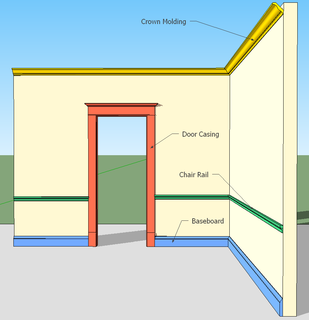
Moulding, also known as coving (United Kingdom, Australia), is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the molding is often carved in marble or other stones.
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO image, simulate an installer DVD, and perform the installation remotely.
A computer-on-module (COM) is a type of single-board computer (SBC), a subtype of an embedded computer system. An extension of the concept of system on chip (SoC) and system in package (SiP), CoM lies between a full-up computer and a microcontroller in nature. It is very similar to a system on module (SOM).
COM Express(R), a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a highly integrated and compact PC that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each COM Express Module COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics (PEG), and Ethernet. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM Express employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a baseboard that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM Express mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM Express is commonly used in Industrial, Military/Aerospace, Gaming, Medical, Transportation, IoT, and General Computing embedded applications.
Host Embedded Controller Interface (HECI) is technology introduced in 2006 used for Active Management Technology (AMT) in Intel chipsets that support Core 2 Duo microprocessors.

The Clay Office and Conference Center is a renovated office complex formerly known as the Clay School. It is located at 453 Martin Luther King, Jr. Boulevard in Midtown Detroit, Michigan. It is the oldest school building in the city of Detroit. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1982.

Radiators and convectors are heat exchangers designed to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of space heating.
NC-SI is an electrical interface and protocol defined by the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF), which enables the connection of a Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) to a set of Network Interface Controller (NICs) in server computer systems for the purpose of enabling out-of-band remote manageability.

The Reisekamera, meaning a "travel camera", is a large-format wooden bellows tailboard view camera of almost standardised design, unlike the much lighter and more flexible field camera, but not as cumbersome as the studio camera. A sturdy tripod is always brought along, but it might just as well be placed on a tabletop. It has equally sized rectangular front and back panels on a full-width double-extension baseboard that is hinged near the front. The front panel, holding the lens plate, has horizontal and vertical movements, while the back is tilt-suspended on brass standards running on brass tracks on either side of the baseboard, providing rack and pinion focusing on the film plane. An almost non-tapering calico double-extension bellows is employed; allowing the projected image to freely reach the photographic plate regardless of lens offset position. The camera folds flat, after the back panel is brought forward to the lens panel, by folding the hinged base board up, and thus conveniently protecting the focusing screen. For insertion of the wooden dark slide plate cassette, the hinged focusing screen is swung up and away. The Reisekamera was made available for several plate sizes; most common are the 13×18 cm, 18×24 cm and 24×30 cm versions. Shutter and lens were normally not part of the original delivery. However, some were made available with a spectacular focal-plane shutter, recognisable by the brass mechanisms either side of the back panel.

The John and Emma Lacey Eberts House is a private house located at 109 Vinewood Avenue in Wyandotte, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2009.

Isaac Young House is an historic wood frame house on Pinesbridge Road in New Castle, New York, United States. It was built about 1872 in the Second Empire style. Its owner, Isaac Young, was a descendant of early settlers in the area. He chose the Second Empire style, more commonly found in cities and villages than on farms, possibly as a way of demonstrating his affluence. The present structure appears to incorporate parts of a vernacular late 18th-century farmhouse, leaving several anomalies in the current house as a result. The house's position atop a low hill would have, in its time, given it a commanding view of the region, including the Hudson River and New York City's skyline.

The James Litchfield House is a private house located at 3512 Central Street in Dexter, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984. The house is an excellent Michigan example of a "basilica type" Greek Revival house.

Millwork building materials are historically any woodmill-produced products for building construction. Stock profiled and patterned millwork building components fabricated by milling at a planing mill can usually be installed with minimal alteration. Today, millwork also encompasses items that are made using alternatives to wood, including synthetics, plastics, and wood-adhesive composites.