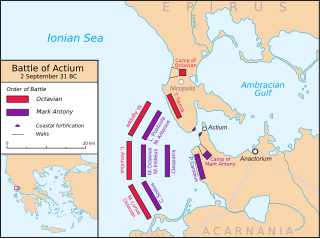
Actium or Aktion was a town on a promontory in ancient Acarnania at the entrance of the Ambraciot Gulf, off which Octavian gained his celebrated victory, the Battle of Actium, over Antony and Cleopatra, on September 2, 31 BCE.

Bayezid I, also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt, was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted the title of Sultan-i Rûm, Rûm being an old Islamic name for the culturally Hellenistic Eastern Roman Empire. He decisively defeated the Crusaders at the Battle of Nicopolis in what is now Bulgaria in 1396. Bayezid unsuccessfully besieged Constantinople. He later was defeated and captured by Timur at the Battle of Ankara in 1402 and died in captivity in March 1403, which triggered the Ottoman Interregnum.
Year 1396 (MCCCXCVI) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar.

The Battle of Alexandria, or Battle of Canope, was fought on 21 March 1801 between the army of Napoleon's French First Republic under General Jacques-François Menou and the British expeditionary corps under Sir Ralph Abercromby. The battle took place near the ruins of Nicopolis, on the narrow spit of land between the sea and Lake Abukir, along which the British troops had advanced towards Alexandria after the actions of Abukir on 8 March and Mandora on 13 March. The fighting was part of the French campaign in Egypt and Syria against the Ottoman Empire, which began in 1798.

Preveza is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula of the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is part of the region of Epirus. The Aktio-Preveza Immersed Tunnel –the first and so far only undersea tunnel in Greece– was completed in 2002. The immersed tunnel connects Preveza in the north, to Aktio of western Acarnania to the south. The ruins of the ancient city of Nicopolis lie 7 kilometres north of the city.

Nicopolis or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus Vetus. It was located in the western part of the modern state of Greece. The city was founded in 29 BC by Caesar Augustus in commemoration of his victory in 31 BC over Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium nearby. It was soon made the major city of the wider region of Epirus. Many impressive ruins of the ancient city may be visited today.

The Battle of Nicopolis took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied crusader army of Hungarian, Croatian, Bulgarian, Wallachian, French, Burgundian, German, and assorted troops at the hands of an Ottoman force, raising the siege of the Danubian fortress of Nicopolis and leading to the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire. It is often referred to as the Crusade of Nicopolis as it was one of the last large-scale Crusades of the Middle Ages, together with the Crusade of Varna in 1443–1444.

Nikopol is a town in northern Bulgaria, the administrative center of Nikopol Municipality, part of Pleven Province, on the right bank of the Danube river, 4 kilometres downstream from the Danube’s confluence with the Osam river. It spreads at the foot of steep chalk cliffs along the Danube and up a narrow valley.

Enguerrand VII de Coucy,, also known as Ingelram de Coucy and Ingelram de Couci, was a medieval French nobleman and the last Lord of Coucy. He became a son-in-law of King Edward III of England following his marriage to the king's daughter, Isabella of England, and the couple was subsequently granted several English estates, among them the title Earl of Bedford. Coucy fought in the Battle of Nicopolis in 1396 as part of a failed crusade against the Ottoman Empire, but was taken prisoner and contracted the bubonic plague. He died in captivity the following year at Bursa.

Pithiviers is a commune in the Loiret department, north central France. It is one of the subprefectures of Loiret. It is twinned with Ashby-de-la-Zouch in Leicestershire, England and Burglengenfeld in Bavaria, Germany.

The Battle of Adamclisi was a major battle in the Dacian Wars, fought in the winter of 101 to 102 between the Roman Empire and the Dacians near Adamclisi, in modern Romania.
The Battle of Karanovasa took place on 10 October 1394 between the Wallachian army led by Voivode Mircea cel Bătrân against an Ottoman invasion led by Sultan Bayezid I. This battle is sometimes confused with the later Battle of Rovine between the same combatants, and which took place also along the valley of the Argeş River.
The Ottoman–Venetian wars were a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice that started in 1396 and lasted until 1718. It included:
Nicopolis was a Roman colony in Lesser Armenia founded by Pompey in 63 BC after conquering the Kingdom of Pontus in the Third Mithridatic War. It became part of the Roman province of Armenia Prima. Today, the city of Koyulhisar in northeastern Turkey occupies the site.

The Ottoman–Hungarian Wars were a series of battles between the Ottoman Empire and the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. Following the Byzantine Civil War, the Ottoman capture of Gallipoli, and the decisive Battle of Kosovo, the Ottoman Empire was poised to conquer the entirety of the Balkans and also sought and expressed desire to expand further north into Central Europe beginning with the Hungarian lands.
Nicopolis was an ancient city and archbishopric in Epirus, now in continental Greece.

Nicopolis was the name of Emmaus under the Roman Empire until the conquest of Palestine by the Rashidun Caliphate in 639. The Church Fathers unanimously considered this city to be the Emmaus of the New Testament where Jesus was said to have appeared after his death and resurrection; it is sometimes distinguished from other Emmauses of Palestine and other Nicopolises of the Roman Empire by the combined name Emmaus Nicopolis or Emmaus-Nicopolis. The site of the ancient city now lies between Tel Aviv and Jerusalem in Israel. A Palestinian Arab village occupied the site until the Six-Day War in 1967, when it was destroyed. The archaeological site has been cared for by a resident French Catholic community since 1993 but are formally organized as a part of Canada Park under the general supervision of the Israel Nature and Parks Authority.

Robert I of Bar was Marquis of Pont-à-Mousson and Count and then Duke of Bar. He succeeded his elder brother Edward II of Bar as count in 1352. His parents were Henry IV of Bar and Yolande of Flanders.

The Battle of Nicopolis ad Istrum was fought between the Roman army of Emperor Decius and his son Herennius Etruscus, and the Gothic army of King Cniva, in 250 AD. The Romans were victorious.













