
The Moselle is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A small part of Belgium is in its basin as it includes the Sauer and the Our.
LucasDavid was a German historian, who from ca. 1550 on compiled extensive volumes on Prussian history.
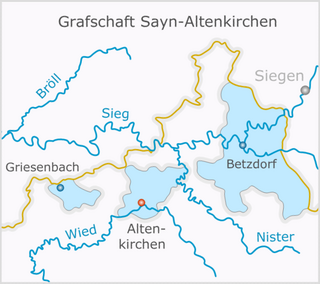
Sayn-Wittgenstein-Sayn-Altenkirchen was a German county located in what is now Rhineland-Palatinate, near the river Sieg.

The County of Sponheim was an independent territory in the Holy Roman Empire that lasted from the 11th century until the early 19th century. The name comes from the municipality of Sponheim, where the counts had their original residence.
Heinrich Marx was a German lawyer who fathered the communist philosopher Karl Marx, as well as seven other children, including Louise Juta.
Siegfried I is considered the progenitor of the Carinthian ducal House of Sponheim (Spanheimer) and all of its lateral branches, including the Counts of Lebenau and the Counts of Ortenburg. He is documented as Count of Sponheim from 1044 and served as margrave of the Hungarian March in 1045/46 and as count in the Puster Valley and the Lavant Valley from 1048 until his death.
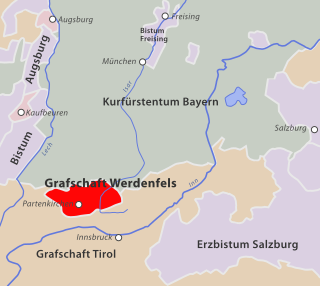
The County of Werdenfels in the present-day Werdenfelser Land in South Germany was a county that enjoyed imperial immediacy that belonged to the Bishopric of Freising from the late 13th century until the secularisation of the Bishopric in 1803.

The Landrecht was the law applying within an individual state in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and Early Modern times. The state laws that emerged in the territories of the empire from the 12th century onwards had been developed from the older tribal laws of the Saxons, Swabians, Bavarians and Bohemians. Through privileges and laws passed by the territorial princes as well as the jurisprudence of the Landgerichte or state courts, these ancient rights were supplemented and developed. Later Roman law was also accepted and incorporated into the Landrechte. The Landrecht was only applied to the burghers of a town in a secondary way, because they came primarily under municipal law and the autonomous jurisdiction of their communities.

Michael Matheus is a German historian.
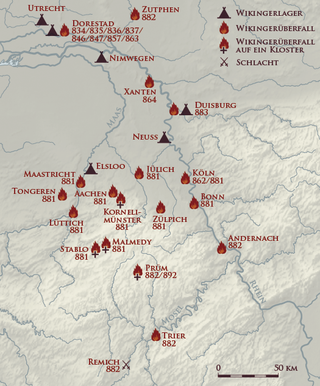
The Viking raids in the Rhineland were part of a series of invasions of Francia by the Vikings that took place during the final decades of the 9th century. From the Rhineland, which can be regarded as the nucleus of Frankish culture, the Franks had previously conquered almost the whole of Central Europe and established a great empire.

Wilderich Freiherr von Walderdorff from the Walderdorff family was Prince-Bishop of Vienna and Reichsvizekanzler (Vice-Chancellor) of the Holy Roman Empire (1660–1669).

Diefflen is a district of Dillingen/Saar in the district of Saarlouis (Saarland) and has about 4700 inhabitants. It is located on the lower Prims, a tributary of the Saar. Since its foundation in the High Middle Ages Diefflen was historically linked to the villages of the former "Hochgericht Nalbacher Tal". This association was broken when Diefflen was incorporated into the city of Dillingen/Saar in 1969.

Hornbach Abbey is a former monastery founded around 741 in the historic town of Gamundias by Saint Pirmin, which soon became a Benedictine abbey. The most important neighbouring abbeys were Bausendorf, Saint-Avold, Glandern, Villers-Bettnach, Fraulautern, Mettlach, Tholey, and the stift of St. Arnual. The neighboring spiritual centers were Trier and Metz. At present, all that remains of Hornbach Abbey are the structural remains of the convent buildings, which have been supplemented by a monastery museum, and a modern chapel with the historical tomb of the monastery's founder.
Gerhard Menk was a German historian and archivist.

Friedrich Uhlhorn was an honorary professor at the Philipps-Universität Marburg, whose scientific focus was on the history of the State of Hesse and was also known for his work outside Hesse. His special scientific interest was mainly focused on the problems of historical cartography. In collaboration with Edmund Ernst Stengel, he published the Geschichtlichen Atlas von Hessen, which is considered his major work. He also wrote the article Die deutschen Territorien. A: The West, which deals with the West German regional history. Likewise he was responsible as editor for the Hessisches Jahrbuch für Landesgeschichte by Bruno Gebhardt.

Georg Hüsing was an Austrian historian and philologist who specialized in Germanic studies and mythography.
Rudolf Kötzschke was a German historian who founded the Seminar for Regional History and Settlement Studies in Leipzig, the first regional history institution at a German university.
Heinz Heinen was a German-Belgian historian of classical antiquity. He was a professor of ancient history at the University of Trier from 1971 to 2006. Heinen's main research areas were Hellenistic Egypt and Roman Egypt, Augusta Treverorum in the Roman era, Crimea in the Roman era and the wider northern Black Sea region, Soviet and Russian historiography and views of antiquity, and slavery in antiquity.

Peter Moraw was a German historian.

The Kärlich palace is a former electoral hunting lodge in Kärlich near Koblenz, Germany. It was situated on the northern side of the village. It served as a summer retreat and hunting lodge for the Prince-Electors and Archbishops of Trier.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













