See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Battle of Rio de Janeiro. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
The Battle of Rio de Janeiro was a naval battle between France and Portugal that took place in September 1711 during the War of Spanish Succession.
Battle of Rio de Janeiro may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Battle of Rio de Janeiro. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

The French colonization of the Americas began in the 17th century, and continued on into the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America. Most colonies were developed to export products such as fish, rice, sugar, and furs.

Gaspard de Coligny, Seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman and Admiral of France, best remembered as a disciplined Huguenot leader in the French Wars of Religion and a close friend of—and advisor to—the French king, Charles IX.

Nicolas Durand, sieur de Villegaignon, also Villegagnon was a Commander of the Knights of Malta, and later a French naval officer who attempted to help the Huguenots in France escape persecution.
Mem de Sá was a Governor-General of the Portuguese colony of Brazil from 1557-1572. He was born in Coimbra, Kingdom of Portugal, around 1500, the year of discovery of Brazil by a naval fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral.
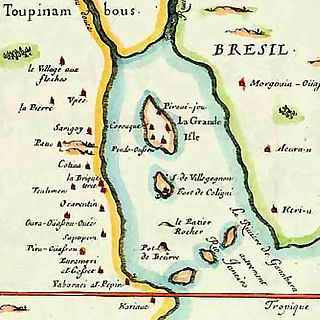
France Antarctique was a French colony south of the Equator, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, which existed between 1555 and 1567, and had control over the coast from Rio de Janeiro to Cabo Frio. The colony quickly became a haven for the Huguenots, and was ultimately destroyed by the Portuguese in 1567.
Equinoctial France was the contemporary name given to the colonization efforts of France in the 17th century in South America, around the line of Equator, before "tropical" had fully gained its modern meaning: Equinoctial means in Latin "of equal nights", i.e., on the Equator, where the duration of days and nights is nearly the same year round. The settlement was made in what is now known as the Bay of São Luis and lasted for 3 years.

Fort Coligny was a fortress founded by Nicolas Durand de Villegaignon in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in 1555, in what constituted the so-called France Antarctique historical episode.

The Cisplatine War, also known as the Argentine-Brazilian War or in the Argentine and Uruguayan historiography as the Brazil War, was an armed conflict over an area known as Banda Oriental or the "Eastern Bank" in the 1820s between the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata and the Empire of Brazil in the aftermath of the United Provinces' independence from Spain.

Estácio de Sá was a Portuguese soldier and officer. Sá travelled to the colony of Brazil on the orders of the Portuguese crown to wage war on the French colonists commanded by Nicolas Durand de Villegaignon. These French colonists had established themselves in 1555 at Guanabara Bay in Rio de Janeiro, in a settlement known as France Antarctique. He was the founder of Rio de Janeiro, now the second largest city in Brazil.

Cunhambebe was an aboriginal Indian chieftain of the Tupinambá tribe, which dominated the region between present-day Cabo Frio and Bertioga. He lived in a village in Iperoig.

Admiral of the Fleet Sir John Leake was a Royal Navy officer and politician. As a junior officer he saw action at the Battle of Texel during the Third Anglo-Dutch War. He then distinguished himself when he led the convoy that broke the barricading boom at Culmore Fort thereby lifting the Siege of Derry during the Williamite War in Ireland. As a captain he saw action in some of the heaviest fighting at the Battle of Barfleur and was also involved in a successful attack on the French ships at the Battle of La Hogue during the Nine Years' War.

The Battle of Rio de Janeiro was a raid in September 1711 on the port of Rio de Janeiro in the War of Spanish Succession by a French squadron under René Duguay-Trouin. The Portuguese defenders, including the city's governor and an admiral of the fleet anchored there, were unable to put up effective resistance in spite of numerical advantages.

The Independence of Brazil comprised a series of political and military events that occurred in 1821–1824, most of which involved disputes between Brazil and Portugal regarding the call for independence presented by the Brazilian Empire.

John Pascoe Grenfell was a British officer of the Empire of Brazil. He spent most of his service in South America campaigns, initially under the leadership of Lord Cochrane and then Commodore Norton. He was the nephew of British politician Pascoe Grenfell and grandfather to General Sir John Grenfell Maxwell. In Brazil, he rose to the rank of admiral and for his achievements was made a knight grand cross of the Imperial Order of the Rose and a knight of the Imperial Order of the Southern Cross.

HMS Kingston was a 60-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Frame in Hull and launched on 13 March 1697. She had an eventful career, taking part in numerous engagements.

The Portuguese conquest of the Banda Oriental was the armed-conflict that took place between 1816 and 1820 in the Banda Oriental, for control of what today comprises the whole of the Republic of Uruguay, the northern part of the Argentine Mesopotamia and southern Brazil. The four-year armed-conflict resulted in the annexation of the Banda Oriental into the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves as the Brazilian province of Cisplatina.
The 1710 Battle of Rio de Janeiro was a failed raid by a French privateering fleet on the Portuguese colonial city of Rio de Janeiro in August 1710, during the War of the Spanish Succession. The raid was a complete failure; its commander, Jean-François Duclerc, and more than 600 men were captured. French anger over the Portuguese failure to properly hold, release, or exchange the prisoners contributed to a second, successful raid, the following year.

The First Battle of Salvador was fought during the Dutch-Portuguese War in Brazil between a Dutch West India Company's army under the governor of the Dutch colony in Brazil, John Maurice, Prince of Nassau-Siegen, numbering about 4,600 men supported by 30 ships and the Portuguese and Spanish defenders of the city, commanded by Giovanni di San Felice, Count of Bagnolo, and Luís Barbalho. The battle resulted in a clear victory for the Portuguese and Spanish.

The Second Battle of Salvador was fought during the Dutch-Portuguese War in Brazil between forces of the Dutch West India Company under the governor of the Dutch Brazil, John Maurice, Prince of Nassau-Siegen, supported by 30 ships and the Portuguese and Spanish defenders of the city, commanded by Giovanni di San Felice and Luís Barbalho. The battle, like the previous one was won by Portugal and Spain.
Events from the year 1567 in France.