Kaman Corporation is an American aerospace company, with headquarters in Bloomfield, Connecticut. It was founded in 1945 by Charles Kaman. During the first ten years the company operated exclusively as a designer and manufacturer of several helicopters that set world records and achieved many aviation firsts.

The Aérospatiale Alouette III is a single-engine, light utility helicopter developed by French aircraft company Sud Aviation. During its production life, it proved to be a relatively popular rotorcraft; including multiple licensed manufacturers, in excess of 2,000 units were constructed.

Safran Helicopter Engines, previously known as Turbomeca, is a French manufacturer of low- and medium-power gas turbine turboshaft engines for helicopters. The company also produces gas turbine engines for aircraft and missiles, as well as turbines for land, industrial and marine applications. SNECMA Group acquired the company in September 2001. Safran Helicopter Engines has 6,300 employees worldwide, with 5000 based in France. In 2015, they produced and delivered 718 new engines, and repaired around 1700 engines.
The Robinson Helicopter Company, based at Zamperini Field in Torrance, California, is a manufacturer of civil helicopters. Robinson produces three models – the two-seat R22, the four-seat R44, both of which use Lycoming piston engines, and the five-seat R66, which uses a turbine engine.
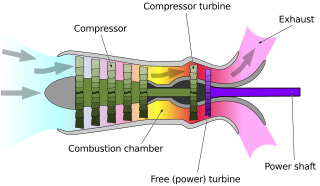
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaft power rather than jet thrust.

The Hiller OH-23 Raven was a three-place, light observation helicopter based on the Hiller Model 360. The Model 360 was designated by the company as the UH-12, which was first flown in 1948. The OH-23 trainer was jokingly nicknamed the "Hiller Killer" by US Army Aviation student pilots who had to fly it.

The Schweizer RSG300 series family of light utility helicopters was originally produced by Hughes Helicopters, as a development of the Hughes 269. Later manufactured by Schweizer Aircraft, the basic design has been in production for almost 50 years. The single, three-bladed main rotor and piston-powered S-300 is mostly used as a cost-effective platform for training and agriculture.

The Hughes TH-55 Osage was a piston-powered light training helicopter produced for the United States Army. It was also produced as the Model 269 family of light utility helicopters, some of which were marketed as the Model 300. The Model 300C was produced and further developed by Schweizer after 1983.

The Rolls-Royce Gnome is a British turboshaft engine originally developed by the de Havilland Engine Company as a licence-built General Electric T58, an American mid-1950s design. The Gnome came to Rolls-Royce after their takeover of Bristol Siddeley in 1968, Bristol having absorbed de Havilland Engines Limited in 1961.

An electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electric motors. Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods including batteries, ground power cables, solar cells, ultracapacitors, fuel cells and power beaming.

A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward, and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of VTOL aircraft cannot perform.

The General Electric T58 is an American turboshaft engine developed for helicopter use. First run in 1955, it remained in production until 1984, by which time some 6,300 units had been built. On July 1, 1959, it became the first turbine engine to gain FAA certification for civil helicopter use. The engine was license-built and further developed by de Havilland in the UK as the Gnome, in the West Germany by Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz, and also manufactured by Alfa Romeo and the IHI Corporation.

The Eurocopter EC635 is a multi-purpose light helicopter developed by Eurocopter as a military version of the Eurocopter EC135. It is a twin-engined aircraft and can carry up to 8 people, including the pilot, and a range of military equipment or armaments. The helicopter is marketed for troop transport, medical evacuation, cargo transport, reconnaissance and surveillance and armed combat support missions.

The Robinson R66 is a helicopter designed and built by Robinson Helicopter Company. It has five seats, a separate cargo compartment and is powered by a Rolls-Royce RR300 turboshaft engine. The R66 is slightly faster and smoother than the Robinson R44 from which it is derived. The R66 received both type and production certificates from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on October 25, 2010.
The Mil V-16 was a Soviet heavy cargo/transport helicopter project of the late 1960s. The Mil V-16 was designed by Mil Design Bureau, a Moscow helicopter plant. The original scheme described a heavy side-by-side twin-rotor aircraft with two Soloviev D-25VF gas turbine engines below six-bladed rotors at the tips of heavily supported wings on each side of the fuselage and tricycle-type landing gear, with both rear landing wheels mounted below the wings while the front wheel was located below the cockpit, as well as located directly under the wings.

The Klimov TV3-117 is a Russian gas turbine aero engine. It is used in most medium lift, utility, and attack helicopters designed by the Mil and Kamov design bureaus. The TV3-117 turboshaft engine was developed in 1974. Later the Klimov TV3-117 was installed on 95% of all helicopters designed by Mil and Kamov Engineering Centre. The engine has been produced in many variants.

The Solar T62 Titan is an American gas turbine engine used mainly as a helicopter auxiliary power unit (APU), ground power generator or helicopter powerplant. A free power turbine version was developed as the Solar T66.

The Dornier Do 32E was a simple, collapsible one-man helicopter, designed for military use in Germany in the 1960s. Despite initial hopes of large orders and some proposed civilian roles, only three flew.
















