
The 1987 Pacific hurricane season was the last year in which the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center was the primary warning center for tropical cyclones in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started May 15, 1987, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1987, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1987. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when the vast majority of tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.

The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific.

The 1999 Pacific typhoon season was the last Pacific typhoon season to use English names as storm names. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1999, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

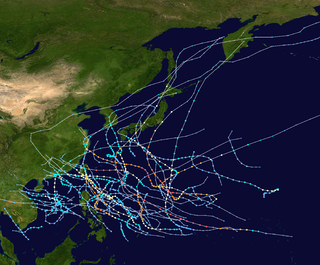
The 1964 Pacific typhoon season was the most active tropical cyclone season recorded globally, with a total of 40 tropical storms forming. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1964, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The 1961 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1961, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is the National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHS) agency of the Republic of the Philippines mandated to provide protection against natural calamities and to insure the safety, well-being and economic security of all the people, and for the promotion of national progress by undertaking scientific and technological services in meteorology, hydrology, climatology, astronomy and other geophysical sciences. Created on December 8, 1972 by reorganizing the Weather Bureau, PAGASA now serves as one of the Scientific and Technological Services Institutes of the Department of Science and Technology.
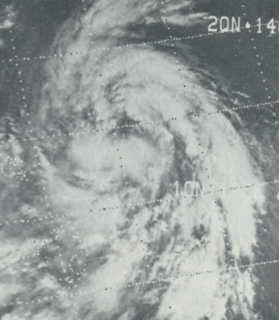
Typhoon Bess, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Susang, was responsible for the disappearance of a United States Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft. Developing out of a poorly organized system on October 8 to the east of the Philippines, Bess featured two centers of circulation. Initially the southern low was monitored; however, a low to the north soon became the dominant center. Tracking generally west-northwestward, the storm gradually intensified before striking northern Luzon as a minimal typhoon on October 11. Temporary weakening took place due to interaction with land. After moving back over water the following morning, Bess regained typhoon intensity. This was short-lived though, as conditions surrounding the cyclone soon caused it to weaken. Now moving due west, the weakening storm eventually struck Hainan Island as a tropical storm on October 12 before diminishing to a tropical depression. The depression briefly moved back over water before dissipating in northern Vietnam on October 14.

Typhoon Babs was a powerful typhoon that struck the Philippines just days after Typhoon Zeb hit the same area. The seventh typhoon of the 1998 season, Babs formed on October 14 between the Philippines and Guam. The storm moved westward initially, failing to intensify initially due to the outflow from Typhoon Zeb to the northwest. Babs slowed and briefly turned to the south before advancing to the northwest, whereupon it rapidly intensified into a strong typhoon. On October 20, the official Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) estimated peak 10‑minute winds of 155 km/h (100 mph), while the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated peak 1‑minute winds of 250 km/h (155 mph), making Babs an unofficial super typhoon. The storm struck the Philippine island of Catanduanes at that intensity and weakened slightly before hitting Luzon. Babs turned northward once in the South China Sea, later weakening due to unfavorable conditions and transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on October 27 in the Taiwan Strait.

The 2008 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 2008, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season was one of the least active South Pacific tropical cyclone season's on record, with only four tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific basin to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2007 until April 30, 2008, although the first cyclone, Tropical Depression 01F, developed on October 17. The most intense tropical cyclone of the season was Severe Tropical Cyclone Daman, which reached a minimum pressure of 925 hPa (27.32 inHg) as it affected Fiji. After the season had ended, the names Daman, Funa, and Gene were retired from the tropical cyclone naming lists.

Typhoon Fengshen, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Frank, was the sixth named storm and the fourth typhoon recognised by the Japan Meteorological Agency. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center recognised Fengshen as the seventh tropical depression, the sixth tropical storm, and fifth typhoon of the 2008 Pacific typhoon season.
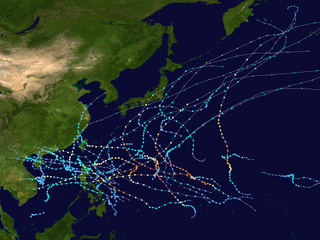
The 2009 Pacific typhoon season was a below average season that spawned only 22 named storms, 13 typhoons, and five super typhoons. It was also recognized as the deadliest season in the Philippines for decades. The first half of the season was very quiet whereas the second half of the season was extremely active. The season's first named storm, Kujira, developed on May 3 while the season's last named storm, Nida, dissipated on December 3.
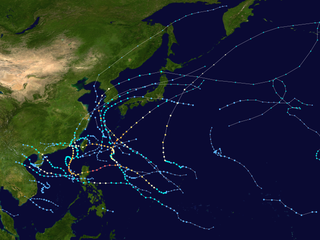
The 2010 Pacific typhoon season was the least active Pacific typhoon season on record, featuring only 14 named storms; seven of them strengthened into typhoons while one reached super typhoon intensity. The Pacific typhoon season during 2010 was in fact less active than the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season, the only such occurrence other than 2005. In the same year, the Pacific hurricane season broke the same record being the least active season on record. During the season no storms have made landfall in mainland Japan, the only second such occurrence since 1988. Also, all of the 14 named storms developed west of 150°E. Moreover, the season had an index total Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) of 115, which is the second lowest in the basin after 1999. It was also the fourth consecutive year with a below average ACE index.
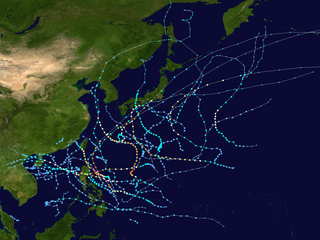
The 2011 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average season that produced a total of 21 named storms, 8 typhoons, and four super typhoons. This season was much more active than the previous season, although both seasons were below the Pacific typhoon average of 26. The season ran throughout 2011, though most tropical cyclone tend to develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Aere, developed on May 7 while the season's last named storm, Washi dissipated on December 19.

The 2017 Pacific typhoon season was a below-average season in terms of Accumulated Cyclone Energy and the number of typhoons and super typhoons, and the first and latest since the 1977 season to not produce a Category 5-equivalent typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson scale. The season produced a total of 27 named storms, 11 typhoons, and only two super typhoons, making it an average season in terms of storm numbers. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2017, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Muifa, developed on April 25, while the season's last named storm, Tembin, dissipated on December 26. This season also featured the latest occurrence of the first typhoon of the year since 1998, with Noru reaching this intensity on July 23.

Severe Tropical Storm Trami, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Maring, was a tropical cyclone that brought heavy rains to Taiwan and East China during mid-August 2013. Trami also made a fujiwhara interaction with Tropical Depression 13W north of it. The storm also enhanced the southwest monsoon causing more than 20 casualties in the Philippines.
The 1940 Pacific typhoon season marked an interruption in meteorological records in both the Philippines and Hong Kong due to the start of World War II. There were 43 reported tropical cyclones, including 27 that attained typhoon status. The first storm was observed in February, and the first typhoon formed two months later, killing three people along Mindanao. Several storms formed in June and July, including reports of a typhoon in the newspapers that killed 52 in South Korea, and another typhoon reported in newspapers that killed one person on Samar after dropping heavy rainfall. The strongest typhoon of the season originated in July and attained a minimum pressure of 927 mbar (27.4 inHg), as reported by a ship northeast of the Philippines.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2015 Pacific typhoon season. Most of the tropical cyclones formed between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. This area, called the Western Pacific basin, is the responsibility of the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA). They host and operate the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC), located in Tokyo. The Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA) is also responsible for assigning names to all tropical storms that are formed within the basin. However, any storm that enters or forms in the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) will be named by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) using a local name. Also of note - the Western Pacific basin is monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), which gives all Tropical depressions a number with a "W" suffix.


















